Abstract
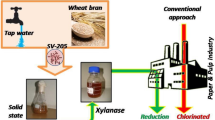
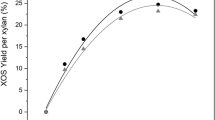
This study focused on the applying endo-xylanases to reduce the use of bleaching agent, coupled with the production of xylooligosaccharides (XOs), in mulberry paper making. Paper mulberry pulp (PMP) was consecutively prepared from paper mulberry bark by traditional NaOH-treatment, and two types of thermostable endo-xylanase from Streptomyces thermovulgaris TISTR1948 (wild-type and recombinant endo-xylanases) were employed in the biobleaching of PMP. This process was optimized to achieve maximum XOs yields and the highest PMP quality. The optimal condition was an enzyme dosage of 125 U/g PMP at 12 h of reaction time, both in a 500 mL laboratory bottle and a 150 L reactor. The mixture obtained from the reactor was separated as liquid of XOs derived from PMP (PMP-XOs) and solid biobleached PMP. The PMP-XOs from wild-type endo-xylanase were composed of 31.6% xylopentaose (X5), 30.9% xylohexaose and higher-degree XOs (X ≥ 6), and 11.7% xylobiose (X2), whereas 76.6% of X5 and 8.6% of X2 were the main products from recombinant endo-xylanase. The PMP-XOs derived from both endo-xylanase types exhibited high antioxidant activities, reducing power, phenolic contents, and prebiotic efficacy. In addition, the application of both endo-xylanases enhanced the brightness of PMP by 5.1% and 3.5%, and reduced the kappa number by 9.1% and 3.6%, respectively. Biobleached PMP was subsequently subjected to the NaOCl bleaching step to produce the mulberry paper. This approach could reduce NaOCl consumption by 20–25%, making it an environmentally friendly alternative. The production of valuable prebiotics, such as PMP-XOs, further enhances the economic viability of this approach.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data availability all data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Peng, X., Liu, H., Chen, P., Tang, F., Hu, Y., Wang, F., Pi, Z., Zhao, M., Chen, N., Chen, H., Zhang, X., Yan, X., Liu, M., Fu, X., Zhao, G., Yao, P., Wang, L., Dai, H., Li, X., Xiong, W., Xu, W., Zheng, H., Yu, H., Shen, S.: A chromosome-scale genome assembly of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera) provides new insights into its forage and papermaking usage. Mol. Plant. 12, 661–677 (2019)
Jitjaicham, M., Kusuktham, B.: Preparation of paper mulberry fibers and possibility of cotton/paper mulberry yarns production. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 1–6 (2016)
Memon, A., Ithisoponakul, S., Pramoonmak, S., Lawsuriyonta, M., Leenoi, D., Passadee, N.: A development of laminating mulberry paper by biodegradable films. Energy Procedia 9, 598–604 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.09.070
Sridevi, A., Ramanjaneyulu, G., Suvarnalatha Devi, P.: Biobleaching of paper pulp with xylanase produced by Trichoderma asperellum. 3 Biotech 266, 1–9 (2017)
Monte, M.C., Fuente, E., Blanco, A., Negro, C.: Waste management from pulp and paper production in the European Union. Waste Manage. 29, 293–308 (2009)
Beg, Q., Kapoor, M., Mahajan, L., Hoondal, G.: Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 326–338 (2001)
Basit, A., Liu, J., Rahim, K., Jiang, W., Lou, H.: Thermophilic xylanases: from bench to bottle. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 38, 989–1002 (2018)
Basit, A., Jiang, W., Rahim, K.: Xylanase and its industrial applications. IntechOpen, London (2020). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.92156
Basit, A., Liu, J., Miao, T., Zheng, F., Rahim, K., Lou, H., Jiang, W.: Characterization of two endo-β-1, 4-xylanases from Myceliophthora thermophila and their saccharification efficiencies, synergistic with commercial cellulase. Front. Microbiol. 9, 1–11 (2018)
Chapla, D., Patel, H., Madamwar, D., Shah, A.: Assessment of a thermostable xylanase from Paenibacillus sp. ASCD2 for application in prebleaching of Eucalyptus kraft pulp. Waste Biomass Valor. 3, 269–274 (2012)
Kumar, V., Marín-Navarro, J., Shukla, P.: Thermostable microbial xylanases for pulp and paper industries: trends, applications and further perspectives. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 1–10 (2016)
Nutongkaew, T., Prasertsan, P., Leamdum, C., Sattayasamitsathit, S., Noparat, P.: Bioconversion of oil palm trunk residues hydrolyzed by enzymes from newly isolated fungi and use for ethanol and acetic acid production under two-stage and simultaneous fermentation. Waste Biomass. Valor. 11, 1333–1347 (2020)
Bhardwaj, N., Kumar, B., Verma, P.: A detailed overview of xylanases: an emerging biomolecule for current and future prospective. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 6, 1–36 (2019)
Viikari, L., Kantelinen, A., Sundquist, J., Linko, M.: Xylanases in bleaching: from an idea to the industry. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 13, 335–350 (1994)
Nie, S., Wang, S., Qin, C., Yao, S., Ebonka, J.F., Song, X., Li, K.: Removal of hexenuronic acid by xylanase to reduce adsorbable organic halides formation in chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. Bioresour. Technol. 196, 413–417 (2015)
Sharma, D., Chaudhary, R., Kaur, J., Arya, S.K.: Greener approach for pulp and paper industry by xylanase and laccase. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 25, 1–16 (2020)
Chaiyaso, T., Kuntiya, A., Techapun, C., Leksawasdi, N., Seesuriyachan, P., Hanmaungjai, P.: Optimization of cellulase-free xylanase production by thermophilic Streptomyces thermovulgaris TISTR1948 through Plackett-Burman and response surface methodological approaches. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 75, 531–537 (2011)
Boonchuay, P., Techapun, C., Seesuriyachan, P., Chaiyaso, T.: Production of xylooligosaccharides from corncob using a crude thermostable endo-xylanase from Streptomyces thermovulgaris TISTR1948 and prebiotic properties. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 23, 1515–1523 (2014)
Boonchuay, P., Takenaka, S., Kuntiya, A., Techapun, C., Leksawasdi, N., Seesuriyachan, P., Chaiyaso, T.: Purification, characterization, and molecular cloning of the xylanase from Streptomyces thermovulgaris TISTR1948 and its application to xylooligosaccharide production. J. Mol. Catal. B 129, 61–68 (2016)
Boonchuay, P., Techapun, C., Leksawasdi, N., Seesuriyachan, P., Hanmoungjai, P., Watanabe, M., Takenaka, S., Chaiyaso, T.: An integrated process for xylooligosaccharide and bioethanol production from corncob. Bioresour. Technol. 256, 399–407 (2018)
Samanta, A.K., Jayapal, N., Jayaram, C., Roy, S., Kolte, A.P., Senani, S., Sridhar, M.: Xylooligosaccharides as prebiotics from agricultural by-products: production and applications. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 5, 62–71 (2015)
Vázquez, M.J., Alonso, J.L., Domínguez, H., Parajó, J.C.: Xylooligosaccharides: manufacture and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 11, 387–393 (2000)
Aachary, A.A., Prapulla, S.G.: Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) as an emerging prebiotic: microbial synthesis, utilization, structural characterization, bioactive properties, and applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 10, 2–16 (2011)
Farhat, W., Venditti, R., Quick, A., Taha, M., Mignard, N., Becquart, F., Ayoub, A.: Hemicellulose extraction and characterization for applications in paper coatings and adhesives. Ind. Crop. Prod. 107, 370–377 (2017)
Takenaka, S., Umeda, M., Senba, H., Koyama, D., Tanaka, K., Yoshida, K., Doi, M.: Heterologous expression and characterisation of the Aspergillus aspartic protease involved in the hydrolysis and decolorisation of red-pigmented proteins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 97, 95–101 (2017)
Sridevi, A., Sandhya, A., Ramanjaneyulu, G., Narasimha, G., Devi, P.S.: Biocatalytic activity of Aspergillus niger xylanase in paper pulp biobleaching. 3 Biotech 165, 1–7 (2016)
Kubata, B.K., Suzuki, T., Horitsu, H., Kawai, K., Takamizawa, K.: Purification and characterization of Aeromonas caviae ME-1 xylanase V, which produces exclusively xylobiose from xylan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 531–535 (1994)
Veenashri, B.R., Muralikrishna, G.: In vitro anti-oxidant activity of xylo-oligosaccharides derived from cereal and millet brans—a comparative study. Food Chem. 126, 1475–1481 (2011)
Malunga, L.N., Beta, T.: Antioxidant capacity of arabinoxylan oligosaccharide fractions prepared from wheat aleurone using Trichoderma viride or Neocallimastix patriciarum xylanase. Food Chem. 167, 311–319 (2015)
Wu, Z., Xu, E., Long, J., Pan, X., Xu, X., Jin, Z., Jiao, A.: Comparison between ATR-IR, Raman, concatenated ATR-IR and Raman spectroscopy for the determination of total antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content of Chinese rice wine. Food Chem. 194, 671–679 (2016)
Miller, G.L.: Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 31, 426–428 (1959)
Lasrado, L.D., Gudipati, M.: Purification and characterization of β-d-xylosidase from Lactobacillus brevis grown on xylo-oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 92, 1978–1983 (2013)
Campos, E., Negro Alvarez, M.J., Sabarís di Lorenzo, G., Gonzalez, S., Rorig, M., Talia, P., Grasso, D.H., Sáez, F., Manzanares Secades, P., Ballesteros Perdices, M., Cataldi, A.A.: Purification and characterization of a GH43 β-xylosidase from Enterobacter sp. identified and cloned from forest soil bacteria. Microbiol. Res. 169, 213–220 (2014)
Technical Association of Pulp and Paper Industry (TAPPI) (2006) Forming handsheets for physical tests of pulp (Reaffirmation of T 205 sp-02), Norcross, GA, USA
Technical Association of Pulp and Paper Industry (TAPPI) (2006) Forming handsheets for reflectance testing of pulp (Büchner funnel procedure) (Reaffirmation of T 218 sp-02), Norcross, GA, USA
Brienzo, M., Carvalho, W., Milagres, A.M.F.: Xylooligosaccharides production from alkali-pretreated sugarcane bagasse using xylanases from Thermoascus aurantiacus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 162, 1195–1205 (2010)
Jayapal, N., Samanta, A.K., Kolte, A.P., Senani, S., Sridhar, M., Suresh, K.P., Sampath, K.T.: Value addition to sugarcane bagasse: xylan extraction and its process optimization for xylooligosaccharides production. Ind. Crop. Prod. 42, 14–24 (2013)
Campioni, T.S., de Jesus Moreira, L., Moretto, E., Sawada Nunes, N.S., de Oliva Neto, P.: Biobleaching of kraft pulp using fungal xylanases produced from sugarcane straw and the subsequent decrease of chlorine consumption. Biomass Bioenergy 121, 22–27 (2019)
Khandeparkar, R., Bhosle, N.B.: Application of thermoalkalophilic xylanase from Arthrobacter sp. MTCC 5214 in biobleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 897–903 (2007)
Juturu, V., Wu, J.C.: Microbial xylanases: Engineering, production and industrial applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 30, 1219–1227 (2012)
Si, B., Tao, H., Zhang, X., Guo, J., Cui, K., Tu, Y., Diao, Q.: Effect of Broussonetia papyrifera L. (paper mulberry) silage on dry matter intake, milk composition, antioxidant capacity and milk fatty acid profile in dairy cows. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 31, 1259–1266 (2018)
Xu, M.L., Wang, L., Hu, J.H., Lee, S.K., Wang, M.H.: Antioxidant activities and related polyphenolic constituents of the methanol extract fractions from Broussonetia papyrifera stem bark and wood. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 19, 677–682 (2010)
Samanta, A.K., Senani, S., Kolte, A.P., Sridhar, M., Sampath, K.T., Jayapal, N., Devi, A.: Production and in vitro evaluation of xylooligosaccharides generated from corn cobs. Food Bioprod. Process. 90, 466–474 (2012)
Melo-Silveira, R.F., Fidelis, G.P., Costa, M.S., Telles, C.B., Dantas-Santos, N., Elias, S.D., Ribeiro, V.B., Barth, A.L., Macedo, A.J., Leite, E.L., Rocha, H.A.: In vitro antioxidant, anticoagulant and antimicrobial activity and in inhibition of cancer cell proliferation by xylan extracted from corn cobs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 409–426 (2012)
Martin Salas-Veizaga, D., Villagomez, R., Linares-Pastén, J.A., Carrasco, C., Álvarez, M.T., Adlercreutz, P., Nordberg Karlsson, E.: Extraction of glucuronoarabinoxylan from quinoa stalks (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and evaluation of xylooligosaccharides produced by GH10 and GH11 xylanases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 65, 8663–8673 (2017)
Morais de Carvalho, D., Martínez-Abad, A., Evtuguin, D.V., Colodette, J.L., Lindström, M.E., Vilaplana, F., Sevastyanova, O.: Isolation and characterization of acetylated glucuronoarabinoxylan from sugarcane bagasse and straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 156, 223–234 (2017)
Alzagameem, A., Klein, S.E., Bergs, M., Do, X.T., Korte, I., Dohlen, S., Hüwe, C., Kreyenschmidt, J., Kamm, B., Larkins, M., Schulze, M.: Antimicrobial activity of lignin and lignin-derived cellulose and chitosan composites against selected pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms. Polymers 11, 1–18 (2019)
Manisseri, C., Gudipati, M.: Bioactive xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat bran soluble polysaccharides. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 43, 421–430 (2010)
Madhukumar, M.S., Muralikrishna, G.: Fermentation of xylo-oligosaccharides obtained from wheat bran and bengal gram husk by lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. J. Food Sci. Technol. 49, 745–752 (2012)
Sreerangaraju, G., Krishnamoorthy, U., Kailas, M.M.: Evaluation of Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum) husk as a source of tannin and its interference in rumen and post-rumen nutrient digestion in sheep. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 85, 131–138 (2000)
Sibakov, J., Lehtinen, P., Poutanen, K.: Cereal brans as dietary fibre ingredients. In: Delcour, J.A., Poutanen, K. (eds.) Fibre-rich and wholegrain foods, pp. 170–192. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge (2013)
Aminzadeh, S., Zhang, L., Henriksson, G.: A possible explanation for the structural inhomogeneity of lignin in LCC networks. Wood Sci. Technol. 51, 1365–1376 (2017)
Bajpai, P.: Paper and its properties. In: Bajpai, P. (ed.) Biermann’s handbook of pulp and paper, 3rd edn., pp. 35–63. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2018)
Dhiman, S.S., Garg, G., Mahajan, R., Garg, N., Sharma, J.: ‘Single lay out’ and ‘mixed lay out’ enzymatic processes for bio-bleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 4736–4741 (2009)
Shen, W., Chen, X.: Measuring and controlling model of pulp kappa number with spectroscopy during batch sulfite pulping process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48, 8980–8984 (2009)
Boruah, P., Sarmah, P., Das, P.K., Goswami, T.: Exploring the lignolytic potential of a new laccase producing strain Kocuria sp. PBS-1 and its application in bamboo pulp bleaching. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 143, 1–12 (2019)
Lin, X., Han, S., Zhang, N., Hu, H., Zheng, S., Ye, Y., Lin, Y.: Bleach boosting effect of xylanase A from Bacillus halodurans C-125 in ECF bleaching of wheat straw pulp. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 52, 91–98 (2013)
Hamedi, J., Vaez Fakhri, A., Mahdavi, S.: Biobleaching of mechanical paper pulp using Streptomyces rutgersensis UTMC 2445 isolated from a lignocellulose-rich soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 128, 161–170 (2020)
Birijlall, N., Manimaran, A., Santhosh Kumar, K., Permaul, K., Singh, S.: High level expression of a recombinant xylanase by Pichia pastoris NC38 in a 5 L fermenter and its efficiency in biobleaching of bagasse pulp. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 9723–9729 (2011)
Nagar, S., Gupta, V.K.: Hyper production and eco-friendly bleaching of kraft pulp by xylanase from Bacillus pumilus SV-205 using agro waste material. Waste Biomass Valor. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01258-0
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Chiang Mai University (CMU) via a Postdoctoral Fellowship 2019 for Pinpanit Boonchuay (Contract No. 07/2019). We also thank the Faculty of Agro-Industry, CMU, and the cluster of the Agro Bio-Circular-Green Industry (Agro BCG), CMU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Information Consent
Informed consent has been obtained from all individual participants of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaiyaso, T., Boonchuay, P., Takenaka, S. et al. Efficient Enzymatic Process for Mulberry Paper Production: An Approach for Xylooligosaccharide Production Coupled with Minimizing Bleaching Agent Doses. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 5347–5360 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01416-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01416-y