Abstract
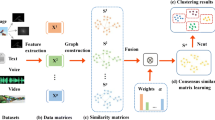
Multi-view clustering utilizes information from diverse views to improve the performance of clustering. For most existing multi-view spectral clustering methods, information of different views is integrated by pursuing a consensus similarity matrix for clustering. However, view-specific structures, which contain the complementary information of multi-view data, may be lost during the clustering process. Actually, in multi-view spectral clustering, similarity matrices of multiple views would have the same clustering structures or properties rather than be numerically uniform. To overcome the aforementioned problem, a novel essential multi-view graph learning (EMGL) method for clustering is proposed in this paper. Different from most existing multi-view spectral clustering, an orthogonal matrix factorization is imposed on multi-view similarity matrices for making them have the same nuclear norm, which indicates the same clustering structures of different views. Furthermore, we also propose an alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) based optimization algorithm to address the objective function of our method. Extensive experiments on several datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brbić M, Piškorec M, Vidulin V, Kriško A, Šmuc T, Supek F (2016) The landscape of microbial phenotypic traits and associated genes. Nucleic Acids Res 21:10074–10090
Cai JF, Candès EJ, Shen Z (2010) A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J Optim 20(4):1956–1982
Chen Z, Lu H, Tian S, Qiu J, Kamiya T, Serikawa S, Xu L (2020) Construction of a hierarchical feature enhancement network and its application in fault recognition. IEEE Trans Ind Inform. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3021688
Cortes C, Mohri M, Rostamizadeh A (2009) Learning non-linear combinations of kernels. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 22:396–404
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2013) Sparse subspace clustering: algorithm, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2765–2781
Fei-Fei L, Fergus R, Perona P (2004) Learning generative visual models from few training examples: an incremental Bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. In: 2004 conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshop. IEEE, pp 178–178
Hu Y, Zhang D, Ye J, Li X, He X (2012) Fast and accurate matrix completion via truncated nuclear norm regularization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(9):2117–2130
Huang L, Lu J, Tan YP (2014) Co-learned multi-view spectral clustering for face recognition based on image sets. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(7):875–879
Kumar A, Daumé H (2011) A co-training approach for multi-view spectral clustering. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on machine learning, pp 393–400
Kumar A, Rai P, Daume H (2011) Co-regularized multi-view spectral clustering. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1413–1421
Lan R, Sun L, Liu Z, Lu H, Pang C, Luo X (2021) Madnet: a fast and lightweight network for single-image super resolution. IEEE Trans Cybern 51(3):1443–1453
Lin Z, Liu R, Su Z (2011) Linearized alternating direction method with adaptive penalty for low-rank representation. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 612–620
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2012) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184
Lu H, Li Y, Mu S, Wang D, Kim H, Serikawa S (2017) Motor anomaly detection for unmanned aerial vehicles using reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J 5(4):2315–2322
Lu H, Li Y, Chen M, Kim H, Serikawa S (2018) Brain intelligence: go beyond artificial intelligence. Mob Netw Appl 23(2):368–375
Lu H, Zhang M, Xu X, Li Y, Shen HT (2021a) Deep fuzzy hashing network for efficient image retrieval. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(1):166–176
Lu H, Zhang Y, Li Y, Jiang C, Abbas H (2020b) User-oriented virtual mobile network resource management for vehicle communications. IEEE trans Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.2991766
Lu W, Zhang Y, Wang S, Huang H, Liu Q, Luo S (2020c) Concept representation by learning explicit and implicit concept couplings. IEEE Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIS.2020.3021188
Luo S, Zhang C, Zhang W, Cao X (2018) Consistent and specific multi-view subspace clustering. In: Thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Ma S, Liu Y, Zheng Q, Li Y, Cui Z (2020) Multiview spectral clustering via complementary information. Concurr Comput-Pract Exp. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5701
Ng A, Jordan M, Weiss Y (2001) On spectral clustering: analysis and an algorithm. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 14:849–856
Nie F, Li J, Li X, et al (2016) Parameter-free auto-weighted multiple graph learning: A framework for multiview clustering and semi-supervised classification. In: International joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1881–1887
Oh TH, Tai YW, Bazin JC, Kim H, Kweon IS (2015) Partial sum minimization of singular values in robust pca: algorithm and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(4):744–758
Ou W, Yu S, Li G, Lu J, Zhang K, Xie G (2016) Multi-view non-negative matrix factorization by patch alignment framework with view consistency. Neurocomputing 204:116–124
Schönemann PH (1966) A generalized solution of the orthogonal procrustes problem. Psychometrika 31(1):1–10
Schütze H, Manning CD, Raghavan P (2008) Introduction to information retrieval, vol 39. Cambridge University Press Cambridge
Serikawa S, Lu H (2014) Underwater image dehazing using joint trilateral filter. Comput Electr Eng 40(1):41–50
Von Luxburg U (2007) A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat Comput 17(4):395–416
Wang H, Yang Y, Liu B (2019) Gmc: graph-based multi-view clustering. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 32(6):1116–1129
Wang P, Wang D, Zhang X, Li X, Peng T, Lu H, Tian X (2020) Numerical and experimental study on the maneuverability of an active propeller control based wave glider. Appl Ocean Res 104:102369
Xia R, Pan Y, Du L, Yin J (2014) Robust multi-view spectral clustering via low-rank and sparse decomposition. In: Proceedings of the twenty-eighth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2149–2155
Xu C, Tao D, Xu C (2013) A survey on multi-view learning. arXiv:13045634
Xu X, Lu H, Song J, Yang Y, Shen HT, Li X (2019) Ternary adversarial networks with self-supervision for zero-shot cross-modal retrieval. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(6):2400–2413
Yin M, Gao J, Lin Z, Shi Q, Guo Y (2015a) Dual graph regularized latent low-rank representation for subspace clustering. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):4918–4933
Yin Q, Wu S, He R, Wang L (2015b) Multi-view clustering via pairwise sparse subspace representation. Neurocomputing 156:12–21
Zhai L, Zhu J, Zheng Q, Pang S, Li Z, Wang J (2019) Multi-view spectral clustering via partial sum minimisation of singular values. Electron Lett 55(6):314–316
Zhang C, Fu H, Liu S, Liu G, Cao X (2015) Low-rank tensor constrained multiview subspace clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1582–1590
Zhang C, Fu H, Hu Q, Cao X, Xie Y, Tao D, Xu D (2018) Generalized latent multi-view subspace clustering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(1):86–99
Zhang L, Zhang D (2015) Visual understanding via multi-feature shared learning with global consistency. IEEE Trans Multimed 18(2):247–259
Zhang Z (2000) A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(11):1330–1334
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Shao L, Yang J (2017) Discriminative block-diagonal representation learning for image recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(7):3111–3125
Zhao J, Xie X, Xu X, Sun S (2017) Multi-view learning overview: Recent progress and new challenges. Inf Fusion 38:43–54
Zheng Q, Zhu J, Li Z, Pang S, Wang J, Li Y (2020) Feature concatenation multi-view subspace clustering. Neurocomputing 379:89–102
Zhou D, Burges CJ (2007) Spectral clustering and transductive learning with multiple views. In: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on machine learning, pp 1159–1166
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No: 2018AAA0102504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, S., Zheng, Q. & Liu, Y. Essential multi-view graph learning for clustering. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13, 5225–5236 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03002-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03002-5