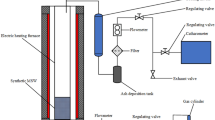
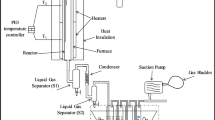
Abstract
With urban dry and wet waste classification utilized, kitchen waste is sorted out and used for achieving anaerobic biogas, in which biogas solid residue is produced meanwhile. The purpose of this article is to clarify the pyrolysis characteristics of the biogas solid residue using thermo-gravimetric analyzer and Py-GC/MS. The main research results include: (1) The dried biogas solid residue sample has more volatile matter, accounting for 62% .The ash accounting for 37.52%. (2) There are two dominant pyrolysis peaks in thermal gravimetric curves of biogas solid residue, located at low temperature about 200–300 °C. The lower activation energy of pyrolysis rate under 100–250 oC is related to the previous anaerobic digestion process. The third peak position occurs at 750 °C due to calcination of CaCO3 in ash. (3) The amount of alcohols and acid in pyrolysis gas increases first and then decreases with the increase of temperature. The pyrolysis of ether organics mainly occurs at lower temperature, 200 °C. Those productions are assumed to be derived from lipid degradation during pyrolysis. (4) The ash of biogas solid residue obtained under 400 oC is rich in Na, K and Cl. A proper approach could convert biogas solid residue to more amount of pyrolysis gas, keeping the temperature under 600 °C. And most Na, K and Cl retain in the residue, as beneficiates the biogas quality and favors the following-up combustion behavior avoiding slagging problem in combustion chamber.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Abbreviations
- ar:
-
As-received
- db:
-
Dried-baisis
- DMS:
-
Direct melting system
- MBT:
-
Mechanical biological treatment
- Py-GC/MS:
-
Pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry
- WtE:
-
Waste-to-Energy
References
Thanopoulos, S., Karellas, S., Kavrakos, M., Konstantellos, G., Tzempelikos, D., Kourkoumpas, D.: Analysis of alternative MSW treatment technologies with the aim of energy recovery in the municipality of vari-voula-vouliagmeni. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 11, 1585–1601 (2020)
Malav, L.C., Yadav, K.K., Gupta, N., Kumar, S., Sharma, G.K., Krishnan, S., Rezania, S., Kamyab, H., Pham, Q.B., Yadav, S., Bhattacharyya, S., Yadav, V.K., Bach, Q.V.: A review on municipal solid waste as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India: current practices, challenges, and future opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 277, 123227 (2020)
Xiao, S., Dong, H., Geng, Y., Francisco, M.J., Pan, H., Wu, F.: An overview of the municipal solid waste management modes and innovations in Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 29943–29953 (2020)
Lopez, V.M., Cruz, F.B.D., Barlaz, M.A.: Chemical composition and methane potential of commercial food wastes. Waste Manag. 56, 477–490 (2016)
Directive 2009/28/EC in Europe. (DIRECTIVE 2009/28/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 23: April 2009 on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources and amending and subsequently repealing directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC)
Molino, A., Nanna, F., Ding, Y., Bikson, B., Braccio, G.: Biomethane production by anaerobic digestion of organic waste. Fuel 103, 1003–1009 (2013)
Christensen, T.: Solid waste technology and management, 1st edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Thanos Bourtsalas, A.C., Themelis, N.J.: Materials and energy recovery at six european MBT plants. Waste Manag. 141, 79–91 (2022)
Neumanna, J., Binder, S., Apfelbacher, A., Gasson, J.R., García, P.R., Hornung, A.: Production and characterization of a new quality pyrolysis oil, char and syngas from digestate-introducing the thermo-catalytic reforming process. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 113, 137–142 (2015)
Odlare, M., Abubaker, J., Lindmark, J., Pell, M., Thorin, E., Nehrenheim, E.: Emissions of N2O and CH4 from agricultural soils amended with two types of biogas residues. Biomass Bioenergy 44, 112–116 (2012)
Arthurson, V.: Closing the global energy and nutrient cycles through application of biogas residue to agricultural land – potential benefits and drawback. Energies 2(2), 226 (2009)
Wang, S.L., Yang, J.S., Wang, R.L., Li, R.Q., Wang, S.T., Liu, K.F.: Effects of biogas residue on soil improvement in peach orchard. Appl. Mech. Mater. 3547(675–677), 738–741 (2014)
Nkoa, R.: Agricultural benefits and environmental risks of soil fertilization with anaerobic digestates: a review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 34(2), 473–492 (2014)
He, J., Zhu, N., Xu, Y., Wang, L., Zheng, J., Li, X.: The microbial mechanisms of enhanced humification by inoculation with Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Trichoderma longibrachiatum during biogas residues composting. Bioresour. Technol. 351, 126973–126973 (2022)
Meng, X., Yan, J., Zuo, B., Wang, Y., Yuan, X., Cui, Z.: Full-scale of composting process of biogas residues from corn stover anaerobic digestion: physical-chemical, biology parameters and maturity indexes during whole process. Bioresour. Technol. 302(C), 122742 (2020)
Govasmark, E., Stäb, J., Holen, B., Hoornstra, D., Nesbakk, T., Salkinoja-Salonen, M.: Chemical and microbiological hazards associated with recycling of anaerobic digested residue intended for agricultural use. Waste Manag. 31(12), 2577–2583 (2011)
Kratzeisen, M., Starcevic, N., Martinov, M., Maurer, C., Müller, J.: Applicability of biogas digestate as solid fuel. Fuel 89, 2544–2548 (2010)
Tao, K., Vladimir, S., Tim, E.: Effect of the heating rate on the thermochemical behavior and biofuel properties of sewage sludge pyrolysis. Energy & Fuels 30(3), 1564–1570 (2016)
Wang, T., Ye, X., Yin, J., Lu, Q., Zheng, Z., Dong, C.: Effects of biopretreatment on pyrolysis behaviors of corn stalk by methanogen. Bioresour. Technol. 164, 416–419 (2014)
Wang, T., Ye, X., Yin, J., Jin, Z., Lu, Q., Zheng, Z., Dong, C.: Fast pyrolysis product distribution of biopretreated corn stalk by methanogen. Bioresour. Technol. 169, 812–815 (2014)
Liang, S., Han, Y., Wei, L., McDonald, A.G.: Production and characterization of bio-oil and bio-char from pyrolysis of potato peel wastes. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 5(3), 237–246 (2015)
Liu, J., Huang, S., Chen, K., Wang, T., Mei, M., Li, J.: Preparation of biochar from food waste digestate: pyrolysis behavior and product properties. Bioresour. Technol. 302(C), 122841 (2020)
Pan, J., Gao, B., Wang, S., Guo, K., Xu, X., Yue, Q.: Waste-to-resources: green preparation of magnetic biogas residues-based biochar for effective heavy metal removals. Sci. Total Environ. 737, 140283–140283 (2020)
Liu, H., Wang, X., Fang, Y., Lai, W., Xu, S., Eric, L.: Enhancing thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste with biogas residue biochar. Renew. Energy 188, 465–475 (2022)
David, E., Kopač, J.: Upgrading the characteristics of the bio-oil obtained from rapeseed oil cake pyrolysis through the catalytic treatment of its vapors. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 141, 104638–104638 (2019)
Shao, J., Yan, R., Chen, H., Yang, H., Lee, D.H.: Catalytic effect of metal oxides on pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Fuel Process. Technol. 91(9), 1113–1118 (2010)
Ansah, E., Wang, L., Shahbazi, A.: Thermogravimetric and calorimetric characteristics during co-pyrolysis of municipal solid waste components. Waste Manag. 56, 196–206 (2016)
Williams Paul, T., Horne Patrick, A.: The role of metal salts in the pyrolysis of biomass. Renew. Energy 4(1), 1–13 (1994)
Sharma, S., Ghoshal, A.K.: Study of kinetics of co-pyrolysis of coal and waste LDPE blends under argon atmosphere. Fuel 89(12), 3943–3951 (2010)
Zhou, L., Luo, T., Huang, Q.: Co-pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of coal and plastic blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 50(3), 705–710 (2009)
Zheng, X., Chen, C., Ying, Z., Wang, B., Chi, Y.: Py-GC/MS study on tar formation characteristics of MSW key component pyrolysis. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 8(2), 313–319 (2017)
Dong, C., Zhang, Z., Lu, Q., Yang, Y.: Characteristics and mechanism study of analytical fast pyrolysis of poplar wood. Energy. Conv. Manag. 57, 49–59 (2012)
Ding, K., Zhong, Z., Wang, J., Zhang, B., Fan, L., Liu, S., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhong, D., Chen, P., Ruan, R.: Improving hydrocarbon yield from catalytic fast co-pyrolysis of hemicellulose and plastic in the dual-catalyst bed of CaO and HZSM-5. Bioresour. Technol. 261, 86–92 (2018)
Wang, D., Xiao, R., Zhang, H., He, G.: Comparison of catalytic pyrolysis of biomass with MCM-41 and CaO catalysts by using TGA–FTIR analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 89(2), 171–177 (2010)
French, R., Czernik, S.: Catalytic pyrolysis of biomass for biofuels production. Fuel Process. Technol. 91(1), 25–32 (2009)
Wang, X., Sheng, L., Yang, X.: Pyrolysis characteristics and pathways of protein, lipid and carbohydrate isolated from microalgae nannochloropsis sp. Bioresour. Technol. 229, 119–125 (2017)
Jan, P., Desmond, R., Scott Donald, S.: On the mechanism of the rapid pyrolysis of cellulose. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 9(2), 121–137 (1986)
Akhtar, J., Amin, N.S.: A review on operating parameters for optimum liquid oil yield in biomass pyrolysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 16(7), 5101–5109 (2012)
Li, J., Yan, R., Xiao, B., Wang, X., Yang, H.: Influence of temperature on the formation of oil from pyrolyzing palm oil wastes in a fixed bed reactor. Energy & Fuels 21(4), 2398–2407 (2007)
Wang, S., Liang, T., Ru, B., Xi, G.: Mechanism of xylan pyrolysis by Py-GC/MS. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 29(4), 782–787 (2013)
Chen, W., Yang, H., Chen, Y., Xia, M., Yang, Z., Wang, X., Chen, H.: Algae pyrolytic poly-generation: influence of component difference and temperature on products characteristics. Energy 131, 1–12 (2017)
Schwab, A.W., Dykstra, G.J., Selke, E., Sorenson, S.C., Pryde, E.H.: Diesel fuel from thermal decomposition of soybean oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 65(11), 1781–1786 (1988)
Silva, J.O., Filho, G.R., Meireles, C.S., Ribeiro, S.D., Vieira, J.G., Silva, C.V., Daniel, A.C.: Thermal analysis and FTIR studies of sewage sludge produced in treatment plants. The case of sludge in the city of Uberlândia-MG, Brazil. Thermochim. Acta 528, 72–75 (2011)
Yang, X., Zhang, J., Zhu, X.: Decomposition and calcination characteristics of calcium-enriched bio-oil. Energy & Fuels 22(4), 2598–2603 (2008)
Nagashima, O., Sato, S., Takahashi, R., Sodesawa, T.: Ketonization of carboxylic acids over CeO2-based composite oxides. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 227(1), 231–239 (2004)
Liu, Y., Li, Z., Wang, J., Zhu, P., Zhao, J., Zhang, C., Guo, Y., Jin, X.: Thermal degradation and pyrolysis behavior of aluminum alginate investigated by TG-FTIR-MS and Py-GC-MS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 118, 59–68 (2015)
Moldoveanu, S.C.: Analytical pyrolysis of proteins. Tech. Instrum. Anal. Chem. 20, 373–397 (1998)
Shigeo, M., Nobutaka, K., Osamu, W., Sekio, I., Kunihiko, A., Masatoshi, M.: Detection of a carcinogen, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo [4,5-b]pyridine, in airborne particles and diesel-exhaust particles. Environ. Pollut. 80(3), 281–286 (1993)
Maher, K.D., Bressler, D.C.: Pyrolysis of triglyceride materials for the production of renewable fuels and chemicals. Bioresour. Technol. 98(12), 2351–2368 (2007)
Carneiro, M.L.N.M., Gomes, M.S.P.: Energy, exergy, environmental and economic analysis of hybrid waste-to-energy plants. Energy. Conv. Manag. 179, 397–417 (2019)
Luz, F.C., Rocha, M.H., Lora, E.E.S., Venturini, O.J., Andrade, R.V., Leme, M.M.V., Olmo, O.A.: Techno-economic analysis of municipal solid waste gasification for electricity generation in Brazil. Energy. Conv. Manag. 103, 321–337 (2015)
Dong, J., Tang, Y., Nzihou, A., Chi, Y.: Key factors influencing the environmental performance of pyrolysis, gasification and incineration Waste-to-energy technologies. Energy. Conv. Manag. 196, 497–512 (2019)
NIPPON STEEL ENGINEERING CO Ltd. Waste to Energy Facility (Shaft Type Gasification Melting Furnace). JASE-W Japanese Smart Energy Products & Technologies. https://www.jase-w.eccj.or.jp/technologies/pdf/electricity/E-20.pdf
Tanigaki, N.: Proven Waste Gasification Technology-Recent operating conditions and measures for scale-up [J]. World Waste to Energy City Summit London (2016). http://worldwastetoenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/NobuhiroTanigaki.pdf
Knudsen, J.N., Jensen, P.A., Dam-Johansen, K.: Transformation and release to the gas phase of cl, K, and S during combustion of annual biomass. Energy Fuels 18(5), 1385–1399 (2004)
Fatehi H, Costa M, Bai XS (2020) Numerical study on K/S/Cl release during devolatilization of pulverized biomass at high temperature. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 38:3909–3917.
Angelo, S.M., Aldrin, C.: Comparative analysis of existing waste-to-energy reference plants for municipal solid waste. Clean. Environ. Syst. 3, 100063 (2021)
Aghbashlo, M., Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H., Shahbeik, H., Tabatabaei, M.: The role of sustainability assessment tools in realizing bioenergy and bioproduct systems. Biofuel Res. J. 35, 1697–1706 (2022)
Li, H., Chen, J., Zhang, W., Zhan, H., He, C., Yang, Z., Peng, H., Leng, L.: Machine-learning-aided thermochemical treatment of biomass: a review. Biofuel Res. J. 37, 1786–1809 (2023)
Shahbeik, H., Rafiee, S., Shafizadeh, A., Jeddi, D., Jafary, T., Lam, S.S., Pan, J., Tabatabaei, M., Aghbashlo, M.: Characterizing sludge pyrolysis by machine learning: towards sustainable bioenergy production from wastes. Renew. Energy 199, 1078–1092 (2022)
Mahari, W.A.W., Azwar, E., Foong, S.Y., Ahmed, A., Peng, W., Tabatabaei, M., Aghbashlo, M., Park, Y.K., Sonne, C., Lam, S.S.: Valorization of municipal wastes using co-pyrolysis for green energy production, energy security and environmental sustainability: a review. Chem. Eng. J. 121, 129749 (2021)
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from National Key Research and Development Project of China (2018YFC1901206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhang, T., Zhang, R. et al. Pyrolysis Characteristics of Anaerobic Biogas Solid Residue from Kitchen Waste. Waste Biomass Valor 15, 1141–1153 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02232-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02232-2