Abstract
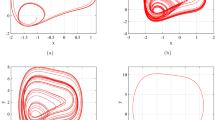
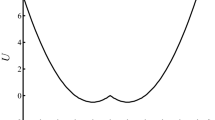
The detection of weak signals has been widely used in communication, radar and other fields. The detection of weak signals in the background of strong noise is an important research hotspot of modern information theory, and prompts people to explore and study new theories and new methods of weak signal detection. The device takes Holmes-type Duffing mapping as the research object, and uses the Lyapunov exponent as the criterion for chaos identification. The chaotic critical value of the equation is changed from chaotic state to periodic state. Whether it contains the detection algorithm of the target signal, the signal detection for the unknown frequency and the Holmes-type Duffing system is improved by the sliding mode variable structure control method in the control theory. The simulation results show that the improved chaotic Duffing system can effectively suppress the noise and detect the frequency of the weak signal through the power spectrum of the system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastian MR, Purwarianti A (2016) Information extraction in statistics indicator tables using rule generalizations and ontology. In: 2016 International Conference on information technology systems and innovation (ICITSI). IEEE, pp. 1–6
Blasch G, Spengler D, Hohmann C, Neumann C, Itzerott S, Kaufmann H (2015) Multitemporal soil pattern analysis with multispectral remote sensing data at the field-scale. Comput Electron Agric 113:1–13
David P, Hawes T, Hansen N, Nolan JJ (2016) Considering context: reliable entity networks through contextual relationship extraction. In: Next-generation analyst IV, vol 9851. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham, p 985107
Devisree V, Raj PR (2016) A hybrid approach to relationship extraction from stories. Procedia Technol 24:1499–1506
Dilpazir H, Mahmood H, Muhammad Z, Malik H (2015) Face recognition: a multivariate mutual information based approach. In: 2015 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Cybernetics (CYBCONF). IEEE, pp 467–471
Dimova D, Stumpfe D, Hu Y, Bajorath J (2015) Activity cliff clusters as a source of structure–activity relationship information. Expert Opin Drug Discov 10(5):441–447
Ferreira AP, Tobyn M (2015) Multivariate analysis in the pharmaceutical industry: enabling process understanding and improvement in the PAT and QbD era. Pharm Dev Technol 20(5):513–527
Glauber R, Claro DB (2018) A systematic mapping study on open information extraction. Expert Syst Appl 112:372–387
Gupta P, Sharma KK, Joshi SD (2016) Fetal heart rate extraction from abdominal electrocardiograms through multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Comput Biol Med 68:121–136
Hsu Y, Chuang M, Hirano T, Ute K (2018) Multivariate analysis of 13 C NMR spectra to extract information about monomer sequences in poly (methyl methacrylate-co-benzyl methacrylate) s prepared by various polymer reactions. Polym J 50(5):355
Jonsson P, Wuolikainen A, Thysell E, Chorell E, Stattin P, Wikström P, Antti H (2015) Constrained randomization and multivariate effect projections improve information extraction and biomarker pattern discovery in metabolomics studies involving dependent samples. Metabolomics 11(6):1667–1678
Juneau PM, Garnier A, Duchesne C (2015) The undecimated wavelet transform–multivariate image analysis (UWT-MIA) for simultaneous extraction of spectral and spatial information. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 142:304–318
Pena W, Melgar A (2015) Ontology-based information extraction from Spanish Forum. Computational collective intelligence. Springer, Cham, pp 351–360
Roldán JB, Miranda E, González-Cordero G, García-Fernández P, Romero-Zaliz R, González-Rodelas P, Jiménez-Molinos F (2018) Multivariate analysis and extraction of parameters in resistive RAMs using the Quantum Point Contact model. J Appl Phys 123(1):014501
Vigneshwari S, Aramudhan M (2015) Web information extraction on multiple ontologies based on concept relationships upon training the user profiles. Artificial intelligence and evolutionary algorithms in engineering systems. Springer, New Delhi, pp 1–8
Yokoyama Y, Kawashima T, Ohkawa M, Iwai H, Aoyagi S (2015) Extraction of hidden information of ToF-SIMS data using different multivariate analyses. Surf Interface Anal 47(4):439–446
Zhou PY, Chan KC (2015) A feature extraction method for multivariate time series classification using temporal patterns. In: Pacific-Asia conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. Springer, Cham, pp 409–421
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Projects of Beijing Education Commission (No. KM201910858005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Q., Lin, F., Li, H. et al. Human-autonomous devices for weak signal detection method based on multimedia chaos theory. J Ambient Intell Human Comput (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02270-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02270-x