Abstract
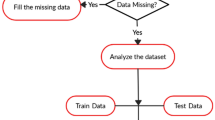
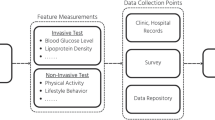
Blood pressure issues are related to many illnesses threatening human health and require continuous control and monitoring. Health telemonitoring is an innovative solution allowing wellbeing and increasing autonomy of patients. Moreover, machine learning algorithms are a viable method used in recent studies for analyzing, predicting, and classifying health data while improving the health conditions of telemonitoring and telediagnosis. The main purpose of this article is to employ machine learning algorithms for Blood Pressure (BP) measurement classification in real-time. Data is gathered from the human body through a multilevel Wireless Medical Sensors Network (WMSN) architecture that is deployed to acquire, analyze, and monitor BP remotely. The first layer of the proposed architecture performs BP measurement, classification, and transmission to the second layer using a wearable sensor. The learning of classifiers is established with Cross-Validation to avoid over-fitting and to improve the performance while comparing the Decision Tree, K-Nearest-Neighbors, and Naive Bayes algorithms. Afterward, the best classifier is implemented in the BP sensor node to identify the BP status. The second layer is responsible for data aggregation in the Cloud and alerting when an anomaly occurs in BP measurement. The third layer is configured to present BP information continuously to the health professionals and patients using the Internet of Things (IoT) platform that retrieves data from the cloud. The evaluation results show better accuracy, i.e. 97.9% using the decision tree classifier. An experimental trial is carried out and the timing of 49 seconds is reached between BP measurement and the display of data on the IoT platform. Besides, the system was tested in real-time trials and produced an accurate classification of each measured BP. The obtained results approve the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed approach in terms of BP measurement, analysis, transmission, and supervision in real-time.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbassi MA El, Jilbab A, Bourouhou A (2016) Detection model based on multi-sensor data for early fire prevention. In: 2016 International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies (ICEIT), pp 214–218. https://doi.org/10.1109/EITech.2016.7519592.
Abidi B, Jilbab A, Mohamed El H (2019) Wireless body area network for health monitoring. J Med Engi Technol 43(2), 124–132. ISSN: 0309-1902. https://doi.org/10.1080/03091902.2019.1620354
Adi PDP, Kitagawa A (2019) ZigBee Radio Frequency (RF) Performance on Raspberry Pi 3 for Internet of Things (IoT) based blood pressure sensors monitoring. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2019.0100504
Cheng C-Hs, et al (2018) Evidence-based personal applications of medical computing models in risk factors of cardiovascular disease for the middle-aged and elderly. en. In: Personal and Ubiquitous Computing 22.5, pp 921–936. ISSN: 1617-4917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-018-1172-z.(visited on 09/08/2020)
Chobanian AV, et al (2003) The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. In: JAMA 289.19, pp 2560–2572. ISSN: 0098-7484. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.19.2560.
Ding S, Wang X (2020) Medical Remote Monitoring of Multiple Physiological Parameters Based on Wireless Embedded Internet. In: IEEE Access 8. Conference Name: IEEE Access, pp. 78279–78292. ISSN: 2169-3536. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990167
Dorado-Díaz PI, et al (2019) Applications of artificial intelligence in cardiology. The future is already here. In: Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition) 72.12, pp. 1065–1075. ISSN: 18855857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rec.2019.05.014. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1885585719302609 (visited on 12/18/2019)
Eddabbah M, Moussaoui M, Laaziz Y (2019) A smart architecture design for health remote monitoring systems and heterogeneous wireless sensor network technologies: a machine learning breathlessness prediction prototype. en. In: International Journal of Intelligent Enterprise 6.2/3/4, p. 293. ISSN: 1745-3232, 1745-3240. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJIE.2019.10022696. http://www.inderscience.com/link.php?id=10022696 (visited on 12/18/2019)
El Attaoui A, et al (2019) Wearable wireless sensors network for ECG telemonitoring using neural network for features extraction. In: Wireless personal communications. ISSN: 1572-834X. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06967- x. (visited on 12/25/2019)
EL Attaoui A, et al. (2020) Wearable wireless sensors node for heart activity telemonitoring. In: 2020 International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies (ICEIT). Rabat, Morocco: IEEE, pp. 1–6. ISBN: 978-1-72814-341-5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEIT48248.2020.9113208. URL:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document / 9113208/ (visited on 07/30/2020)
Fajar MZ, Hadiyoso S, Rizal A (2017) An interfacing digital blood pressure meter with arduino-GSM module for real-time monitoring. en. In: 2017 International Conference on Control, Electronics, Renewable Energy and Communications (ICCREC). Yogyakarta: IEEE, pp. 98–102. ISBN: 978-1-5386-1667- 3. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCEREC.2017.8226669. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8226669/ (visited on 12/18/2019)
Ghazali NF, et al (2018) Wearable device for Malaysian ringgit banknotes recognition based on embedded decision tree classifier. en. In: 10.1, p. 9
Kilic A (2019) Artificial intelligence and machine learning in cardiovascular healthcare. Ann Thorac Surg, S0003497519316121. ISSN: 00034975. DOIurlhttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2019.09.042. (visited on 12/14/2019)
Kuncoro C, Dwi B, Luo W-J, Kuan Y-D (2020) Wireless photoplethysmography sensor for continuous blood pressure biosignal shape acquisition. Research Article. ISSN: 1687-725X Pages: e7192015 Publisher: Hindawi Volume: 2020. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7192015. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/js/2020/7192015/ (visited on 10/23/2020)
Lalos AS, Alonso L, Verikoukis C (2014) Model based compressed sensing reconstruction algorithms for ECG telemonitoring in WBANs. en. In: Digital Signal Processing 35, pp. 105–116. ISSN: 10512004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2014.08.007.https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1051200414002553 (visited on 01/17/2020)
Liang Y, et al (2018) PPG-BP Database. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.5459299.v3. https://figshare.com/articles/PPG-BP_Database_zip/5459299 (visited on 12/16/2019)
Marolleau B, Bacle C, Lalevée C (2018) \(\copyright\) Copyright IBM Corp. 2018 Materials may not be reproduced in whole or in part without the prior written permission of IBM. en. In: p. 41
Microchip Technology Inc (2020) ATmega328 - 8-bit AVR Microcontrollers. EN. URL: https://www.microchip.com/wwwproducts/en/atmega328 (visited on 10/23/2020)
MPS20N0040D-S Datasheet – ETC - Datasheetspdf.com (2020). https://datasheetspdf.com/datasheet/MPS20N0040D-S.html (visited on 01/17/2020)
Nimmala S, et al (2018) Predicting high blood pressure using decision tree-based algorithm. In: Damodar Reddy Edla, Pawan Lingras, and Venkatanareshbabu K (eds) Advances in machine learning and data science, vol.705. Springer, Singapore, pp 53– 60. ISBN: 978-981-10-8568-0 978-981-10-8569-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8569-7_6.(visited on 12/18/2019)
NORDIC SEMICONDUCTOR (2007) nRF24L01 Single Chip 2.4GHz Transceiver Product Specification
Organization Whorl Healt (2013) WHO EMRO – World Health Day 2013: Measure your blood pressure, reduce your risk—Sudan-news—Sudan. http://www.emro.who.int/sdn/sudan-news/whd-2013.html (visited on 11/23/2019)
Pi Raspberry (2016) Raspberry Pi Compute Module (CM1) Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3 (CM3) Raspberry Pi Compute Module 3 Lite (CM3L). https://www.raspberrypi.org
Samouni N, Jilbab A, Hammouch A (2019) A critical review on recent research on reliable communication for wireless body area network. 9(4):432–442
Satoto BD, et al (2019) Wireless health monitoring with fuzzy decision tree for the community patients of chronic hypertension. J Phys Conf Ser 1211, p. 012041. ISSN: 1742-6588, 1742-6596. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1211/1/012041. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1211/1/012041 (visited on 12/18/2019)
Satyanarayana N, Ramadevi Y, Chari KK (2018) High blood pressure prediction based on AAA using J48 classifier. en. In: 2018 Conference on Signal Processing And Communication Engineering Systems (SPACES). Vijayawada: IEEE, pp. 121–126. ISBN: 978-1- 5386-2369-5. https://doi.org/10.1109/SPACES.2018.8316330.http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8316330/ (visited on 12/18/2019)
Singha SK, Sarkar K, Ahmad M (2019) An easy approach to develop a digital blood pressure meter. In: 2019 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE). Cox’sBazar, Bangladesh: IEEE, pp. 1–5. ISBN: 978-1-5386-9111-3. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECACE.2019.8679246. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8679246/ (visited on 12/18/2019)
Singh B, et al (2019) Blood pressure monitoring system using wireless technologies. Procedia Comput Sci 152:267–273. ISSN: 18770509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.05.017. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877050919306684 (visited on 12/18/2019)
Subito Mery, Alamsyah, Amir Ardi (2019) Web-Based Wireless Monitoring System on Patient’s Vital Sign. en. In: E3S Web of Conferences 125. Ed. by Hadiyanto, Budi Warsito, and Maryono, p. 25003. ISSN: 2267-1242. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/201912525003.URL: https://www.e3sconferences. org/10.1051/e3sconf/201912525003 (visited on 12/18/2019)
Torti E, et al (2019) Embedding recurrent neural networks in wearable systems for real-time fall detection. Microprocessors Microsyst 71:102895. ISSN: 0141-9331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2019.102895. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141933119300584 (visited on 10/23/2020)
Waguespack DR, Dwyer JP (2019) Assessment of blood pressure: techniques and implications from clinical trials. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 26(2):87–91. ISSN: 15485595. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2019.02.002. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1548559519300278D (visited on 12/18/2019)
Wang Q, et al (2018) Continuous blood pressure estimation based on two-domain fusion model. Research Article. ISSN: 1748-670X Pages: e1981627 Publisher: Hindawi Volume: 2018. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1981627. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cmmm/2018/1981627/ (visited on 10/23/2020)
WHO (2017) WHO EMRO—High blood pressure: a public health problem – World Health Day 2013 – World Health Days. http://www.emro.who.int/media/world-healthday/public-health-problem-factsheet-2013.html (visited on 12/18/2019)
WHO (2019) Hypertension. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension (visited on 11/23/2019)
Wood A (2019) Private naive bayes classification of personal biomedical data: application in cancer data analysis 105(144–150), p 12
Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015 (2017) Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: a pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19\(\cdot\)1 million participants. English. In: The Lancet 389.10064. Publisher: Elsevier, pp. 37–55. ISSN: 0140-6736, 1474-547X. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31919-5https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(16)31919-5/abstract (visited on 10/23/2020)
Zhang B, et al (2019) Health data driven on continuous blood pressure prediction based on gradient boosting decision tree algorithm. In: IEEE Access 7, pp 32423– 32433. ISSN: 2169-3536. https://doi.org/10.110/ACCESS.2019.29022179. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8662767/ (visited on 12/18/2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EL ATTAOUI, A., Largo, S., Jilbab, A. et al. Wireless medical sensor network for blood pressure monitoring based on machine learning for real-time data classification. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 12, 8777–8792 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02660-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02660-1