Abstract
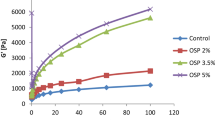
Peanut skin, a by-product of the peanut processing industry, is typically disposed of as an inexpensive agricultural by-product. However, peanut skin is a rich source of bioactive compounds that can be used to enrich foods that are better for your health and provide more nutrition. Therefore, this research article focuses on the valorisation of peanut skin by developing functional skin and its addition into peanut butter with improved nutritional value and sensory quality. The study explored the effect of pressure-cooking on the development of peanut skin-fortified peanut butter and studied its physicochemical, functional and organoleptic characteristics. The results indicated that adding peanut skin significantly improved the colour attributes (L* = 40.73–44.76, a* = 4.35–5.57 and b* = 7.83–12.43) and phenolic content. Different processing conditions like pressure cooking improved the phenolic contents and anti-oxidant activities of peanut butter. Moreover, rheological properties and textural properties have been increased with the application of moist heat treatment. Functional peanut butter had increased viscosity and hardness but decreased spreadability and oil separation compared to the control. Sensory evaluation showed that the skin-on the product had desirable sensory attributes, including appearance, flavour and overall acceptability. The study concludes that incorporating peanut skin into peanut butter enhanced its functional and nutritional properties without compromising sensory quality. These findings provide valuable insights for the food industry to develop healthier and value-added peanut butter products with different treatment methods.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Bonku, R., Yu, J.: Health aspects of peanuts as an outcome of its chemical composition. Food Sci. Human Wellness 9(1), 21–30 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2019.12.005
Pidatala, P.K., Bellemer, D., McGlynn, W.: Oxidative stability of a new peanut butter bite product. Int. J. Food Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/552831
A-na, G., Ai-min, S., Hong-zhi, L., Hong-wei, Y., Li, L., Wei-jing, L., Qiang, W.: Relationship of chemical properties of different peanut varieties to peanut butter storage stability. J. Integra. Agri. 17(5), 1003–1010 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(18)61919-7
Jung, M., Kim, J., Ahn, S.M.: Factors associated with frequency of peanut consumption in Korea: a national population-based study. Nutrients 12(5), 1207 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051207
Dean, L.L.: Extracts of peanut skins as a source of bioactive compounds: methodology and applications. Appl. Sci. 10(23), 8546 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238546
Çiftçi, S., Suna, G.: Functional components of peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.) and health benefits: a review. Future Foods. 5, 100140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fufo.2022.100140
Bodoira, R., Cittadini, M.C., Velez, A., Rossi, Y., Montenegro, M., Martínez, M., Maestri, D.: An overview on extraction, composition, bioactivity and food applications of peanut phenolics. Food Chem. 381, 132250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132250
Rossi, Y.E., Bohl, L.P., Braber, V.N.L., Ballatore, M.B., Escobar, F.M., Bodoira, R., Maestri, D.M., Porporatto, C., Cavaglieri, L.R., Montenegro, M.A.: Polyphenols of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) skin as bioprotectors of normal cells: studies of cytotoxicity, cytoprotection and interaction with ROS. J. Fun. Food. 67, 103862 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2020.103862
Christman, L.M., Dean, L.L., Allen, J.C., Godinez, S.F., Toomer, O.T.: Peanut skin phenolic extract attenuates hyperglycaemic responses in-vivo and in-vitro. PLoS ONE 14(3), e0214591 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214591
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Du, P., Liang, X., Li, H., Lu, Q., Li, S., Liu, H., Hong, Y., Varshney, R.K., Chen, X.: Impact of different cooking methods on the chemical profile of high-oleic acid peanut seeds. Food Chem. 379(15), 131970 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131970
Salve, A.R., LeBlanc, J.G., Arya, S.S.: Effect of processing on polyphenol profile, aflatoxin concentration and allergenicity of peanuts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 58(7), 2714–2724 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04779-7
Larrauri, M., Zunino, M.P., Zygadlo, J.A., Grosso, N.R., Nepote, V.: Chemical characterization and antioxidant properties of fractions separated from extract of peanut skin derived from different industrial processes. Ind. Crops Prod. 94, 964–971 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.09.066
Hu, H., Shi, A., Liu, H., Liu, L., Fauconnier, M.L., Wang, Q.: Study on key aroma compounds and its precursors of peanut oil prepared with normal- and high-oleic peanuts. Foods. 10, 3036 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123036
Parilli-Moser, I., Domínguez-López, I., Trius-Soler, M., Castellví, M., Bosch, B., Castro-Barquero, S., Estruch, R., Hurtado-Barroso, S., Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.: Consumption of peanut products improves memory and stress response in healthy adults from the ARISTOTLE study: a 6-month randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 40(11), 5556–5567 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.09.020
Ma, Y., Kerr, W.L., Swanson, R.B., Hargrove, J.L., Pegg, R.B.: Peanut skins-fortified peanut butters: effect of processing on the phenolics content, fibre content and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 145, 883–891 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.125
Wilkin, J.D., Ashton, I.P., Fielding, L.M., Tatham, A.S.: Storage stability of whole and nibbed, conventional and high oleic peanuts (Arachis hypogeae L.). Food Bioprocess Technol. 7(1), 105–113 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-1033-0
Shevkani, K., Kaur, A., Kumar, S., Singh, N.: Cowpea protein isolates: functional properties and application in gluten-free rice muffins. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 63, 927–933 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.04.058
Rozalli, N.H.M., Chin, N.L., Yusof, Y.A., Mahyudin, N.: Quality changes of stabilizer-free natural peanut butter during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 53(1), 694–702 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2006-x
Rashidinejad, A., Birch, E.J., Sun-Waterhouse, D., Everett, D.W.: Effects of catechin on the phenolic content and antioxidant properties of low-fat cheese. Int. J. Food Sci. and Technol. 48(12), 2448–2455 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12234
Bandonienė, D., Murkovic, M., Pfannhauser, W., Venskutonis, P., Gruzdienė, D.: Detection and activity evaluation of radical scavenging compounds by using DPPH free radical and on-line HPLC-DPPH methods. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 214(2), 143–147 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-001-0430-9
Huang, H.H., Dikkala, P.K., Sridhar, K., Yang, H.T., Lee, J.T., Tsai, F.J.: Effect of heat treatment and γ-irradiation on pasting, rheological, and fungal load of whole and dehulled millets. Food Sci. Technol. Int. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15355
Yu, H., Liu, H., Erasmus, S.W., Zhao, S., Wang, Q., van Ruth, S.M.: An explorative study on the relationships between the quality traits of peanut varieties and their peanut butters. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 151, 112068 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112068
Riveros, C.G., Mestrallet, M.G., Gayol, M.F., Quiroga, P.R., Nepote, V., Grosso, N.R.: Effect of storage on chemical and sensory profiles of peanut pastes prepared with high-oleic and normal peanuts. J. Sci. Food Agri. 90, 2694–2699 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4142
Huang, W., Tan, H., Nie, S.: Beneficial effects of seaweed-derived dietary fiber: highlights of the sulfated polysaccharides. Food Chem. 373, 131608 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131608
Muñoz-Arrieta, R., Esquivel-Alvarado, D., Alfaro-Viquez, E., Alvarez-Valverde, V., Krueger, C.G., Reed, J.D.: Nutritional and bioactive composition of Spanish, Valencia, and Virginia type peanut skins. J. Food Compos. Anal. 98, 103816 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103816
Silva, M.P., Farsoni, E.G., Gobato, C.F., Thomazini, M., Favaro-Trindade, C.S.: Simultaneous encapsulation of probiotic and guaraná peel extract for development of functional peanut butter. Food Control 138, 109050 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109050
Yang, R., Wei, L., Dai, J.J.: Thermal death kinetics of Salmonella Enteritidis PT30 in peanut butter as influenced by water activity. Food Res. Int. 157, 111288 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111288
Win, M.M., Abdul-Hamid, A., Baharin, B.S., Anwar, F., Sabu, M.C., Pak-Dek, M.S.: Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of peanut’s skin, hull, raw kernel and roasted kernel flour. Pak. J. Bot. 43(3), 1635–1642 (2011)
Sanders, C.T., III., DeMasie, C.L., Kerr, W.L., Hargrove, J.L., Pegg, R.B., Swanson, R.B.: Peanut skins-fortified peanut butters: effects on consumer acceptability and quality characteristics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 59, 222–228 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.04.001
Arya, S.S., Salve, A.R., Chauhan, S.: Peanuts as functional food: a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 53, 31–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2007-9
Boukid, F.: Peanut protein—an underutilised by-product with great potential: a review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.15495
Sithole, T.R., Ma, Y.X., Qin, Z., Liu, H.M., Wang, X.D.: Technical aspects of peanut butter production processes: roasting and grinding processes review. J. Food Process. Preserv. 46, e16430 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.16430
Masaka, V.P., Ndlovu, N., Tshalibe, R.S., Mhande, T.C., Jombo, T.Z.: Prevalence of aflatoxin contamination in peanuts and peanut butter from an informal market, Harare, Zimbabwe. Int. J. Food Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3761078
Wang, S., Adhikari, K., Hung, Y.C.: Acceptability and preference drivers of freshly roasted peanuts. J. Food Sci. 82(1), 174–184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13561
Liu, Y., Yu, Y., Liu, C., Regenstein, J.M., Liu, X., Zhou, P.: Rheological and mechanical behaviour of milk protein composite gel for extrusion-based 3D food printing. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 102, 338–346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.12.053
Hanim, M.R.N., Chin, N.L., Yusof, Y.A.: Effects of grinding time on rheological, textural and physical properties of natural peanut butter stored at different temperatures. J. Texture Stud. 47(2), 131–141 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/jtxs.12167
Ma, Y., Kerr, W.L., Cavender, G.A., Swanson, R.B., Hargrove, J.L., Pegg, R.B.: Effect of peanut skin incorporation on the colour, texture and total phenolics content of peanut butters. J. Food Process Eng 36, 316–328 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4530.2012.00693.x
Dhamsaniya, N.K., Patel, N.C., Dabhi, M.N.: Selection of groundnut variety for making a good quality peanut butter. J. Food Sci. Technol. 49, 115–118 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0361-9
Arrieta-Escobar, J.A., Bernardo, F.P., Orjuela, A., Camargo, M., Morel, L.: Incorporation of heuristic knowledge in the optimal design of formulated products: application to a cosmetic emulsion. Comput. Chem. Eng. 122, 265–274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2018.08.032
McNeill, K.L., Sanders, T.H., Civille, G.V.: Using focus groups to develop a quantitative consumer questionnaire for peanut butter. J. Sens. Stud. 15, 163–174 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-459X.2000.tb00263.x
Sanders, T.H., Calhoun, R.S.: Effect of oil and dry roasting of peanuts at various temperatures and times on survival of Salmonella and Enterococcus Faecium. Peanut Sci. 41, 65–71 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3146/PS13-16.1
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no declaration of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dikkala, P.K., Kaur, A., Kaur, K. et al. Valorization of Peanut Skin: Development of Functional Skin-on Peanut Butter and Quality Characteristics. Waste Biomass Valor (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02367-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02367-2