Abstract
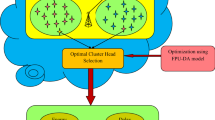
A major concern in wireless sensor network (WSN) is energy efficiency as they utilize small sized batteries, which can neither be replaced nor be recharged. Hence, there are many research efforts in designing energy efficient hierarchical clustering model. Most of the hierarchical models have created improper clusters which induces increased communication overhead and quick depletion of energy in the network. In this paper, advertisement valid time triggered firefly and fruit-fly based bio-inspired algorithm is adapted in WSN for the efficient cluster formation and electing stand by CH to avoid unnecessary reelection process, respectively. These bio-inspired computational approaches ensure the formation of energy efficient hierarchical networking model. The firefly and fruit-fly based energy efficient routing protocol are implemented using the J-Sim tool and the effectiveness of algorithms are analyzed using the result parameters Viz. reelection, data delivery ratio, network lifetime and delay. Further, the results are compared with other variant Hierarchical routing approaches such as LEACH-FA, GA-ABC, and GWO. Our results demonstrate clear superiority of FA and FFA based clustering against other variant approaches.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 June 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-04179-z
References
Akyildiz IF, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, Cayirci E (2002) A survey on sensor network. IEEE Commun Mag 40(8):102–111
Al-Karaki JN, Kamal AE (2004) Routing techniques in wireless sensor networks: a survey. IEEE Wirel Commun 11(6):6–28
Anamika D, Tamal S, Sharafat A (2016) Fruit fly algorithm based clustering protocol in wireless sensor networks. In: 9th international conference on electrical and computer engineering, pp 295–298
Bajaber F, Awan I (2010) Energy efficient clustering protocol to enhance lifetime of wireless sensor network. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 4:239–248
Brian K, Habermanand JS (2012) Overlapping particle swarms for energy-efficient routing in sensor networks. Wirel Netw 18(4):351–363
Chauhan V, Soni S (2019) Mobile sink-based energy efficient cluster head selection strategy for wireless sensor networks. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01509-6
Chen B, Jamieson K, Balakrishnan H, Morris R (2002) Span: an energy-efficient coordination algorithm for topology maintenance in ad hoc wireless networks. ACM Wirel Netw 8(5):481–494
Farooq M, Di Caro GA (2008) Routing protocols for next-generation intelligent networks inspired by collective behaviors of insect societies. In: Blum C, Merkle D (eds) Swarm intelligence: introduction and applications. Springer, natural computing series. Springer, Berlin, pp 101–160
Heinzelman WR, Chandrakasan A, Balakrishnan H (2000) Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In: IEEE computer society proceedings of the thirty third Hawaii international conference on system sciences (HICSS ‘00), Washington, DC, USA, vol 2, pp 3005–3014
Heinzelman WR, Chandrakasan A, Balakrishnan H (2002) An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 1(4):660–670
Jiang A, Zheng L (2018) An effective hybrid routing algorithm in WSN: ant colony optimization in combination with hop count minimization’. Sensors (Basel) 18(4):1–17
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J Glob Optim 39(3):459–571
Kaur M, Jain A, Goel AK (2014) Energy efficient two level distributed clustering scheme to prolong stability period of wireless sensor network. In: International conference on advances in computing, communications and informatics, pp 68–73
Kuila P, Jana PK (2014) Energy efficient clustering and routing algorithms for wireless sensor networks: particle swarm optimization approach. Eng Appl Artif Intell 33:127–140
Lee S, Chung T (2005) Data aggregation for wireless sensor networks using self-organizing map. Artif Intell Simul Lect Notes Comput Sci 3397(2005):508–517
Lindsey S, Raghavendra CS (2002) PEGASIS: power efficient gathering in sensor information system. Proc IEEE Aerosp Conf 3:1125–1130
Liu JS, Lin C-HR (2005) Energy-efficiency clustering protocol in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw 3:371–388
Manjeshwar A, Agrawal DP (2001) TEEN: a protocol for enhanced efficiency in wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 15th international symposium on parallel and distributed computing, pp 2009–2015
Marwa S, Eid E (2017) Impact of grey wolf optimization on WSN cluster formation and lifetime expansion. In: Ninth international conference on advanced computational intelligence (ICACI), pp 157–162
Mehrjoo S, Aghaee H, Karimi H (2011) A novel hybrid GAABC based energy efficient clustering in wireless sensor network. Can J Multimed Wirel Netw 2(2):41–45
Mini S, Siba K, Udgata (2011) Coverage and deployment Algorithms in wireless sensor networks. Special issue of IJCCT, first student research symposium in conjunction with seventh ICDCIT-2011, vol 2, no 5, pp 50–56
Murugan TS, Sarkar A (2018) Optimal cluster head selection by hybridisation of firefly and grey wolf optimisation. Int J Wirel Mob Comput 14(3):296–305
Muruganathan SD, Ma DCF, Bhasin RI, Fapojuwoy AO (2005) A centralized energy efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor network. In: Proceedings of IEEE radio communication, March 2005
Ossama Y, Sonia F (2004) Heed: a hybrid, energy-efficient, distributed clustering approach for ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 3(4):366–379
Pan WT (2012) A new fruit fly optimization algorithm: taking the financial distress model as an example. Knowl-Based Syst 26:69–74
Pawan SM, Doja MN, Alam B (2019) Fuzzy based enhanced cluster head selection (FBECS) for WSN. J King Saud Univ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.04.031
Praveen L, Isba G, Haider B (2016) FARW: firefly algorithm for routing in wireless sensor networks. In: 3rd international conference on recent advances in information technology I RAIT-2016, pp 248–252
Rostami A, Mottar MH (2014) Wireless sensor network clustering using particle swarm optimization for reducing energy consumption. Int J Manag Inf Technol 6(4):1–15
Saleem M, Di Caro GA, Farooq M (2011) Swarm intelligence based routing protocol for wireless sensor networks: survey and future directions. Inf Sci 181(20):4597–4624
Sandeep KE, Kusuma SM, Kumar VBP (2014) Fire-LEACH: a novel clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks based on firefly algorithm. Int J Comput Sci Theory Appl 1(1):12–17
Shu T, Krunz M, Liu S (2010) Secure data collection in wireless sensor networks using randomized dispersive routes. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 9(7):941–954
Wang Y, Song M, Wei Y, Wang Y, Wang X (2014) Improved ant colony-based multi-constrained QoS energy-saving routing and throughput optimization in wireless ad hoc networks. J China Univ Posts Telecommun 21(1):43–53
Xingjuan C, Xiao-zhi G, Yu X (2016) Improved bat algorithm with optimal forage strategy and random disturbance strategy. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput 8(4):205–214
Yourui H, Liguo Q, Chaoli T (2012) Optimal converage scheme based on QPSO in wireless sensor networks. J Netw 7(9):1362–1368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-04179-z
About this article
Cite this article
Roshni, S., Senthilkumar, J., Suresh, Y. et al. RETRACTED ARTCILE: Advertisement valid time triggered firefly and fruit-fly inspired approach for efficient cluster formation and standby CH selection in hierarchical wireless sensor network. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 12, 4697–4713 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01873-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01873-8