Abstract
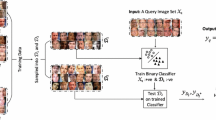
Halftone classification is a primary requisite for the perfect reconstruction of binary patterns during inverse halftone process. Majority of the halftone classification techniques are either limited to error diffused halftone or to limited categories, and cannot be generalized to all halftone versions. In this scenario, a new classification approach is proposed based on the premise that the stochastic analysis can uniquely characterize the halftone patterns. The proposed scheme exploits inherent association of halftone patterns and stochastic geometry, and utilizes its spatial and spectral parameters for feature vector construction. Extreme learning machine based multi-classifier model is adopted resulting in rapid and accurate classification. A digital halftone database comprises of 96 reference images along with the 21 varieties of halftone and multitone class is developed. From extensive analysis, it has been validated that the proposed scheme can achieve a 100% classification rate on many halftone versions and exhibit superior performance over the exiting classification techniques.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baqai FA, Allebach JP (2003) Halftoning via direct binary search using analytical and stochastic printer models. IEEE Trans Image Process 12(1):1–15
Bayer B (1973) An optimum method for two-level rendition of continuous-tone pictures. IEEE Int Conf Commun 1:11–26
Burkes D (1988) Presentation of the Burkes error filter for use in preparing continuous-tone images for presentation on bi-level devices. The file BURKES. ARC
Camastra F, Ciaramella A, Staiano A (2013) Machine learning and soft computing for ICT security: an overview of current trends. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 4(2):235–247
Chandu K, Stanich M, Wu CW, Trager B (2012). Direct multi-bit search (DMS) screen algorithm. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), vol 1, pp 817–820
Chang PC, Yu CS (1998) Neural net classification and LMS reconstruction to halftone images. Proc SPIE 3309(2):592–602
Chen YW, Wang JL, Cai YQ, Du JX (2015) A method for Chinese text classification based on apparent semantics and latent aspects. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 6(4):473–480
Floyd RW, Steinberg L (1976) An adaptive algorithm for spatial greyscale. Proc Soc Inf Disp 17:75–77
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1):489–501
Huang GB, Zhou H, Ding X, Zhang R, Part B (Cybernetics (2012) Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 42(2):513–529
Jarvis J, Roberts C (1976) A new technique for displaying continuous tone images on a bi-level display. IEEE Trans Commun 24(8):891–898
Jarvis JF, Judice CN, Ninke WH (1976) A survey of techniques for the display of continuous tone pictures on bi-level displays. Comput Graph Image Process 5:13–40
Joshi S, Nitin Khanna (2017) Single classifier-based passive system for source printer classification using local texture features. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security 13(7):1603–1614
Kacker D, Camis T, Allebach JP (2002) Electro photographic process embedded in direct binary search. IEEE Trans Image Process 11(3):243–257
Knuth DE (1987) Digital halftones by dot diffusion. ACM Trans Graph (TOG) 6(4):245–273
Lau DL, Gonzalo R, Arce (2001) Modern digital halftoning. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Liu YF, Guo JM (2016) Clustered-dot screen design for digital multitoning. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(7):2971–2982
Liu YF, Guo JM, Lee JD (2011) Halftone image classification using LMS algorithm and naive Bayes. IEEE Trans on Image Process 20(10):2837–2847
Mese M, Vaidyanathan PP (2000) Optimized halftoning using dot diffusion and methods for inverse halftoning. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(4):691–709
Seckar J, Pokorny P (2010) Relation of statistical information and visual quality in halftone images. In: Proceedings of the 21st International DAAAM Symposium, vol 21(1)
Shiau J, Fan Z (1994) Method for quantization gray level pixel data with extended distribution set. U.S. patent 5,353,127
Singh YK (2015) Generalized error diffusion method for halftoning. IEEE Int Conf Electr, Comput Commun Technol 1:1–6
Stucki P (1981) Multiple error correction computation algorithm for bi level image hardcopy reproduction. IBM Res RZ1060
Tsai MJ, Yuadi M, Tao YH, Yin JS (2017) Source identification for printed documents. IEEE 3rd Int Conf Collab Internet Comput (CIC) 1:54–58
Ulichney RA (1987) Digital halftoning. MIT Press, Cambridge
Ulichney RA (1988) Dithering with blue noise. Proc IEEE 76(1):56–79
Ulichney RA (1993) Void-and-cluster method for dither array generation. Hum Vis, V Process Digit Disp Int Soc Opt Photonics 4:332–344
Wen ZQ, Hu YX, Zhu WQ (2014) A novel classification method of halftone image via statistics matrices. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(11):4724–4736
Zeng Z, Wen Z, Yi S, Zeng S, Zhu Y, Liu Q, Tong Q (2016) Classification of error-diffused halftone images based on spectral regression kernel discriminant analysis. Adv Multimed 1:1–10
Zhang Y, Zhang E, Chen W (2016) Deep neural network for halftone image classification based on sparse auto-encoder. Eng Appl Artif Intell 50:245–255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J.M., Seshathiri, S. Generalized halftone classification approach using stochastic analysis. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 14907–14919 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0812-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0812-5