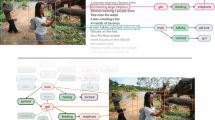
Abstract
Existing methods focus on destination image construction by textual description or visual content separately. However, descriptions and images are closely related since they are taken from the same reviews and represent tourists impression of the city. It’s questionable to study them separately. In this paper, we used both images and descriptions from the reviews to construct Xi’an tourism destination image. More concretely, scene recognition, landmark recognition and food image recognition are utilized to obtain visual image. Lexical analysis is applied to obtain semantic image. We further compared the differences between visual image and semantic image then we proposed the fusion image. Finally, the top 300 key words and differences of the photo contents between the adjacent 2 years are selected to discovering new changes of the destination image. Results show that the visual image and semantic image are significant different from each other and the new changes of semantic image are closely related to the events or things that happened in that year and changes of visual image are not significant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Bai Y, Zhang W, Mei T (2019) Destruction and construction learning for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5157–5166
Crandall DJ, Li Y, Lee S, Huttenlocher DP (2016) Recognizing landmarks in large-scale social image collections. In: Large-scale visual geolocalization. Springer, Cham, pp 121–144
Deng N, Li XR (2018) Feeling a destination through the “right” photos: a machine learning model for DMOs’ photo selection. Tour Manage 65:267–278
Fu J, Zheng H, Mei T (2017) Look closer to see better: recurrent attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4438–4446
Gao G, Yang J, Wu S, Jing X, Yue D (2015) Bayesian sample steered discriminative regression for biometric image classification. Appl Soft Comput 37:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.07.034
Gao G, Yang J, Jing X-Y, Shen F, Yang W, Yue D (2017) Learning robust and discriminative low-rank representations for face recognition with occlusion. Pattern Recogn 66:129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.12.021
Gao G, Yu Y, Yang M, Chang H, Huang P, Yue D (2020) Cross-resolution face recognition with pose variations via multilayer locality-constrained structural orthogonal procrustes regression. Inf Sci 506:19–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.08.004
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Jang S, Moutinho L (2019) Do price promotions drive consumer spending on luxury hotel services? The moderating roles of room price and user-generated content. Int J Hospital Manage 78:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.11.010
Jiang S, Min W, Liu L, Luo Z (2019) Multi-scale multi-view deep feature aggregation for food recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:265–276
Jung H, Choi M-K, Jung J, Lee J-H, Kwon S, Young Jung W (2017) ResNet-based vehicle classification and localization in traffic surveillance systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 61–67
Kim SB, Kim DY, Wise K (2014) The effect of searching and surfing on recognition of destination images on Facebook pages. Comput Hum Behav 30:813–823
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Lee I, Cai G, Lee K (2014) Exploration of geo-tagged photos through data mining approaches. Expert Syst Appl 41(2):397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.07.065
Li X, Ratti C (2018) Mapping the spatial distribution of shade provision of street trees in Boston using Google Street View panoramas. Urban For Urban Green 31:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2018.02.013
Liu Y, Huang K, Bao J, Chen K (2019a) Listen to the voices from home: an analysis of Chinese tourists’ sentiments regarding Australian destinations. Tour Manage 71:337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.10.004
Liu Z, Wang J, Liu G, Zhang L (2019b) Discriminative low-rank preserving projection for dimensionality reduction. Appl Soft Comput 85:105768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105768
Lu Z, Jiang X, Kot A (2018) Deep coupled resnet for low-resolution face recognition. IEEE Signal Process Lett 25(4):526–530
Lu H, Wang D, Li Y, Li J, Li X, Kim H, Serikawa S, Humar I (2019) CONet: a cognitive ocean network. IEEE Wirel Commun 26(3):90–96
Luo R, Xu J, Zhang Y, Ren X, Sun X (2019) PKUSEG: a toolkit for multi-domain chinese word segmentation. ArXiv:1906.11455
Mak AHN (2017) Online destination image: comparing national tourism organisation’s and tourists’ perspectives. Tour Manage 60:280–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.12.012
Miah SJ, Vu HQ, Gammack J, McGrath M (2017) A big data analytics method for tourist behaviour analysis. Inf Manage 54(6):771–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2016.11.011
Nair V, Hinton GE (2010) Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning (ICML-10), pp 807–814
Önder I (2017) Classifying multi-destination trips in Austria with big data. Tour Manage Perspect 21:54–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2016.11.002
Pan S, Lee J, Tsai H (2014) Travel photos: motivations, image dimensions, and affective qualities of places. Tour Manage 40:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.05.007
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 91–99
Salas-Olmedo MH, Moya-Gómez B, García-Palomares JC, Gutiérrez J (2018) Tourists’ digital footprint in cities: comparing Big Data sources. Tour Manage 66:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.11.001
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. ArXiv:1409.1556
Slak Valek N, Williams RB (2018) One place, two perspectives: destination image for tourists and nationals in Abu Dhabi. Tour Manage Perspect 27:152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2018.06.004
Xu X, He L, Lu H, Gao L, Ji Y (2019a) Deep adversarial metric learning for cross-modal retrieval. World Wide Web 22(2):657–672
Xu X, Lu H, Song J, Yang Y, Shen HT, Li X (2019b) Ternary adversarial networks with self-supervision for zero-shot cross-modal retrieval. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(6):2400–2413. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2928180
Xu X, Wang T, Yang Y, Zuo L, Shen F, Shen HT (2020) Cross-modal attention with semantic consistence for image-text matching. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2967597
Yang J, Zhang L, Xu Y, Yang J (2012) Beyond sparsity: the role of L1-optimizer in pattern classification. Pattern Recogn 45(3):1104–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2011.08.022
Yang J, Chu D, Zhang L, Xu Y, Yang J (2013) Sparse representation classifier steered discriminative projection with applications to face recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(7):1023–1035
Yu Y, Tang S, Aizawa K, Aizawa A (2019) Category-based deep CCA for fine-grained venue discovery from multimodal data. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(4):1250–1258. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2856253
Zhang X, Xiong H, Zhou W, Lin W, Tian Q (2016) Picking deep filter responses for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1134–1142
Zhang K, Chen Y, Li C (2019) Discovering the tourists’ behaviors and perceptions in a tourism destination by analyzing photos’ visual content with a computer deep learning model: the case of Beijing. Tour Manage 75:595–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.07.002
Zhang Z, Zhu Q, Xie G-S, Chen Y, Li Z, Wang S (2020) Discriminative margin-sensitive autoencoder for collective multi-view disease analysis. Neural Netw 123:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.11.013
Zheng H, Fu J, Mei T, Luo J (2017) Learning multi-attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 5209–5217
Zhou X, Xu C, Kimmons B (2015) Detecting tourism destinations using scalable geospatial analysis based on cloud computing platform. Comput Environ Urban Syst 54:144–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2015.07.006
Zhou B, Lapedriza A, Khosla A, Oliva A, Torralba A (2017) Places: a 10 million image database for scene recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(6):1452–1464
Acknowledgements
The work is partially supported by the Philosophy and Social Sciences Project for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (nos. 2019SJA0649), National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 41901174, 61503188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, F., Zhang, Y., Shi, C. et al. Xi’an tourism destination image analysis via deep learning. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13, 5093–5102 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02344-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02344-w