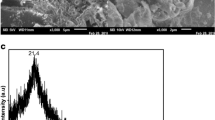
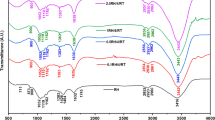
Abstract
The effect of different treatments on the depollution properties of rice husk to improve its biosorption efficiency has been investigated. The dye and heavy metal removal of treated rice husk samples were studied using methylene blue and Cu2+ as pollutant indicators. Moreover, olive oil has been used for oil removal performance tests. Although the adsorption investigation revealed that dye and Cu2+ removal is the highest using raw rice husk and steam-explosion acid-treated rice husk, respectively, steam-explosion rice husk presents more sustainability considering its cost and performance in both pollutant environments, while its oil removal capacity is outstanding compared to the raw rice husk too. Then, steam-explosion rice husks can be considered low-cost biosorbent materials for wastewater treatment that do not require high initial investments. The samples were characterized by FTIR, SEM, and EDX to compare the effect of composition and morphology on their depollution properties. The variety of functional groups present in treated rice husk based on the FTIR results improves the adsorption of MB and Cu2+.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper. Should any raw data files be needed in another format they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Albadarin, A.B., Mo, J., Glocheux, Y., Allen, S., Walker, G., Mangwandi, C.: Preliminary investigation of mixed adsorbents for the removal of copper and methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 255, 525–534 (2014)
Asim, N., Amin, M.H., Alghoul, M.A., Sulaiman, S.N.A., Razali, H., Akhtaruzzaman, M., Amin, N. Sopian, K.: Developing of chemically treated waste biomass adsorbent for dye removal. J. Nat. Fibers 18, 1–10 (2019)
Girgis, B.S., Temerk, Y.M., Gadelrab, M.M., Abdullah, I.D.: X-ray diffraction patterns of activated carbons prepared under various conditions. Carbon Lett 8, 95–100 (2007)
Bandyopadhyay-Ghosh, S., Ghosh, S.B., Sain, M.: The use of biobased nanofibres in composites. In: Faruk, O., Sain, M. (eds.) Biofiber Reinforcements in Composite Materials. Woodhead Publishing, Chapter 9, 571–647 (2015)
Baruah, J., Nath, B.K., Sharma, R., Kumar, S., Deka, R.C., Baruah, D.C., Kalita, E.: Recent trends in the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for value-added products. Front. Energy Res. 6, 1–19 (2018)
Bhatia, L., Sahu, D.K.: SEM & FTIR analysis of rice husk to assess the impact of physiochemical pretreatment. J. Agric. Ecol. Res. Int. 24, 1–13 (2023)
Boakye, P., Tran, H.N., Lee, D.S., Woo, S.H.: Effect of water washing pretreatment on property and adsorption capacity of macroalgae-derived biochar. J. Environ. Manage. 233, 165–174 (2019)
Brodeur, G., Yau, E., Badal, K., Collier, J., Ramachandran, K.B., Ramakrishnan, S.: Chemical and physicochemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Enzyme Res. 2011, 17 (2011)
Chen, D., Gao, D., Huang, S., Capareda, S.C., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Niu, W.: Influence of acid-washed pretreatment on the pyrolysis of corn straw: a study on characteristics, kinetics and bio-oil composition. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 155, 105027 (2021)
Chen, R.S., Ahmad, S., Gan, S., Tarawneh, M.A.A.: High loading rice husk green composites: dimensional stability, tensile behavior and prediction, and combustion properties. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 33, 882–897 (2020)
Davis, T.A., Volesky, B., Mucci, A.: A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 37, 4311–4330 (2003)
Davoodbeygi, Y., Askari, M., Salehi, E., Kheirieh, S.: A review on hybrid membrane-adsorption systems for intensified water and wastewater treatment: Process configurations, separation targets, and materials applied. J. Environ. Manage. 335, 117577 (2023)
Derrouiche, I.: Study of extraction and characterization of ultimate date palm fibers. Adv. Mater. 4, 7–14 (2015)
Emdadi, Z., Asim, N., Yarmo, A., Sopian, K.: Effect of chemical treatments on Rice Husk (RH) water absorption property. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Applic. 6, 273–276 (2015)
Fourest, E., Roux, J.-C.: Heavy metal biosorption by fungal mycelial by-products: mechanisms and influence of pH. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37, 399–403 (1992)
Girgis, B.S., El-Hendawy, A.-N.A.: Porosity development in activated carbons obtained from date pits under chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 52, 105–117 (2002)
Gupta, V.K., Nayak, A., Agarwal, S.: Bioadsorbents for remediation of heavy metals: current status and their future prospects. Environ. Eng. Res. 20, 1–18 (2015)
Ighalo, J.O., Omoarukhe, F.O., Ojukwu, V.E., Iwuozor, K.O., Igwegbe, C.A.: Cost of adsorbent preparation and usage in wastewater treatment: a review. Clean. Chem. Eng. 3, 100042 (2022)
Johar, N., Ahmad, I., Dufresne, A.: Extraction, preparation and characterization of cellulose fibres and nanocrystals from rice husk. Ind. Crops Prod. 37, 93–99 (2012)
Kainth, S., Sharma, P., Pandey, O.P.: Green sorbents from agricultural wastes: a review of sustainable adsorption materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 19, 100562 (2024)
Kolar, P., Jin, H.: Baseline characterization data for raw rice husk. Data Brief 25, 104219 (2019)
Kordi, M., Farrokhi, N., Pech-Canul, M.I., Ahmadikhah, A.: Rice husk at a glance: from agro-industrial to modern applications. Rice Sci. 31, 14–32 (2024)
Lin, Q., Ding, X.-L., Hou, Y.-S., Ali, W., Li, Z.-C., Han, X., Meng, Z., Sun, Y. Liu, Y.: Adsorption and separation technologies based on supramolecular macrocycles for water treatment. Eco-Environ. Health (2024, In press)
Mason, W.H.: Process and apparatus for disintegration of wood and the like. William H., United States, Mason (1926)
Mochidzuki, K., Sakoda, A., Suzuki, M., Izumi, J., Tomonaga, N.: Structural behavior of rice husk silica in pressurized hot-water treatment processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 40, 5705–5709 (2001)
Mohamad Yusop, M.F., Nasehir Khan, M.N., Zakaria, R., Abdullah, A.Z., Ahmad, M.A.: Mass transfer simulation on remazol brilliant blue R dye adsorption by optimized teak wood Based activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 16, 104780 (2023)
Mohamad Yusop, M.F., Tamar Jaya, M.A., Idris, I., Abdullah, A.Z., Ahmad, M.A.: Optimization and mass transfer simulation of remazol brilliant blue R dye adsorption onto meranti wood based activated carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 16, 104683 (2023)
Mor, S., Chhoden, K., Ravindra, K.: Application of agro-waste rice husk ash for the removal of phosphate from the wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 129, 673–680 (2016)
Ndazi, B.S., Karlsson, S., Tesha, J.V., Nyahumwa, C.W.: Chemical and physical modifications of rice husks for use as composite panels. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 38, 925–935 (2007)
Pielhop, T., Amgarten, J., von Rohr, P.R., Studer, M.H.: Steam explosion pretreatment of softwood: the effect of the explosive decompression on enzymatic digestibility. Biotechnol. Biofuels 9, 152 (2016)
Rowell, R. M.: A new generation of composite materials from agro-based fiber. In: Prasad, P.N., Mark J.E., Fai T.J. (eds.) Polymers and Other Advanced Materials: Emerging Technologies and Business Opportunities, pp. 659–665. Boston, MA, Springer US, (1995)
Russo, B., Causse, J., Rey, C., Lautru, J., Rebiscoul, D., Ayral, A.: Biosourced adsorbent prepared with rice husk part 1: a complete understanding of the structure of materials, the major role of mineral impurities for metal extraction. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 36, e00601 (2023)
Saravanan, A., Karishma, S., Kumar, P.S., Thamarai, P., Yaashikaa, P.R.: Recent insights into mechanism of modified bio-adsorbents for the remediation of environmental pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 339, 122720 (2023)
Shamsollahi, Z., Partovinia, A.: Recent advances on pollutants removal by rice husk as a bio-based adsorbent: a critical review. J. Environ. Manage. 246, 314–323 (2019)
Shang, X., Wu, S., Liu, Y., Zhang, K., Guo, M., Zhou, Y., Zhu, J., Li, X., Miao, R.: Rice husk and its derived biochar assist phytoremediation of heavy metals and PAHs co-contaminated soils but differently affect bacterial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 466, 133684 (2024)
Shrotri, A., Kobayashi, H., Fukuoka, A.: Chapter two - catalytic conversion of structural carbohydrates and lignin to chemicals. In: Song, C. (ed.) Advances in Catalysis. Academic Press, pp. 59-123 (2017)
Shukla, S.S., Chava, R., Appari, S., A, B., Kuncharam, B.V.R.: Sustainable use of rice husk for the cleaner production of value-added products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10, 106899 (2022)
Soltani, N., Bahrami, A., Pech-Canul, M.I., González, L.A.: Review on the physicochemical treatments of rice husk for production of advanced materials. Chem. Eng. J. 264, 899–935 (2015)
Sumangala Devi, N., Hariram, M., Vivekanandhan, S.: Modification techniques to improve the capacitive performance of biocarbon materials. J. Energy Storage 33, 101870 (2021)
Sun, X.F., Xu, F., Sun, R.C., Wang, Y.X., Fowler, P., Baird, M.S.: Characteristics of degraded lignins obtained from steam exploded wheat straw. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 86, 245–256 (2004)
Tsai, C.-H., Tsai, W.-T., Kuo, L.-A.: Effect of post-washing on textural characteristics of carbon materials derived from pineapple peel biomass. Materials 16, 7529 (2023)
Tsai, W.-T., Hsu, C.-H., Lin, Y.-Q., Tsai, C.-H., Chen, W.-S., Chang, Y.-T.: Enhancing the pore properties and adsorption performance of Cocoa Pod Husk (CPH)-derived biochars via post-acid treatment. Processes. 8, 144 (2020)
Villota-Enríquez, M.D., Rodríguez-Páez, J.E.: Bio-silica production from rice husk for environmental remediation: removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 301, 127671 (2023)
Volesky, B., Holan, Z.R.: Biosorption of heavy metals. Biotechnol. Prog. 11, 235–250 (1995)
Wang, J., Chen, C.: Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 27, 195–226 (2009)
Wei, X., Huang, S., Wu, Y., Wu, S.: Effects of washing pretreatment on properties and pyrolysis biochars of penicillin mycelial residues. Biomass Bioenerg. 161, 106477 (2022)
Wood, I.P., Cao, H.-G., Tran, L., Cook, N., Ryden, P., Wilson, D.R., Moates, G.K., Collins, S.R.A., Elliston, A., Waldron, K.W.: Comparison of saccharification and fermentation of steam exploded rice straw and rice husk. Biotechnol. Biofuels 9, 193 (2016)
Yan, Y., Herzele, S., Mahendran, A., Edler, M., Griesser, T., Saake, B., Li, J., Gindl-Altmutter, W.: Microfibrillated lignocellulose enables the suspension-polymerisation of unsaturated polyester resin for novel composite applications. Polymers 8, 255 (2016)
Emdadi, Z., Asim, N., Ramli, Z.A.C., Yarmo, M.A., Shamsudin, R., Sopian, K.: Feasibility study of using rice husk and its treated forms with alkali solution as a desiccant material. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 10, 306–311 (2014)
Zhang, P., He, M., Teng, W., Li, F., Qiu, X., Li, K., Wang, H.: Ordered mesoporous materials for water pollution treatment: adsorption and catalysis. Green Energy Environ. (2023, In press)
Zhang, Y.H.P., Lynd, L.R.: Toward an aggregated understanding of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose: noncomplexed cellulase systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 88, 797–824 (2004)
Zheng, G., Wei, K., Kang, X., Fan, W., Ma, N.L., Verma, M., Ng, H.S., Ge, S.: A new attempt to control volatile organic compounds (VOCs) pollution - modification technology of biomass for adsorption of VOCs gas. Environ. Pollut. 336, 122451 (2023)
Zou, Y., Yang, T.: Rice husk, rice husk ash and their applications. In: Cheong, L.-Z., Xu, X. (eds.), Rice Bran and Rice Bran Oil, AOCS Press. Chapter 9 pp. 207–246 (2019)
Funding
This study was supported by the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia’s grant GUP-2021-072.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Asim, N., Badiei, M., bin Sahari, N. et al. Green Remediation of Pollutions Utilizing Modified Rice Husk by Steam Explosion and Acid Treatment. Waste Biomass Valor (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-024-02566-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-024-02566-5