Abstract
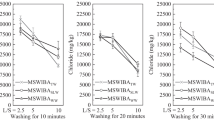
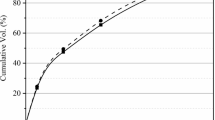
Ash stabilization is important for realizing safe and reliable disposal sites and promoting MSW bottom ash (BA) recycling. An on-site technology that uses a modified detachable container and stabilizes BA with sprinkling water (watering) and flowing 100% CO2 through the ash layer (carbonation) was developed. Experimental verification of this technology was undertaken (Treatment condition: L/S = 0.6–0.7, 24 h duration, 2.2 t/time). Two treatment methods were investigated using unsieved BA: (1) sprinkling water only (2) sprinkling water combined with carbonation. In the verification test, the chlorine (Cl) content of the BA decreased by up to 72% after the watering treatment. The BA treated by watering and carbonation showed reduction in solubility of Pb by up to 90%. An exothermic reaction due to carbonation was also confirmed. In the lysimeter test (column size: ø104 × 400 mmH) conducted to evaluate the long-term leaching performance of the BA treated to promote stabilization, leachate data was acquired over 400 days from both treated and untreated BA. It was confirmed that the leachate of BA treated with watering showed lower EC, cumulative Cl and TOC than untreated BA. The leachate of BA treated with watering and carbonation showed lower pH, Pb concentration and higher cumulative Cl, Ca after 400 days than the one treated with watering alone.
Graphic abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
ISWA: Management of Bottom ash from WTE plants (2006)
Chimenos, J.M., Fernandez, A.I., Nadal, R., Espiell, F.: Short-term natural weathering of MSWI bottom ash. J Hazard Mater B79, 287–299 (2000)
Steketee, J.J., Urlings, L.G.C.M.: Enhanced natural stabilization of MSW bottom ash: a method for minimization of leaching. Stud. Environ. Sci. 60, 233–238 (1994)
Steketee, J.J., Duzijn, R.F., Born, J.G.P.: Quality improvement of MSWI bottom ash by enhanced aging, washing and combination processes. Stud. Environ. Sci. 71, 13–23 (1997)
Lombardi, L., Carnevale, E., Paradisi, A.: Bottom ash treatment at the site of producing plant for reutilization. Waste Biomass Valor 7, 965–974 (2016)
Ministry of the Environment (Government of Japan): Municipal solid waste emissions and disposal in FY2017 (2019)
Kida, A., Noma, Y.: Elution characteristics of incineration ash. J. Jpn. Waste Manag. Assoc. 41(164), 17–22 (1989)
Ministry of Environment Japan: Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution. https://www.env.go.jp/en/water/soil/sp.html
Namli, U., Seong-Young, N., Ji-Whan, A.: Effect of accelerated carbonation on the leaching behavior of Cr in municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash and the carbonation kinetics. Mater. Trans. 54(8), 1510–1516 (2013)
Kubota, H., Shigeizumi, K., Sakanakura, H., Sato, K.: Combination of sprinkling and Pb insolubilization treatments for the early stabilization of MSW bottom ash. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. Res. 30, 48–61 (2019)
Yamada, H.: Thermal carbonation of calcium hydroxide. Gypsum Lime 178, 9–16 (1982)
Fujikawa, T., Sato, K., Koga, C., Sakanakura, H.: Effective utilization of incineration bottom ash from municipal solid waste using aging method. Geo-Environ. Eng. 2017, 1–6 (2017)
Bertos, M.F., Simons, S.J.R., Hills, C.D., Carey, P.J.: A review of accelerated carbonation technology in the treatment of cement-based materials and sequestration of CO2. J. Hazard. Mater. B112, 193–205 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubota, H., Shigeizumi, K., Fujikawa, T. et al. An Accelerated, On-Site Bottom Ash Aging and Washing Treatment and Its Effect for Long-Term Leaching. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 7067–7077 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01136-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01136-9