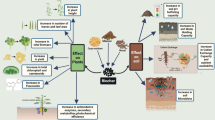
Abstract
Corncob contains nutrients for the growth of mushrooms. Since wood, the original substrate for mushroom production, is becoming difficult to obtain these days, the study aims to evaluate the effect of using corncob as a substrate for Lentinula edodes (shiitake) cultivation, and to provide an economic and eco-friendly approach to transform waste biomass into high quality edible mushrooms. Six formulas containing gradient proportions of corncob were assessed (100 cultivation bed-log per group) together with an oak sawdust control. Chemical profile analysis suggested corncob substitution reduced the substrate’s carbon level and increased nitrogen level. Formulas containing 18–58% corncob obtained higher yield comparing to the sawdust control, indicating a strong boosting effect of corncob. The formula composing of 50% corncob, 28% oak sawdust, 20% wheat bran, and 2% gypsum showed the best performance with the fastest mycelia growth, better log browning, the highest yield (722.08 g/log) and summit biological efficiency (80.23%). The determined carbon/nitrogen in this substrate was 67.21. The size (pileus diameter) of fruit bodies were not much affected by the change in formulas. Addition of corncob had an influence on nutritional composition of mushrooms. The highest polysaccharide content in fruit bodies (4.51 g/100 g) was found when the substrate contains 40% corncob. Corncob is a major agricultural waste in the world. These results revealed an excellent potential of corncob when used as a main substrate ingredient for L. edodes cultivation.
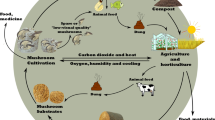
Graphic Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finimundy, T.C., Dillon, A.J.P., Henriques, J.A.P., Ely, M.R.: A review on general nutritional compounds and pharmacological properties of the Lentinula edodes mushroom. Food Nutr. Sci. 05(12), 1095–1105 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2014.512119
Royse, D.J., Baars, J., Tan, Q.: Current overview of mushroom production in the world. edible and medicinal mushrooms: technology and applications, 1edn. John Wiley & Sons Ltd (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119149446.ch2
Ogawa, K., Yashima, T.: MRI visualization of shiitake mycelium growing in woodchip blocks used for shiitake mushroom cultivation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 58, 90–96 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2019.01.004
F EIRA, MEIRELLES, W: Shiitake production in corncob substrates. Revista Brasileira de Milho e Sorgo 4(02), 141–148 (2005). https://doi.org/10.18512/1980-6477/rbms.v4n2p141-148
Yu, H., Gao, C., Wang, Q., Zhang, L., Shang, X., Song, C., Zhang, M., Li, Y., Zhou, F., Tan, Q.: Effects of sawdust particle size on selected growth parameters of a Lentinula edodes cultivar. Acta Edulis Fungi 24(2), 5–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2017.02.02
Royse, D.J., Sanchez, J.E.: Ground wheat straw as a substitute for portions of oak wood chips used in shiitake (Lentinula edodes) substrate formulae. Bioresour. Technol. 98(11), 2137–2141 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.08.023
Baktemur, G., Elik, Z.D., Kara, E., Takn, H.: The effect of different agricultural wastes on aroma composition of shiitake (Lentinula edodes (berk.) pegler) mushroom. Turk. J. Agric. 8(7), 1540–1547 (2020)
Ozcelik, E., Peksen, A.: Hazelnut husk as a substrate for the cultivation of shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes). Bioresour. Technol. 98(14), 2652–2658 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.020
Silva, E.M., Machuca, A., Milagres, A.M.: Effect of cereal brans on Lentinula edodes growth and enzyme activities during cultivation on forestry waste. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 40(4), 283–288 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01669.x
Zhen, F.: Physical and chemical properties of corncob for thermal conversions. Fuel Sci. Technol. Int. 11(8), 1037–1045 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1080/08843759308916115
Wang, H., Zhang, X., Wang, D., Cui, C., Gao, C., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Bi, Y.: Estimation and utilization of corncob resources in China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 37(1), 1–8 (2016)
Li, W., Chen, W.C., Wang, J.B., Feng, J., Wu, D., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J.S., Yang, Y.: Effects of enzymatic reaction on the generation of key aroma volatiles in shiitake mushroom at different cultivation substrates. Food Sci. Nutr. 9, 2247–2256 (2021)
Zhao, D., Tao, T., Bu, W., Zhou, J.: Technology research on the use of corn cob cultivation of Pleurotus eryngii. North. Hortic. 05, 168–170 (2012)
Liang, X., Zang, Y., Sun a, Dong, Q., Qin, W., Wang, X., Chen, Z., Ji, L.: A comparative study of the influence of cultivation with rice straw and corn cob on nutrients in fruit bodies of Agaricus brunnescens. Peck Food Sci. 36(16), 180–185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201516033
Yu, H., Lv, B., Song, C., Shang, X., Zhang, L., Zhang, M., Tan, Q.: Effects of composite nitrogen source on growth and yield of Lentinus edodes. Acta Agric. Shanghai 32(3), 63–66 (2016)
Zou, Y., Du, F., Zhang, H., Hu, Q.: Evaluation of Korshinsk Peashrub (Caragana korshinskii Kom.) as a substrate for the cultivation of Pleurotus eryngii. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 10(10), 2879–2885 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0301-2
Mattila, P., Salo-Väänänen, P., Könkö, K., Aro, H., Jalava, T.: Basic composition and amino acid contents of mushrooms cultivated in Finland. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(22), 6419–6422 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020608m
Haltiwanger, R.S., Chaplin, M.F., Kennedy, J.F.: Carbohydrate analysis: a practical approach. Q. Rev. Biol. 71(1), 117 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1086/419284
Hoa, H.T., Wang, C.L., Wang, C.H.: The effects of different substrates on the growth, yield, and nutritional composition of two oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus cystidiosus). Mycobiology 43(4), 423–434 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5941/MYCO.2015.43.4.423
Ivarsson, E., Gruden, B.A.M., Sodergren, C., Hultberg, M.: Use of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) hulls as substrate for Pleurotus ostreatus - Potential for combined mushroom and feed production. J. Clean. Prod. 313, 127969 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127969
Pardo-Giménez, A., Catalán, L., Carrasco, J., Álvarez-Ortí, M., Zied, D., Pardo, J.: Effect of supplementing crop substrate with defatted pistachio meal on Agaricus bisporus and Pleurotus ostreatus production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 96(11), 3838–3845 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7579
Huang, N.L.: China shiitake cultivation, 1stedn., p.65. Shanghai Scientific and Technological Literature Press (1994)
Zhang, J.X., Cai, W.M., Huang, C.Y.: China edible fungi cultivation, 1stedn., p.163. China Agricultural Press (2020)
Chicatto, J.A., Costa, A., Nunes, H., Helm, C.V., Tavares, L.B.: Evaluation of hollocelulase production by Lentinula edodes (Berk.) Pegler during the submerged fermentation growth using RSM. Braz. J. Biol. 74(1), 243–250 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.21712
Zou, Y., Du, F., Hu, Q., Yuan, X., Dai, D., Zhu, M.: Integration of Pleurotus tuoliensis cultivation and biogas production for utilization of lignocellulosic biomass as well as its benefit evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 317, 124042 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124042
Naresh Kumar, M., Ravikumar, R., Thenmozhi, S., Kirupa Sankar, M.: Development of natural cellulase inhibitor mediated intensified biological pretreatment technology using Pleurotus florida for maximum recovery of cellulose from paddy straw under solid state condition. Bioresour. Technol. 244(Pt 1), 353–361 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.105
Carrasco, J., Zied, D.C., Pardo, J.E., Preston, G.M., Pardo-Giménez, A.: Supplementation in mushroom crops and its impact on yield and quality. AMB Express 8, 146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0678-0
Girmay, Z., Gorems, W., Birhanu, G., Zewdie.: Growth and yield performance of Pleurotus ostreatus (Jacq. Fr.) Kumm (oyster mushroom) on different substrates. AMB Express 6(1), 87 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-016-0265-1
Aleksandrova, E., Zav’yalova, L., Tereshina, V., Garibova, L., Feofilova, E.: Obtaining of fruiting bodies and submerged mycelium of Lentinus edodes (Berk.) Sing [Lentinula edodes Pegler]. Microbiology 67, 535–539 (1998)
Hong, C.P., Moon, S., Yoo, S.I., Noh, J.H., Ko, H.G., Kim, H.A., Ro, H.S., Cho, H., Chung, J.W., Lee, H.Y., Ryu, H.: Functional analysis of a novel ABL (abnormal browning related to light) gene in mycelial brown film formation of Lentinula edodes. J. Fungi (Basel) 6, 4 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040272
Tang, L.H., Jian, H.H., Song, C.Y., Bao, D.P., Shang, X.D., Wu, D.Q., Tan, Q., Zhang, X.H.: Transcriptome analysis of candidate genes and signaling pathways associated with light-induced brown film formation in Lentinula edodes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97(11), 4977–4989 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4832-y
Sano, H., Narikiyo, T., Kaneko, S., Yamazaki, T., Shishido, K.: Sequence analysis and expression of a blue-light photoreceptor gene, Le.phrA from the basidiomycetous mushroom Lentinula edodes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 71(9), 2206–2213 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.70170
Tsivileva, O., Pankratov, A., Nikitina, V., Garibova, L.: Effect of media components on the mycelial film formation in submerged culture of Lentinus edodes (Shiitake). Food Technol. Biotechnol. 43(3), 227–234 (2005)
Meng, L., Fu, Y., Li, D., Sun, X., Chen, Y., Li, X., Xu, S., Li, X., Li, C., Song, B., Li, Y.: Effects of corn stalk cultivation substrate on the growth of the slippery mushroom (Pholiota microspora). RSC Adv. 9(10), 5347–5353 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra10627d
Kihumbu, A.G., Anakalo, S.A., Maina, M.S., Khare, K.B., Sharma, H.K.: Nutritional composition of pleurotus sajor-caju grown on water hyacinth, wheat straw and corncob substrates. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 4(4), 321–326 (2008)
Barros, L., Venturini, B.A., Baptista, P., Estevinho, L.M., Ferreira, I.C.F.R.: Chemical composition and biological properties of portuguese wild mushrooms: a comprehensive study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 3856–3862 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8003114
Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Tian, Q.: Mushroom polysaccharide lentinan for treating different types of cancers: a review of 12 years clinical studies in China. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 163, 297–328 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2019.02.013
Brauer, D., Kimmons, T., Phillips, M.: Effects of management on the yield and high-molecular-weight polysaccharide content of shiitake (Lentinula edodes) mushrooms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(19), 5333–5337 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020080l
Zhu, H., Tian, L., Zhang, L., Bi, J., Song, Q., Yang, H., Qiao, J.: Preparation, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from spent Lentinus edodes substrate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 6, 272 (2018)
Funding
This study was supported by Agriculture Research System of Shanghai, China (Grant No. 201710), China Agriculture Research System (CARS20), National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFD1000300), Shanghai Agriculture Applied Technology Development Program, China (2019-02-08-00-08-F01114) and SAAS Program for Excellent Research Team, Grant/Award Number: 2017(A-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Zhang, D., Zhang, L. et al. Corncob as a Substrate for the Cultivation of Lentinula edodes. Waste Biomass Valor 13, 929–939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01575-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01575-y