Abstract
Purpose
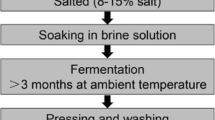
The aim of this work was to monitor the microflora and the changing principle of the fungi family at the natural fermented soybean paste different fermentation stage.
Methods
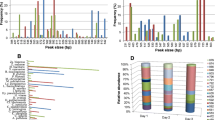
It obtained the V4 and V5 regions of the 18S rDNA by extracting the fungal genomic DNA from the natural fermented soybean paste. DGGE fingerprint of fungal 18S rDNA V4 (partial), V5 sections during the different soybean paste fermentation periods of 17 samples were line analyzed. The abundance, the absorbance and the degree of dominance and diversity indexes of fungal community were determined by the denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE).
Results
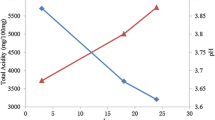
The V4, V5 regions of 18S rDNA of the complex microbial community in the fermentation of traditional soybean paste were around 762 bp and 422 bp, and there were 9 kinds of microorganisms discovered, which were Penicillium expansum, Aspergillus oryzae, Mucor, P. commune, Absidia corymbifera, M. racemosus, Actinomucor elegans, Aspergillus, and an unculturable fungi. The DGGE ecological analysis showed that the unculturable fungi and A. oryzae were dominant microorganisms all the time, and the highest diversion index of 2.87 was reached at 56 days of fermentation.
Conclusion
This study laid a foundation for researching suitable soybean paste artificial inoculation and also provided a good help for the fermentation process of soybean paste.
Graphic Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shin, D., Jeong, D.: Korean traditional fermented soybean products: Jang. J Ethnic Foods 2(1), 2–7 (2015)
Jeong, Y.H., Jin, K.H., Jung, K.M., Suna, K., Sol, K.D., Daily, J.W., Youn, J.D., Young, K.D., Sunmin, P.: Standardized chungkookjang, short-term fermented soybeans with Bacillus lichemiformis, improves glucose homeostasis as much as traditionally made chungkookjang in diabetic rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 52(1), 49–57 (2013)
Kwon, D.Y., Sang, M.H., Ahn, I.S., Min, J.K., Yang, H.J., Park, S.: Isoflavonoids and peptides from, long-term fermented soybeans, increase insulin sensitivity and exert insulinotropic effects in vitro. Nutrition 27(2), 244–252 (2011)
Yang, H.J., Kwon, D.Y., Min, J.K., Kang, S., Park, S.: Meju, unsalted soybeans fermented with Bacillus subtilis and Aspergilus oryzae, potentiates insulinotropic actions and improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in diabetic rats. Nutr. Metab. 9(1), 37–37 (2012)
Zhang, W., Luo, Q., Zhu, Y., Ma, J., Cao, L., Yang, M., Wen, P., Zhang, Z., He, X.: Microbial diversity in two traditional bacterial douchi from Gansu province in northwest China using Illumina sequencing. PLoS ONE 13(3), e0194876 (2018)
Xie, M., Wu, J., An, F., Yue, X., Tao, D., Wu, R., Lee, Y.: An integrated metagenomic/metaproteomic investigation of microbiota in dajiang-meju, a traditional fermented soybean product in Northeast China. Food Res. Int. 115, 414–424 (2019)
Sun, X., Lu, G., Luan, Y., Zhao, Z., Yang, H., Dan, S.: Analyses of microbial community of naturally homemade soybean pastes in Liaoning Province of China by Illumina Miseq Sequencing. Food Res. Int. 111, 50–57 (2018)
Zhang, P., Zhang, P., Xie, M., An, F., Qiu, B., Wu, R.: Metaproteomics of microbiota in naturally fermented soybean paste, da-jiang. J. Food Sci. 83(5), 1342–1349 (2018)
Gao, X.Z., Xin-Xin, Y.I., Liu, H., Wang, X.D., Cui, Z.J.: Microbial diversity of traditional soybean paste during fermentation in northeastern China. Biotechnol. Bull. 32(4), 251–255 (2016)
Zhao, H., Weizhen, X.U., Yang, G., Liu, Y., Yue, P., Zhang, L.: Bacterial community analysis of Pixian soybean paste during post-fermentation by high-throughput sequencing. Food Sci. 38(10), 117–122 (2017)
Muyzer, G., De Waal, E.C., Uitterlinden, A.G.: Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microb. 59(3), 695–700 (1993)
Hirsch, P.R., Mauchline, T.H., Clark, I.M.: Culture-independent molecular techniques for soil microbial ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 42(6), 878–887 (2010)
Ei Sheikha, A.F.: Molecular detection of mycotoxigenic fungi in foods: the case for using pcr-dgge. Food Biotechnol. 33(1), 54–108 (2019)
Zhang, W.J., Mo, Y.Y., Yang, J., Zhou, J., Lin, Y.S., Alain, I., Zhang, J., Gao, X., Yu, Z.: Genetic diversity pattern of microeukaryotic communities and its relationship with the environment based on pcr-dgge and t-rflp techniques in dongshan bay, southeast China. Cont. Shelf Res. 164, 1–9 (2018)
Han, R., Yuan, Y.Z., Cao, Q.W., Li, Q.H., Chen, L.S., Zhu, D.R., Liu, D.L.: Pcr-dgge analysis on microbial community structure of rural household biogas digesters in qinghai plateau. Curr. Microbiol. 75(5), 1–9 (2017)
Orlewska K., Piotrowska-Seget Z., Bratosiewicz-Wąsik J., Cycoń M.: Characterization of bacterial diversity in soil contaminated with the macrolide antibiotic erythromycin and/or inoculated with a multidrug-resistant Raoultella sp. strain using the pcr-dgge approach. Appl Soil Ecol. 126, 57–64 (2018)
Garofalo, C., Bancalari, E., Milanović, V., Cardinali, F., Osimani, A., Sardaro, M.L.S., Bottari, B., Bernini, V., Aquilanti, L., Clementi, F.: Study of the bacterial diversity of foods: PCR-DGGE versus LH-PCR. Int J Food Microbiol. 242, 24–36 (2017)
Singh, T.A., Devi, K.R.: Ahmed, Giasuddin, Jeyaram, Kumaraswamy: Microbial and endogenous origin of fibrinolytic activity in traditional fermented foods of northeast India. Food Res Int. 55(2), 356–362 (2014)
Milanović, V., Osimani, A., Garofalo, C., De, F.F., Ercolini, D., Cardinali, F., Taccari, M., Aquilanti, L., Clementi, F.: Profiling white wine seed vinegar bacterial diversity through viable counting, metagenomic sequencing and PCR-DGGE. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 286, 66–74 (2018)
Chahorm K., Prakitchaiwattana C.: Application of reverse transcriptase PCR-DGGE as a rapid method for routine determination of Vibrio spp. in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 264, 46–52 (2018)
Ahmadsah, L.S., Min, S.G., Han, S.K., Hong, Y., Kim, H.Y.: Effect of low salt concentrations on microbial changes during kimchi fermentation monitored by PCR-DGGE and their sensory acceptance. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25(12), 2049–2057 (2015)
Ramezani, M., Hosseini, S.M., Fazeli, S.A.S., Amoozegar, M.A., Fakhari, J.: PCR-DGGE analysis of fungal community in manufacturing process of a traditional Iranian cheese. Iran J. Biotechnol. 10(3), 180–186 (2018)
Li, X., Cai, G., Wu, D., Zhang, M., Lin, C., Lu, J.: Microbial community dynamics of Dan'er barley grain during the industrial malting process. Food Microbiol. 76, 110–116 (2018)
Jeong, M., Kim, J., Choi, E., Kim, J.S., Wang, J.K.: PCR-DGGE analysis of population dynamics of lactic acid bacteria in kimchi by addition of bacteriocins. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 25(4), 1123–1128 (2016)
Yang, Y., Deng, Y., Jin, Y., Liu, Y., Xia, B., Sun, Q.: Dynamics of microbial community during the extremely long-term fermentation process of a traditional soy sauce. J. Sci. Food Agric. 97(10), 3220–3227 (2017)
Xu, W., Huang, Z., Zhang, X., Li, Q., Lu, Z., Shi, J., Xu, Z., Ma, Y.: Monitoring the microbial community during solid-state acetic acid fermentation of Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar. Food Microbiol. 28(6), 1175–1181 (2011)
Rui, W.J., Chao, Z.J., Pu, S., Rina, W., Qing, Y.X., Ping, Z.H.: Bacterial community involved in traditional fermented soybean paste dajiang made in northeast China. Ann. Microbiol. 63(4), 1417–1421 (2013)
Borneman, J., Hartin, R.J.: PCR primers that amplify fungal rRNA genes from environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microb. 66(10), 4356–4360 (2000)
Wang, X.D., Liu, M., Gao, P., Ding, W., Gao, Q., Sun, Q.: Succession of fungal community and growth and decline of aflatoxin B1 during natural fermentation of watercress. Food Sci. 33(11), 142–146 (2012)
Qi, W., Hou, L.H., Guo, H.L., Wang, C.L., Fan, Z.C., Liu, J.F., Cao, X.H.: Effect of salt-tolerant yeast of Candida versatilis and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii on the production of biogenic amines during soy sauce fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 94(8), 1537–1542 (2014)
Shuji, Y., Daisuke, Y., Koji, N., Koji, Y., Hideyuki, K., Tomoki, O., Yuji, K.: Microbiota during fermentation of chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) sauce mash inoculated with halotolerant microbial starters: analyses using the plate count method and PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). Food Microbiol. 27(4), 509–514 (2010)
Sun, S.Y., Jiang, W.G., Zhao, Y.P.: Profile of volatile compounds in 12 Chinese soy sauces produced by a high-salt-diluted state fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 116(3), 316–328 (2012)
Hong, S.B., Kim, D.H., Samson, R.A.: Aspergillus associated with meju, a fermented soybean starting material for traditional soy sauce and soybean paste in Korea. Mycobiology. 43(3), 218–224 (2015)
Liang, Y., Pan, L., Lin, Y.: Analysis of extracellular proteins of Aspergillus oryzae grown on soy sauce koji. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 73(1), 192–195 (2009)
Lee, S., Lee, S., Singh, D., Ji, Y.O., Jeon, E.J., Ryu, H.S., Dong, W.L., Kim, B.S., Lee, C.H.: Comparative evaluation of microbial diversity and metabolite profiles in doenjang, a fermented soybean paste, during the two different industrial manufacturing processes. Food Chem. 221, 1578–1586 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31570492, 31770544) and Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Plant Genetic Engineering and Biological Fermentation Engineering for Cold Region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, J., Wang, J., Chen, L. et al. The Dynamics Analysis of Fungal Community Diversity During the Fermentation Process of Chinese Traditional Soybean Paste. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 4789–4797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00800-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00800-z