Abstract
Purpose
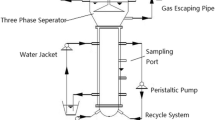
The up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor (UASB) treated effluent does not meet the national disposal standards of certain countries, such as India and Brazil. To meet the required standards, it is necessary to upgrade the UASB technology through a post-treatment system. The present work aimed to investigate the optimal operating conditions for the formation of granules in an anaerobic/oxic/anoxic (A/O/A) cyclic mode aerobic granular biomass reactor (AGBR) for the treatment of anaerobic effluent (UASB effluent).
Methods
Two rectangular reactors, R1 and R2, were used to cultivate aerobic granular biomass (AGB). R1 served as the control reactor and was fed with low-strength synthetic wastewater throughout the study, while R2 was fed with medium strength sewage and UASB effluent over the study periods.
Results
Granules start-ups were observed on the 30th and 20th days in R1 and R2, respectively. In R1, the removal efficiency of COD, NH4+-N, total nitrogen (TN), and PO43−-P was achieved 80.86%, 97.46%, 53.6%, and 45%, respectively. Whereas the removal efficiency of COD, NH4+-N, TN, and PO43−-P was observed 63.61%, 58.18%, 50%, and 40%, respectively, in R2. The results indicated that the short aeration time, comprising 50% of the total cycle time over a 3-h duration, was the most effective operational phase for achieving high removal of organics and nutrients.
Conclusion
The study demonstrates that the A/O/A AGBR effectively cultivates AGB and removes organics and nutrients from anaerobic effluent. The use of medium-strength sewage as a substrate in R2 proved beneficial in reducing the granule start-up time for treating low-strength anaerobic effluent.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Alattabi, A.W., Harris, C.B., Alkhaddar, R.M., Ortoneda-Pedrola, M., Alzeyadi, A.T.: An investigation into the effect of MLSS on the effluent quality and sludge settleability in an aerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactor (AASBR). J Water Process Eng 30, 100479 (2019)
Arthur, P.M., Konaté, Y., Sawadogo, B., Sagoe, G., Dwumfour-Asare, B., Ahmed, I., Williams, M.N.: Performance evaluation of a full-scale upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor coupled with trickling filters for municipal wastewater treatment in a developing country. Heliyon 8(8), e10129 (2022)
Daud, M. K., Rizvi, H., Akram, M. F., Ali, S., Rizwan, M., Nafees, M., & Jin, Z. S. (2018). Review of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor technology: effect of different parameters and developments for domestic wastewater treatment. J. Chem., 2018.
De Kreuk, M.K., Kishida, N., Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.: Aerobic granular sludge–state of the art. Water Sci. Technol. 55(8–9), 75–81 (2007)
de Sousa Rollemberg, S.L., Ferreira, T.J.T., Firmino, P.I.M., Dos Santos, A.B.: Impact of cycle type on aerobic granular sludge formation, stability, removal mechanisms and system performance. J. Environ. Manag. 256, 109970 (2020)
de Sousa Rollemberg, S.L., Barros, A.R.M., Firmino, P.I.M., Dos Santos, A.B.: Aerobic granular sludge: cultivation parameters and removal mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 270, 678–688 (2018)
Devlin, T.R., Di Biase, A., Kowalski, M., Oleszkiewicz, J.A.: Granulation of activated sludge under low hydrodynamic shear and different wastewater characteristics. Biores. Technol. 224, 229–235 (2017)
Franca, R.D., Pinheiro, H.M., van Loosdrecht, M.C., Lourenço, N.D.: Stability of aerobic granules during long-term bioreactor operation. Biotechnol. Adv. 36(1), 228–246 (2018)
Gao, D., Liu, L., Liang, H., Wu, W.M.: Aerobic granular sludge: characterization, mechanism of granulation and application to wastewater treatment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 31(2), 137–152 (2011)
Grube, M., Lin, J.G., Lee, P.H., Kokorevicha, S.: Evaluation of sewage sludge-based compost by FT-IR spectroscopy. Geoderma 130(3–4), 324–333 (2006)
Hamza, R., Rabii, A., Ezzahraoui, F.Z., Morgan, G., Iorhemen, O.T.: A review of the state of development of aerobic granular sludge technology over the last 20 years: full-scale applications and resource recovery. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 5, 100173 (2022)
He, Q., Song, J., Zhang, W., Gao, S., Wang, H., Yu, J.: Enhanced simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal through mixed carbon source by aerobic granular sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 382, 121043 (2020)
He, Q., Chen, L., Zhang, S., Chen, R., Wang, H.: Hydrodynamic shear force shaped the microbial community and function in the aerobic granular sequencing batch reactors for low carbon to nitrogen (C/N) municipal wastewater treatment. Biores. Technol. 271, 48–58 (2019)
He, Q., Chen, L., Zhang, S., Wang, L., Liang, J., Xia, W., Zhou, J.: Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in aerobic granular sequencing batch reactors with high aeration intensity: impact of aeration time. Bioresour Technol 263, 214–222 (2018)
He, Q., Zhang, W., Zhang, S., Wang, H.: Enhanced nitrogen removal in an aerobic granular sequencing batch reactor performing simultaneous nitrification, endogenous denitrification and phosphorus removal with low superficial gas velocity. Chem. Eng. J. 326, 1223–1231 (2017)
Iorhemen, O.T., Liu, Y.: Effect of feeding strategy and organic loading rate on the formation and stability of aerobic granular sludge. J. Water Process Eng. 39, 101709 (2021)
Iorhemen, O.T., Hamza, R.A., Zaghloul, M.S., Tay, J.H.: Simultaneous organics and nutrients removal in side-stream aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor (AGMBR). J. Water Process Eng. 21, 127–132 (2018)
Jiang, W., Ma, Y., Nie, Z., Wang, N., Yu, G., Shi, X., Bian, D.: Improving nitrogen and phosphorus removal and sludge reduction in new integrated sewage treatment facility by adjusting biomass concentration. J. Water Process Eng. 50, 103203 (2022)
Khan, A. A. (2011). Integrated UASB reactor and its different aerobic post treatment options for sewage treatment (Doctoral dissertation, Ph. D. thesis, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India).
Kishida, N., Kim, J., Tsuneda, S., Sudo, R.: Anaerobi c/oxic/anoxic granular sludge process as an effective nutrient removal process utilizing denitrifying polyphosphate-accumulating organisms. Water Res. 40(12), 2303–2310 (2006)
Liang, D., Guo, W., Li, D., Ding, F., Li, P., Zheng, Z., Li, J.: Enhanced aerobic granulation for treating low-strength wastewater in an anaerobic-aerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactor by selecting slow-growing organisms and adding carriers. Environ. Res. 205, 112547 (2022)
Lin, J., Zhang, P., Li, G., Yin, J., Li, J., Zhao, X.: Effect of COD/N ratio on nitrogen removal in a membrane-aerated biofilm reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 113, 74–79 (2016)
Liu, W., Wang, J., Shen, Y., Ji, X., Yang, D.: Response of nitritation granules to anaerobically pre-treated municipal wastewater at low temperatures in a continuous-flow reactor. Chemosphere 294, 133831 (2022)
Liu, X., Liu, J., Deng, D., Li, R., Guo, C., Ma, J., Chen, M.: Investigation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in four types of sludge: factors influencing EPS properties and sludge granulation. J. Water Process Eng. 40, 101924 (2021)
Liu, Y. Q., & Tay, J. H.: Fast formation of aerobic granules by combining strong hydraulic selection pressure with overstressed organic loading rate. Water. Res. 80, 256–266 (2015)
Liu, Y., Niu, Q., Wang, S., Ji, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., Li, Y.Y.: Upgrading of the symbiosis of Nitrosomanas and anammox bacteria in a novel single-stage partial nitritation–anammox system: nitrogen removal potential and Microbial characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 244, 463–472 (2017)
Lotti, T., Carretti, E., Berti, D., Martina, M.R., Lubello, C., Malpei, F.: Extraction, recovery and characterization of structural extracellular polymeric substances from anammox granular sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 236, 649–656 (2019)
Luo, J., Hao, T., Wei, L., Mackey, H.R., Lin, Z., Chen, G.H.: Impact of influent COD/N ratio on disintegration of aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 62, 127–135 (2014)
Ma, J., Ji, Y., Fu, Z., Yan, X., Xu, P., Li, J., & He, Q. (2023). Performance of anaerobic/oxic/anoxic simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal system overwhelmingly dominated by Candidatus_Competibacter: Effect of Aeration Time. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4434902
Mai, D.T., Kunacheva, C., Stuckey, D.C.: A review of post-treatment technologies for anaerobic effluents for discharge and recycling of wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48(2), 167–209 (2018)
Mirza, M.W., D’Silva, T.C., Gani, K.M., Afsar, S.S., Gaur, R.Z., Mutiyar, P.K., Lew, B.: Cultivation of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria (AnAOB) using different sewage sludge inoculums: process performance and microbial community analysis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 96(2), 454–464 (2021)
Moawad, A., Mahmoud, U.F., El-Khateeb, M.A., El-Molla, E.: Coupling of sequencing batch reactor and UASB reactor for domestic wastewater treatment. Desalination 242(1–3), 325–335 (2009)
Mohan, T.K., Nancharaiah, Y.V., Venugopalan, V.P., Sai, P.S.: Effect of C/N ratio on denitrification of high-strength nitrate wastewater in anoxic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Ecol. Eng. 91, 441–448 (2016)
Nancharaiah, Y.V., Reddy, G.K.K.: Aerobic granular sludge technology: mechanisms of granulation and biotechnological applications. Biores. Technol. 247, 1128–1143 (2018)
Owaes, M., Gaur, R.Z., Hasan, M.N., Gani, K.M., Kumari, S., Bux, F., Kazmi, A.A.: Performance assessment of aerobic granulation for the post treatment of anaerobic effluents. Environ. Technol. Innov. 17, 100588 (2020)
Peyong, Y.N., Zhou, Y., Abdullah, A.Z., Vadivelu, V.: The effect of organic loading rates and nitrogenous compounds on the aerobic granules developed using low strength wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 67, 52–59 (2012)
Su, B., Cui, X., Zhu, J.: Optimal cultivation and characteristics of aerobic granules with typical domestic sewage in an alternating anaerobic/aerobic sequencing batch reactor. Biores. Technol. 110, 125–129 (2012)
Tang, R., Han, X., Jin, Y., Yu, J.: Do increased organic loading rates accelerate aerobic granulation in hypersaline environment? J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10(6), 108775 (2022)
Vassalle, L., García-Galán, M.J., Aquino, S.F., Afonso, R.J.D.C.F., Ferrer, I., Passos, F., Mota, C.R.: Can high rate algal ponds be used as post-treatment of UASB reactors to remove micropollutants? Chemosphere 248, 125969 (2020)
Wang, S., Huang, X., Liu, L., Yan, P., Chen, Y., Fang, F., Guo, J.: Insight into the role of exopolysaccharide in determining the structural stability of aerobic granular sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 298, 113521 (2021)
Wang, H., Song, Q., Wang, J., Zhang, H., He, Q., Zhang, W., Li, H.: Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor with high dissolved oxygen: effects of carbon to nitrogen ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 642, 1145–1152 (2018)
Weissbrodt, D.G., Neu, T.R., Kuhlicke, U., Rappaz, Y., Holliger, C.: Assessment of bacterial and structural dynamics in aerobic granular biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 4, 175 (2013)
Winkler, M.K.H., Meunier, C., Henriet, O., Mahillon, J., Suárez-Ojeda, M.E., Del Moro, G., Weissbrodt, D.G.: An integrative review of granular sludge for the biological removal of nutrients and recalcitrant organic matter from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 336, 489–502 (2018)
Zhang, C., Zhang, H., Yang, F.: Optimal cultivation of simultaneous ammonium and phosphorus removal aerobic granular sludge in A/O/A sequencing batch reactor and the assessment of functional organisms. Environ. Technol. 35(15), 1979–1988 (2014)
Funding
“The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
“All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [MR] and [MAK]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [MR] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.”
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
“The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.”
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rayaz, M., Khan, M.A., Khan, A.A. et al. Start-up of Aerobic Granular Biomass System: Fate of Organics and Nutrients Removal From Anaerobic Effluent. Waste Biomass Valor 15, 945–958 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02198-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02198-1