Abstract
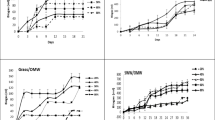
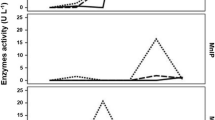
Due to OMW toxicity, low pH values, polyphenols, oils and fats content, and high organic load their uncontrolled disposal to the sea, rivers and soil causes problems to both environment and public health. Olive mill wastewater (OMW) is a phenolic-rich industrial effluent that can be advantageously valorized by the anaerobic digestion to the methane and agricultural fertilizer productions. The aim of this study was to determine the influence of anaerobic co-digestion of OMW in mixture with cheese whey (CW) and liquid cow manure (LCM) on phenolic fraction derived from OMW. Total phenol content of the two-stage anaerobically co-digested agro-industrial mixtures was significantly decreased (up to 50% degradation for both mixtures in a ratio of 55% OMW:40% CW:5% LCM, v/v/v and 80% OMW:20% CW). Main phenolic compounds namely Gallic acid, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, p-coumaric acid and oleuropein were identified in OMW samples. All five individual phenols in all OMW mixtures were degraded to a large extent (80% degradation for the mixture in a ratio of 55 OMW:40 CW:5% LCM and 80 OMW:20% CW and 100% degradation for 20 OMW:80% LCM.
Graphic Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paraskeva, P., Diamadopoulos, E.: Technologies for olive mill wastewater (OMW) treatment: a review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 81, 1475–1485 (2006)
Obied, H.K., Allen, M.S., Bedgood, D.R., Prenzler, P.D., Robards, K., Stockmann, R.: Bioactivity and analysis of biophenols recovered from olive mill waste. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 823–837 (2005)
Mantzavinos, D., Kalogerakis, N.: Treatment of olive mill effluents Part I. Organic matter degradation by chemical and biological processes—an overview. Environ. Int. 31, 289–295 (2005)
Borja, R., Rincn, B., Raposo, F.: Anaerobic biodegradation of two-phase olive mill solid wastes and liquid effluents: kinetic studies and process performance. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 81, 1450–1462 (2006)
Roig, A., Cayuela, M.L., Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.: An overview on olive mill wastes and their valorisation methods. Waste Manage. 26, 960–969 (2006)
Kalogerakis, N., Politi, M., Foteinis, S., Chatzisymeon, E., Mantzavinos, D.: Recovery of antioxidants from olive mill wastewaters: a viable solution that promotes their overall sustainable management. J. Envir. Manag. 128, 749–758 (2013)
Mantzavinos, D., Kalogerakis, N.: Treatment of olive mill effluents Part I. Organic matter degradation by chemical and biological processes—an overview. Envir. Intern. 31, 289–295 (2005)
Rahmanian, N., Jafari, S.M., Galanakis, C.M.: Recovery and removal of phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater. JAOCS 91, 1–18 (2014)
Dareioti, M.A., Dokianakis, S.N., Stamatelatou, K., Zafiri, C., Kornaros, M.: Biogas production from anaerobic Co-digestion of agroindustrial wastewaters under mesophilic conditions in a two-stage process. Desalination 248, 891–906 (2009)
Hamdi, M.: Future prospects and constraints of olive mill wastewaters use and treatment: a review. Bioprocess. Eng. 8, 209–214 (1993)
Tabatabaei, M., Rahim, R.A., Abdullah, N., Wright, A.D.G., Shirai, Y., Sakai, K., Sulaiman, A., Hassan, M.A.: Importance of the methanogenic archaea populations in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Proc. Biochem. 45, 1214–1225 (2010)
Chen, Y., Cheng, J.J., Creamer, K.S.: Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Biores. Technol. 99, 4044–4064 (2008)
Beccari, M., Carucci, G., Majone, M., Torrisi, L.: Role of lipids and phenolic compounds in the anaerobic treatment of olive oil mill effluents. Environm. Technol. 20, 105–110 (1999)
Borja, R., Martin, A., Maestro, R., Alba, J., Fiestas, J.A.: Enhancement of the anaerobic digestion of olive mill wastewater by the removal of phenolic inhibitors. Proc. Biochem. 27, 231–237 (1992)
Hamdi, M.: Anaerobic digestion of olive mill wastewaters. Process Biochem. 31, 105–110 (1996)
Aktas, E., Imre, S., Ersoy, L.: Characterization and lime treatment of olive mill wastewater. Water Res. 35, 2336–2340 (2001)
Hamdi, M.: Thermoacidic precipitation of darkly coloured polyphenols of olive mill wastewaters. Environ. Technol. 14, 495–500 (1993)
Sabbah, I., Marsook, T., Basheer, S.: The effect of pretreatment on anaerobic activity of olive mill wastewater using batch and continuous systems. Process. Biochem. 39, 1947–1951 (2004)
Scoma, A., Bertin, L., Zanaroli, G., Fraraccio, S., Fava, F.: A physicochemical–biotechnological approach for an integrated valorization of olive mill wastewater. Biores. Technol. 102, 10273–10279 (2011)
Borja, R., Martin, A., Alonso, V., Garcia, I., Banks, C.J.: Influence of different aerobic pretreatments on the kinetics of anaerobic digestion of olive mill wastewater. Water Res. 29, 489–495 (1995)
Fountoulakis, M.S., Dokianakis, S.N., Kornaros, M.E., Aggelis, G.G., Lyberatos, G.: Removal of phenolics in olive mill wastewaters using the white-rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Water Res. 36, 4735–4744 (2002)
Gonçalves, M.R., Costa, J.C., Marques, I.P., Alves, M.M.: Strategies for lipids and phenolics degradation in the anaerobic treatment of olive mill wastewater. Water Res. 46, 1684–1692 (2012)
Gelegenis, J., Georgakakis, D., Angelidaki, I., Christopoulou, N., Goumenaki, M.: Optimization of biogas production from olive-oil mill wastewater, by codigesting with diluted poultry-manure. Appl. Energy 84, 646–663 (2007)
Sampaio, M.A., Goncalves, M.R., Marques, I.P.: Anaerobic digestion challenge of raw olive mill wastewater. Biores. Technol. 102, 10810–10818 (2011)
Fezzani, B., Cheikh, R.B.: Two-phase anaerobic co-digestion of olive mill wastes in semi-continuous digesters at mesophilic temperature. Biores. Technol. 101, 1628–1634 (2010)
Rincón, B., Borja, R., Martín, M.A., Martín, A.: Evaluation of the methanogenic step of a two-stage anaerobic digestion process of acidified olive mill solid residue from a previous hydrolytic–acidogenic step. Waste Manage. 29, 2566–2573 (2009)
Abbassi, B.E.: Anaerobic co-digestion of solid residue and wastewater from olive-oil mills. J. Solid Waste Technol. Manag. 30, 226–232 (2004)
La Cara, F., Ionata, E., Del Monaco, G., Marcolongo, L., Gonçalves, M.R., Marques, I.P.: Olive mill wastewater anaerobically digested: phenolic compounds with antiradical activity. Chem. Eng. Trans. 27, 325–330 (2012)
Marques, I.P.: Anaerobic digestion treatment of olive mill wastewater for effluent re-use in irrigation. Desalination 137, 233–239 (2001)
Azaizeh, H., Jadoun, J.: Co-digestion of olive mill wastewater and swine manure using up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor for biogas production. J. Water Res. Prot. 2, 314–321 (2010)
Dareioti, M.A., Dokianakis, S.N., Stamatelatou, K., Zafiri, C., Kornaros, M.: Exploitation of olive mill wastewater and liquid cow manure for biogas production. Waste Manage. 30, 1841–1848 (2010)
Khoufi, S., Louhichi, A., Sayadi, S.: Optimization of anaerobic co-digestion of olive mill wastewater and liquid poultry manure in batch condition and semi-continuous jet-loop reactor. Biores. Technol. 182, 67–74 (2015)
Kougias, P.G., Kotsopoulos, T.A., Martzopoulos, G.G.: Effect of feedstock composition and organic loading rate during the mesophilic co-digestion of olive mill wastewater and swine manure. Renew. Energ. 69, 202–207 (2014)
Azbar, N., Keskin, T., Yuruyen, A.: Enhancement of biogas production from olive mill effluent (OME) by co-digestion. Biomass Bioenerg. 32, 1195–1201 (2008)
Dareioti, M.A., Vavouraki, A.I., Kornaros, M.: Effect of pH on the anaerobic acidogenesis of agroindustrial wastewaters for maximization of bio-hydrogen production: a lab-scale evaluation using batch tests. Biores. Technol. 162, 218–227 (2014)
Dareioti, M.A., Kornaros, M.: Effect of hydraulic retention time (HRT) on the anaerobic co-digestion of agro-industrial wastes in a two-stage CSTR system. Biores. Technol. 167, 407–415 (2014)
Angelidaki, I., Ahring, B.K.: Codigestion of olive oil mill wastewaters with manure, household waste or sewage sludge. Biodegradation 8, 221–226 (1997)
Martinez-Garcia, G., Johnson, A.C., Bachmann, R.T., Williams, C.J., Burgoyne, A., Edyvean, R.G.J.: Two-stage biological treatment of olive mill wastewater with whey as co-substrate. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 59, 273–282 (2007)
Martinez-Garcia, G., Johnson, A.C., Bachmann, R.T., Williams, C.J., Burgoyne, A., Edyvean, R.G.J.: Anaerobic treatment of olive mill wastewater and piggery effluents fermented with Candida tropicalis. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 1398–1405 (2009)
De Marco, E., Savarese, M., Paduano, A., Sacchi, R.: Characterization and fractionation of phenolic compounds extracted from olive oil mill wastewaters. Food Chem. 104, 858–867 (2007)
Juárez, M.J.B., Zafra-Gómez, A., Luzón-Toro, B., Ballesteros-García, O.A., Navalón, A., González, J., Vílchez, J.L.: Gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric study of the degradation of phenolic compounds in wastewater olive oil by Azotobacter Chroococcum. Biores. Technol. 99, 2392–2398 (2008)
Zafra, A., Juárez, M.J.B., Blanc, R., Navalón, A., González, J., Vílchez, J.L.: Determination of polyphenolic compounds in wastewater olive oil by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta 70, 213–218 (2006)
Daâssi, D., Lozano-Sánchez, J., Borrás-Linares, I., Belbahri, L., Woodward, S., Zouari-Mechichi, H., Mechichi, T., Nasri, M., Segura-Carretero, A.: Olive oil mill wastewaters: phenolic content characterization during degradation by Coriolopsis gallica. Chemosphere 113, 62–70 (2014)
Tzathas, K., Chrysagi, E., Lyberatos, G., Vlyssides, A., Vlysidis, A.: Pretreatment of olive mill wastes for the extraction of residual oil and high added value compounds. Waste Biomass Valori. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00727-5
Achma, R.B., Ghorbel, A., Dafinov, A., Medina, F.: Anaerobic digestion of olive oil mill wastewater pre-treated with catalytic wet peroxide photo-oxidation using copper supported pillared clay catalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2, 9–17 (2014)
El-Gohary, F.A., Badawy, M.I., El-Khateeb, M.A., El-Kalliny, A.S.: Integrated treatment of olive mill wastewater (OMW) by the combination of Fenton’s reaction and anaerobic treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 162, 1536–1541 (2009)
Dareioti, M.A., Kornaros, M.: Anaerobic mesophilic co-digestion of ensiled sorghum, cheese whey and liquid cow manure in a two-stage CSTR system: effect of hydraulic retention time. Biores. Technol. 175, 553–562 (2015)
Tsintavi, E., Pontillo, N., Dareioti, M.A., Kornaros, M.: Ozone pretreatment of olive mill wastewaters (OMW) and its effect on OMW biochemical methane potential (BMP). Water Sci. Technol. 68, 2712–2717 (2013)
Mulinacci, N., Romani, A., Galardi, C., Pinelli, P., Giaccherini, C., Vincieri, F.F.: Polyphenolic content in olive oil waste waters and related olive samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 49, 3510–3514 (2001)
Romani, A., Mulinacci, N., Pinelli, P., Vincieri, F.F., Cimato, A.: Polyphenolic content in five Tuscany cultivars of Olea europaea L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 47, 964–967 (1999)
Khoddami, A., Wilkes, M.A., Roberts, T.H.: Techniques for analysis of plant phenolic compounds. Molecules 18, 2328–2375 (2013)
Obied, H.K., Allen, M.S., Bedgood, D.R., Prenzler, P.D., Robards, K.: Investigation of Australian olive mill waste for recovery of biophenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 9911–9920 (2005)
Lesage-Meessen, L., Navarro, D., Maunier, S., Sigoillot, J.C., Lorquin, J., Delattre, M., Simon, J.L., Asther, M., Labat, M.: Simple phenolic content in olive oil residues as a function of extraction systems. Food Chem. 75, 501–507 (2001)
Huang, D., Ou, B., Prior, R.L.: The chemistry behind antioxidant capacity assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 1841–1856 (2005)
Brenes, M., Garcia, A., Garcia, P., Rios, J.J., Garrido, A.: Phenolic compounds in Spanish olive oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 47, 3535–3540 (1999)
Beccari, M., Bonemazzi, F., Majone, M., Riccardi, C.: Interactions between acidogenesis and methanogenesis in the anaerobic treatment of olive oil mill effluents. Wat. Res. 30, 183–189 (1996)
Hernandez, J.E., Edyvean, R.G.: Anaerobic treatment of phenol in a two-stage anaerobic reactor. In: 7th World congr. chem. engin. GLASGOW 2005, incorp. 5th European congr. chem. eng., p. 8 (2005)
Beccari, M., Majone, M., Torrisi, L.: Two-reactor system with partial phase separation for anaerobic treatment of olive oil mill effluents. Water Sci. Technol. 38, 53–60 (1998)
Zagklis, D.P., Vavouraki, A.I., Kornaros, M.E., Paraskeva, C.A.: Purification of olive mill wastewater phenols through membrane filtration and resin adsorption/desorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 285, 69–76 (2015)
El-Abbassi, A., Kiai, H., Hafidi, A.: Phenolic profile and antioxidant activities of olive mill wastewater. Food Chem. 132, 406–412 (2012)
Tafesh, A., Najami, N., Jadoun, J., Halahlih, F., Riepl, H., Azaizeh, H. Synergistic antibacterial effects of polyphenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater. J. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/431021
Achak, M., Hafidi, A., Ouazzani, N., Sayadi, S., Mandi, L.: Low cost bio-sorbent for the removal of phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 117–125 (2009)
Allouche, N., Fki, I., Sayadi, S.: Toward a high yield recovery of antioxidants and purified hydroxytyrosol from olive mill wastewaters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 52, 267–273 (2004)
Azaizeh, H., Halahlih, F., Najami, N., Brunner, D., Faulstich, M., Tafesh, A.: Antioxidant activity of phenolic fractions in olive mill wastewater. Food Chem. 134, 2226–2234 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the European Commission project LIFE08/ENV/GR578-INTEGRASTE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vavouraki, A.I., Zakoura, M.V., Dareioti, M.A. et al. Biodegradation of Polyphenolic Compounds from Olive Mill Wastewaters (OMW) During Two-Stage Anaerobic Co-digestion of Agro-industrial Mixtures. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 5783–5791 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00887-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00887-4