Abstract
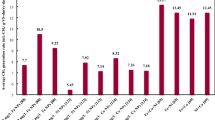
Anaerobic digestion (AD) of organic matter (OM) has always been questioned, because of its time taking bio-disintegration process. In the last few years, nanoparticles (NPs) have been reported as the biodegradation accelerators due to their unique physicochemical properties. For this, iron oxide (Fe3O4) and carbamide (generally known as Urea) capped Fe3O4 (U–Fe3O4) NPs were synthesized by modifying the chemical co-precipitation method and then characterized by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and energy dispersive x-ray (EDX) techniques. In this study, the effect of Fe3O4 and U–Fe3O4 nanoparticles on methane generation was experimentally determined in batch mode AD under mesophilic conditions (38 ± 1 °C). 500 mL culture bottles with 300 mL working volume were used as bioreactors for 50 days. The highest concentration of both types of NPs was 75 mg/L; the other two were 25 and 50 mg/L. The addition of NPs enhanced the CH4 generation compared to the control (without NPs). Hence, the maximum methane generation was achieved at 75 mg/L concentration in both cases 1.45 and 1.52 times more enhancement more than the blank, respectively. Additionally, the experimental methane generation on a cumulative basis was kinetically described by modified Gompertz model (MGM). Thereafter, the model accuracy was further determined by statistical analysis by estimating the coefficient of determination (R2), which was in the range of 0.976–0.999 and the root mean square error (RMSE). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was also conducted to examine the significance of methane generation within the treatments applied ɑ = 0.05.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braguglia, C.M., Gallipoli, A., Gianico, A., Pagliaccia, P.: Anaerobic bioconversion of food waste into energy: a critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 248, 37–56 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.145
Ali, A., Mahar, R.B., Sheerazi, S.T.H.: Renewable electricity generation from food waste through anaerobic digestion in Pakistan: a mini-review. Earth Syst. Environ. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-018-0084-4
Kibler, K.M., Reinhart, D., Hawkins, C., Motlagh, A.M., Wright, J.: Food waste and the food-energy-water nexus: a review of food waste management alternatives. Waste Manag. 74, 52–62 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.014
Sun, S.K., Lu, Y.J., Gao, H., Jiang, T.T., Du, X.Y., Shen, T.X., Wu, P.T., Wang, Y.B.: Impacts of food wastage on water resources and environment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 185, 732–739 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.029
Xin, X., Ma, Y., Liu, Y.: Electric energy production from food waste: microbial fuel cells versus anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 255, 281–287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.099
Xiao, B., Qin, Y., Zhang, W., Wu, J., Qiang, H., Liu, J., Li, Y.Y.: Temperature-phased anaerobic digestion of food waste: a comparison with single-stage digestions based on performance and energy balance. Bioresour. Technol. 249, 826–834 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.084
Zhang, C., Su, H., Baeyens, J., Tan, T.: Reviewing the anaerobic digestion of food waste for biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.038
Kiran, E.U., Trzcinski, A.P., Ng, W.J., Liu, Y.: Bioconversion of food waste to energy: a review. Fuel 134, 389–399 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.05.074
Nguyen, H.H., Heaven, S., Banks, C.: Energy potential from the anaerobic digestion of food waste in municipal solid waste stream of urban areas in Vietnam. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 5, 365–374 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-014-0133-1
Zamanzadeh, M., Hagen, L.H., Svensson, K., Linjordet, R., Horn, S.J.: Anaerobic digestion of food waste—effect of recirculation and temperature on performance and microbiology. Water Res. 96, 246–254 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.058
Ali, A., Mahar, R.B., Abdelsalam, E.M., Sherazi, S.T.H.: Kinetic modeling for bioaugmented anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste by using Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Waste Biomass Valoriz. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0375-x
Yu, Z., Leng, X., Zhao, S., Ji, J., Zhou, T., Khan, A., Kakde, A., Liu, P., Li, X.: A review on the applications of microbial electrolysis cells in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 255, 340–348 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.003
Ali, A., Rundong, L., Shah, F., Mahar, R., WajidIjaz, M., Muqueet, M.: Predictive modeling of biogas production from anaerobic digestion of mixed kitchen waste at mesophilic temperature. Int. Waste Resour. (2016). https://doi.org/10.4172/2252-5211.1000230
Ali, A., Mahar, R.B., Soomro, R.A., Sherazi, S.T.H.: Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles facilitated anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste for enhancement of methane production. Energy Sources Part A 39, 1815–1822 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0375-x
Guo, Z., Liu, W., Yang, C., Gao, L., Thangavel, S., Wang, L., He, Z., Cai, W., Wang, A.: Computational and experimental analysis of organic degradation positively regulated by bioelectrochemistry in an anaerobic bioreactor system. Water Res. 125, 170–179 (2017)
Vanwonterghem, I., Jensen, P.D., Ho, D.P., Batstone, D.J., Tyson, G.W.: ScienceDirect linking microbial community structure, interactions and function in anaerobic digesters using new molecular techniques. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 27, 55–64 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.11.004
Park, J., Lee, B., Tian, D., Jun, H.: Bioelectrochemical enhancement of methane production from highly concentrated food waste in a combined anaerobic digester and microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour. Technol. 247, 226–233 (2018)
Abdelsalam, E., Samer, M., Attia, Y.A., Abdel-hadi, M.A., Hassan, H.E., Badr, Y.: Effects of Co and Ni nanoparticles on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of slurry. Energy Convers. Manag. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.05.051
Li, Y., Zhang, R., He, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, X., Chen, C., Liu, G.: Anaerobic co-digestion of chicken manure and corn stover in batch and continuously stirred tank reactor (CSTR). Bioresour. Technol. 156, 342–347 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.054
Luna-delRisco, M., Orupõld, K., Dubourguier, H.C.: Particle-size effect of CuO and ZnO on biogas and methane production during anaerobic digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 189, 603–608 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.085
Qiang, H., Lang, D.L., Li, Y.Y.: High-solid mesophilic methane fermentation of food waste with an emphasis on Iron, Cobalt, and Nickel requirements. Bioresour. Technol. 103, 21–27 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.036
Facchin, V., Cavinato, C., Fatone, F., Pavan, P., Cecchi, F., Bolzonella, D.: Effect of trace element supplementation on the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste in batch trials: the influence of inoculum origin. Biochem. Eng. J. 70, 71–77 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2012.10.004
Vintiloiu, A., Lemmer, A., Oechsner, H., Jungbluth, T.: Mineral substances and macronutrients in the anaerobic conversion of biomass: an impact evaluation. Eng. Life Sci. 12, 287–294 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201100159
Santosh, Yadvika, Sreekrishnan, T.R., Kohli, S., Rana, V.: Enhancement of biogas production from solid substrates using different techniques—a review. Bioresour. Technol. 95, 1–10 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.02.010
Abdelsalam, E., Samer, M., Attia, Y.A., Abdel-hadi, M.A., Hassan, H.E., Badr, Y.: In fluence of zero valent iron nanoparticles and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of manure. Energy. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.11.137
Chen, Y., Cheng, J.J., Creamer, K.S.: Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 4044–4064 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.057
Forster, S.P., Olveira, S., Seeger, S.: Nanotechnology in the market: promises and realities. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 8, 592–613 (2011)
Tratnyek, P.G., Johnson, R.L.: Nanotechnologies for environmental cleanup. Nano Today. 1, 44–48 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(06)70048-2
Yang, Y., Guo, J., Hu, Z.: Impact of nano zero valent iron (NZVI) on methanogenic activity and population dynamics in anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 47, 6790–6800 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.012
Honetschlägerová, L., Škarohlíd, R., Martinec, M., Šír, M., Luciano, V.: Interactions of nanoscale zero valent iron and iron reducing bacteria in remediation of trichloroethene. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 127, 241–246 (2018)
Puyol, D., Flores-alsina, X., Segura, Y., Molina, R., Padrino, B., Fierro, J.L.G., Gernaey, K.V., Melero, J.A., Martinez, F.: Exploring the e ff ects of ZVI addition on resource recovery in the anaerobic digestion process graphical abstract. Chem. Eng. J. 335, 703–711 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.029
Antwi, P., Li, J., Boadi, P.O., Meng, J., Shi, E., Chi, X., Deng, K., Ayivi, F.: Dosing effect of zero valent iron (ZVI) on biomethanation and microbial community distribution as revealed by 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 123, 191–199 (2017)
Zhang, J., Sui, Q., Zhong, H., Meng, X., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Wei, Y.: Impacts of zero valent iron, natural zeolite and Dnase on the fate of antibiotic resistance genes during thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 258, 135–141 (2018)
Park, J.H., Kang, H.J., Park, K.H., Park, H.D.: Direct interspecies electron transfer via conductive materials: a perspective for anaerobic digestion applications. Bioresour. Technol. 254, 300–311 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.095
Zhang, J., Lu, Y.: Conductive Fe3O4 nanoparticles accelerate syntrophic methane production from butyrate oxidation in two different lake sediments. Front. Microbiol. 7, 1316 (2016)
Wang, T., Zhang, D., Dai, L., Dong, B., Dai, X.: Magnetite triggering enhanced direct interspecies electron transfer: a scavenger for the blockage of electron transfer in anaerobic digestion of high-solids sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 7160–7169 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00891
Ali, A., Mahar, R.B., Soomro, R.A., Sherazi, S.T.H.: Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles facilitated anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste for enhancement of methane production. Energy Sources Part A 39, 1815–1822 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2017.1384866
Ye, Q., Zhang, Z., Huang, Y., Fang, T., Cui, Q., He, C., Wang, H.: Enhancing electron transfer by magnetite during phenanthrene anaerobic methanogenic degradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 129, 109–116 (2018)
Suanon, F., Sun, Q., Mama, D., Li, J., Dimon, B., Yu, C.-P.: Effect of nanoscale zero-valent iron and magnetite (Fe3O4) on the fate of metals during anaerobic digestion of sludge. Water Res. 88, 897–903 (2016)
Casals, E., Barrena, R., García, A., González, E., Delgado, L., Busquets-Fité, M., Font, X., Arbiol, J., Glatzel, P., Kvashnina, K.: Programmed iron oxide nanoparticles disintegration in anaerobic digesters boosts biogas production. Small 10, 2801–2808 (2014)
Bai, H., Liu, Z., Sun, D.D.: Highly water soluble and recovered dextran coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for brackish water desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 81, 392–399 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.08.007
Jiang, J., Zhang, Y., Li, K., Wang, Q., Gong, C., Li, M.: Volatile fatty acids production from food waste: effects of pH, temperature, and organic loading rate. Bioresour. Technol. 143, 525–530 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.025
Chen, X., Romano, R.T., Zhang, R.: Anaerobic digestion of food wastes for biogas production. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 3, 61–72 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3965/j.issn.1934-6344.2010.04.061-072
APHA: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA, Washington (1995)
Hariani, P.L., Faizal, M., Setiabudidaya, D.: Synthesis and properties of Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles by co-precipitation method to removal procion dye. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. (2013). https://doi.org/10.7763/ijesd.2013.v4.366
Laurent, S., Forge, D., Port, M., Roch, A., Robic, C., Vander Elst, L., Muller, R.N.: Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 108, 2064–2110 (2008)
Ariunbaatar, J., Panico, A., Esposito, G., Pirozzi, F., Lens, P.N.L.: Pretreatment methods to enhance anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste. Appl. Energy 123, 143–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.02.035
Tsapekos, P., Kougias, P.G., Kuthiala, S., Angelidaki, I.: Co-digestion and model simulations of source separated municipal organic waste with cattle manure under batch and continuously stirred tank reactors. Energy Convers. Manag. 159, 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.01.002
Algapani, D.E., Wang, J., Qiao, W., Su, M., Goglio, A., Wandera, S.M., Jiang, M., Pan, X., Adani, F., Dong, R.: Improving methane production and anaerobic digestion stability of food waste by extracting lipids and mixing it with sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 244, 996–1005 (2017)
Kafle, G.K., Kim, S.H., Sung, K.I.: Ensiling of fish industry waste for biogas production: a lab scale evaluation of biochemical methane potential (BMP) and kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 127, 326–336 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.032
Membere, E., Sallis, P.: Effect of temperature on kinetics of biogas production from macroalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 263, 410–417 (2018)
Yong, Z., Dong, Y., Zhang, X., Tan, T.: Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and straw for biogas production. Renew. Energy. 78, 527–530 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.01.033
Nagao, N., Tajima, N., Kawai, M., Niwa, C., Kurosawa, N., Matsuyama, T., Yusoff, F.M., Toda, T.: Maximum organic loading rate for the single-stage wet anaerobic digestion of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 118, 210–218 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.045
Park, J.Y., Aliaga, C., Renzas, J.R., Lee, H., Somorjai, G.A.: The role of organic capping layers of platinum nanoparticles in catalytic activity of CO oxidation. Catal. Lett. 129, 1–6 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-009-9871-8
Banerjee, A., Qi, J., Gogoi, R., Wong, J., Mitragotri, S.: Role of nanoparticle size, shape and surface chemistry in oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 238, 176–185 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.07.051
Yu, M., Zhao, M., Huang, Z., Xi, K., Shi, W., Ruan, W.: A model based on feature objects aided strategy to evaluate the methane generation from food waste by anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 72, 218–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.10.038
Feng, X.M., Karlsson, A., Svensson, B.H., Bertilsson, S.: Impact of trace element addition on biogas production from food industrial waste–linking process to microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 74, 226–240 (2010)
Ni, S.Q., Ni, J., Yang, N., Wang, J.: Effect of magnetic nanoparticles on the performance of activated sludge treatment system. Bioresour. Technol. 143, 555–561 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.041
Wang, K., Yin, J., Shen, D., Li, N.: Anaerobic digestion of food waste for volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production with different types of inoculum: effect of pH. Bioresour. Technol. 161, 395–401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.088
De Gioannis, G., Muntoni, A., Polettini, A., Pomi, R.: A review of dark fermentative hydrogen production from biodegradable municipal waste fractions. Waste Manag. 33, 1345–1361 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.02.019
Phan, C.M., Nguyen, H.M.: Role of capping agent in wet synthesis of nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. A 121, 3213–3219 (2017)
Paramaguru, G., Kannan, M., Lawrence, P., Thamilselvan, D.: Effect of pH on biogas production through anaerobic digestion of food waste. J. Adv. Eng. Res. 4, 59–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20167
Sivakumar, P., Bhagiyalakshmi, M., Anbarasu, K.: Anaerobic treatment of spoiled milk from milk processing industry for energy recovery—a laboratory to pilot scale study. Fuel 96, 482–486 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.01.046
Wu, X., Yao, W., Zhu, J.: Effect of pH on continuous biohydrogen production from liquid swine manure with glucose supplement using an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 35, 6592–6599 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.03.097
Deepanraj, B., Sivasubramanian, V., Jayaraj, S.: Experimental and kinetic study on anaerobic digestion of food waste: the effect of total solids and pH. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy. 7, 63104 (2015)
Zhao, C., Mu, H., Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Zuo, B.: Microbial characteristics analysis and kinetic studies on substrate composition to methane after microbial and nutritional regulation of fruit and vegetable wastes anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 249, 315–321 (2018)
Wu, C., Yu, M., Huang, Q., Ma, H., Gao, M., Wang, Q., Sakai, K.: Stimulation of methane yield from food waste by aerobic pre-treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 261, 279–287 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research work was sponsored financially by the US-Pakistan Center for Advanced Studies in Water, Mehran, UET, Jamshoro, Pakistan. Furthermore, the authors acknowledge the important material analysis provided by the Department of Geology, University of Sindh, Pakistan. The authors are also grateful to Prof. Dr. Rick Bereit, University of Utah, USA, for English editing and correction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, A., Mahar, R.B. & Sherazi, S.T.H. Methane Augmentation of Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste in the Presence of Fe3O4 and Carbamide Capped Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 4093–4107 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00732-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00732-8