Abstract
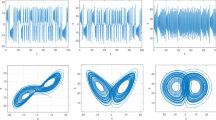
In order to characterize a system and to analyze the predictability of the time series under investigation, the detection of chaos and fractal behavior in experimental data is essential. In this work, support vector regression with two different kernel types namely, the linear kernel and sigmoid kernel, has been utilized for the calculation of the Lyapunov exponents of the given time series. The developed technique for the estimation of Lyapunov exponents has been validated with the help of time series generated from well known chaotic maps and also by comparing the Lyapunov exponents obtained using Rosenstein method. The results of this work reveal that the proposed technique is capable of producing accurate positive exponents for all the considered chaotic maps.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambikapathy B, Krishnamurthy K (2018) Analysis of electromyograms recorded using invasive and noninvasive electrodes: a study based on entropy and Lyapunov exponents estimated using artificial neural networks. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 1–9
Ataei M, Khaki-Sedigh A, Lohmann B, Lucas C (2003) Estimating the Lyapunov exponents of chaotic time series: a model based method. European control conference
Basak D, Pal S, Patranabis DC (2007) Support vector regression. Neural Information Processing-Letters and Reviews 11(10):203–224
Beck C, Schlgl F (1993) Thermodynamics of chaotic systems. Volume 4 of Cambridge nonlinear science series. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Cao L (2003) Support vector machines experts for time series forecasting. Neurocomputing 51:321–339
Chen P (1988) Empirical and theoretical evidence of economic chaos. Syst Dyn Rev 4:81
Das A, Das P, Roy AB (2002) Applicability of Lyapunov exponent in EEG data analysis. Complex Int 9:1–8
Devaney RL (1989) An introduction to chaotic dynamical systems, 2nd edn. Addison Wesley, Redwood City
Eckmann J-P, Ruelle D (1985) Ergodic theory of chaos and strange attractors. Rev Mod Phys 57:617–656
Eckmann JP, Kamphorst SO, Ruelle D, Ciliberto S (1986) Liapunov exponents from time series. Phys Rev A 34(6):4971–4979
Edmonds AN (1996) Time series prediction using supervised learning and tools from chaos theory, Ph.D Thesis
Fernnandez R (1999) Predicting time series with a local support vector regression machine, ACAI 99
Frank GW, Lookman T, Nerenberg MAH, Essex C, Lemieux J, Blume W (1990) Chaotic time series analysis of epileptic seizures. Physica D 46:427
Frontzek T, Lal TN, Eckmiller R (2001) Predicting the nonlinear dynamics of biological neurons using support vector machines with different kernels. Proc Int Joint Conf Neural Netw 2:1492–1497
Fukunaga M, Arita S, Ishino S, Nakai Y (2000) Quantitative analysis of gastric electric stress response with chaos theory. Biomed Soft Comput Hum Sci 5(2):59–64
Gunn S (1998) Support vector machines for classification and regression, ISIS Technical Report
Huang K, Yang H, King I, Lyu MR (2006) Local support vector regression for financial time series prediction, International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Jaeseung J, Jeong-Ho C, Kim SY, Seol-Heui H (2001) Nonlinear dynamical analysis of the EEG in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vacular dementia. Clin Neurophysiol 18:58–67
Kamalanand K (2012) A method for estimating the Lyapunov exponents of chaotic time series corrupted by random noise using Extended Kalman Filter. Commun Comput Sci Inf Syst 283:237–244
Kamalanand K, Jawahar PM (2013) Unscented transformation for estimating the Lyapunov exponents of chaotic time series corrupted by random noise. Int J Math Sci 7(4):1–6
Kamalanand K, Ramakrishnan S (2010) A Method for classification of normal and MyopathicEmg signals using chaos Theory, Proceedings of ICAMMM 2010, 13–15 Dec 2010, Sultan Qaboos University, Oman
Kodba S, Perc M, Marhl M (2005) Detecting Chaos from a time series. Eur J Phys 26(1):205
Lillekjendlie B, Kugiumtzis D, Christophersen N (1995) Chaotic time series Part II System identification and prediction
McCaffrey DF, Ellner S, Gallant AR, Nychka DW (1992) Estimating the Lyapunov exponent of a chaotic system with nonparametric regression. J Am Stat Assoc 87(419):682–695
Mehr AD, Nourani V, Khosrowshahi VK, Ghorbani MA (2019) A hybrid support vector regression–firefly model for monthly rainfall forecasting. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(1):335–346
Michel RG, Glass L, Mackey M, Shrier A (1983) Chaos in neurobiology. IEEE Trans Sys Man Cybern 13(5):790–798
Mohammadi S (2009) LYAPEXPAN: MATLAB function to calculate Lyapunov exponents with Taylor expansion. http://ideas.repec.org/c/boc/bocode/t741505.html
Mukherjee S, Osuna E, Girosi F (1997) Nonlinear prediction of chaotic time series using support vector machines, Proceedings of IEEE NNSP’97, Amelia Island, FL
Muller KR, Smola A, Scholkopf B (1997) Prediction time series with support vector machines. Proceedings of International Conference on Artifcial Neural Networks, Lausanne, Switzerland, 999
Murillo-Escobar J, Sepulveda-Suescun JP, Correa MA, Orrego-Metaute D (2019) Forecasting concentrations of air pollutants using support vector regression improved with particle swarm optimization: case study in Aburrá Valley, Colombia. Urban Clim 29:100473
Nychka D, Ellner S, Gallant AR, McCaHrey D (1992) Finding chaos in noisy system. J R Stat Soc B 54:399–426
Ricker WE (1954) Stock and recruitment. J Fisheries Res Board Can 11:559–623
Rosenstein MT, Collins JJ, De Luca CJ (1993) A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Physica D 65:117–134
Sano M, Sawada Y (1985) Measurement of the Lyapunov spectrum from a chaotic time series. Phys Rev Lett 55(10):1082–1085
Shintani M, Linton O (2004) Nonparametric neural network estimation of Lyapunov exponents and a direct test for chaos. J Econom 120:1–33
Smola AJ (1998) Learning with Kernels. PhD Thesis, GMD, Birlinghoven, Germany
Sprott JC (2003) Chaos and time series analysis. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Strogatz SH (1994) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos. Perseus Publishing, New York
Tay FEH, Cao LJ (2001) Application of support vector machines in financial time series forecasting. Omega 29(4):309–317
Vapnik VN, Golowich SE, Smola AJ (1996) Support vector method for function approximation, regression estimation, and signal processing. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 9:281–287
Wolf A, Swift JB, Swinney HL, Vastano JA (1985) Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Physica D 16:285–317
Zeng X, Eykholt R, Pielke RA (1991) Estimating the Lyapunov-Exponent spectrum from short time series of low precision. Phys Rev Lett 66:3229
Zhang J, Teng YF, Chen W (2019) Support vector regression with modified firefly algorithm for stock price forecasting. Appl Intell 49(5):1658–1674
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnamurthy, K., Manoharan, S.C. & Swaminathan, R. A Jacobian approach for calculating the Lyapunov exponents of short time series using support vector regression. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 11, 3329–3335 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01525-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01525-6