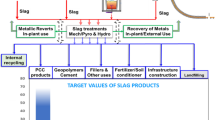
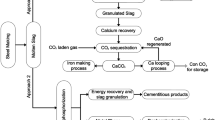
Abstract
Electric steelworks can be considered virtuous industries, as they recover end-of-life products, the scrap, but margins of improvement exist for the sustainability of their production process. An increased internal reuse of by-products (e.g. slags) can provide economic advantages reducing raw material exploitation and avoiding disposal of wastes. Although slags reuse can imply significant advantages, their internal recycling is sometimes hampered because of their composition variability, which might lead to not perfectly known process behavior and effects on the final product. The paper faces this problem and presents a study related to the analyses of process behavior and performance in the case of slags’ reuse in an Italian steelworks. An ad-hoc developed general purpose-monitoring tool was exploited to simulate and evaluate the technical feasibility of two case studies related to the replacement of lime and dolime with Ladle Furnace slag with or without the partial recovery of Electric Arc Furnace slag for the production of two steel families. The effect on the production route, the environmental and energy impacts and steel composition were evaluated through advanced simulations. In particular, the simulations show that lime and dolime replacement is possible by recovering only Ladle Furnace slag, as a small increase of 3–4% of required electric energy is compensated by a reduction of non-metallic raw materials of about 14–16% without negative effects on steel composition and metallic yield. In addition, the exploited tool proved to be valid to monitor slags’ composition and to evaluate the suitability of slags’ reuse on a cast-by-cast basis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
EAF Technology: State of the art and future trends. World Steel Association, Brussels (2000)
World Coal Association. How is steel produced? https://www.worldcoal.org/ (2017). Accessed 01 October 2017
European Commission.: Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on waste and repealing certain directives
World Steel Association. Steel industry by-products. https://www.worldsteel.org/ (2016). Accessed 01 October 2017
Peters, K., Malfa, E., Colla, V., Brimacombe, L.: Resource efficiency in the strategic research agenda of the European steel technology platform. In: 2015 world congress on sustainable technologies, WCST 2015, IEEE, London, pp. 14–16, 34–39 Dec 2015
Praolini, F.: Il ruolo dei sottoprodotti dell’industria nell’economia circolare—Scenario attuale e futuri sviluppi, Attualità industriale/Industry news, La Metallurgia Italiana n.10/2016–ISSN 0026-0843, 2016
Mihok, Ľ, Demeter, P., Baricova, D., Seilerova, K.: Utilization of ironmaking and steelmaking slags. Metalurgija 45(3), 163–168 (2006)
Li, G., Guo, M.: Current development of slag valorisation in China. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 5(3), 317–325 (2014)
Geiseler, J.: Use of steelworks slag in Europe. Waste Manag. 16(1-3), 59–63 (1996)
Matino, I., Branca, T.A., Alcamisi, E., Colla, V., Romaniello, L., Evaluation of a BOF slag recovery treatment combining experimental and simulation studies. In: 3rd international conference on sustainable solid waste management, TINOS: 2015, Tinos Island, Greece, 2015
Bölükbaşı, ÖS., Tufan, B.: Steelmaking slag beneficiation by magnetic separator and impacts on sinter quality. Sci. Sinter. 46(3), 331–344 (2014)
Pistocchi, C., Ragaglini, G., Branca, T.A., Bonari, E., Colla, V., Use of BOF steel slag in agriculture: column test evaluation of effects on alkaline soils and drainage water. In: Proceedings, 7th conference on sustainable development of energy, water and environment system, faculty of mechanical engineering and naval architecture, 2012
Morillon, A., Mudersbach, D., Rex, M., Spiegel, H., Mauhart, M., Tuomikoski, S., Branca, T.A., Ragaglini, G., Colla, V., Romaniello, L., Impact of long-term application of blast furnace and steel slags as liming materials on soil fertility and crop yields. In: Proceedings of the 8th European Slag Conference EUROSLAG 2015, Linz, Austria, 2015
Branca, T.A., Pistocchi, C., Colla, V., Ragaglini, G., Amato, A., Tozzini, C., Mudersbach, D., Morillon, A., Rex, M., Romaniello, L.: Investigation of (BOF) converter slag use for agriculture in europe. Metall. Res. Technol. 111(3), 155–167 (2014)
Kawatra, S.K., Ripke, S.J.: Pelletizing steel mill desulfurization slag. Int. J. Miner. Process. 65, 165–175 (2002)
Matino, I., Colla, V., Branca, T.A., Romaniello, L.: Optimization of by-products reuse in the steel industry: valorization of secondary resources with a particular attention on their pelletization. Waste Biomass Valoriz. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9768-x
Matino, I., Branca, T.A., Colla, V., Fornai, B., Romaniello, L.: Assessment of treatment configurations through process simulations to improve basic oxygen furnace slag reuse. Chem. Eng. Trans. 61, 529–534 (2017)
Baciocchi, R., Costa, G., Di Bartolomeo, E., Polettini, A., Pomi, R.: Carbonation of stainless steel slag as a process for CO2 storage and slag valorization. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 1(4), 467–477 (2010)
Morone, M., Costa, G., Polettini, A., Pomi, R., Baciocchi, R.: Valorization of steel slag by a combined carbonation and granulation treatment. Miner. Eng. 59, 82–90 (2014)
Morone, M., Costa, G., Georgakopoulos, E., Manovic, V., Stendardo, S., Baciocchi, R.: Granulation–carbonation treatment of alkali activated steel slag for secondary aggregates production. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 8(5), 1381–1391 (2017)
Ong, S.K., Mo, K.H., Alengaram, U.J., Jumaat, M.Z., Ling, T.C.: Valorization of wastes from power plant, steel-making and palm oil industries as partial sand substitute in concrete. Waste Biomass Valoriz. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9937-6
Mombelli, D., Mapelli, C., Di Cecca, C., Barella, S., Gruttadauria, A.: Scorie da forno elettrico ad arco: studio sui meccanismi di rilascio e trattamenti di stabilizzazione, La Metallurgia Italiana n.10/2016–ISSN 0026-0843 (2016)
Bianco, L., Porisiensi, S.: Trasformazione da lineare a circolare del processo EAF. Esperienza in FERRIERE NORD SPA: il caso della scoria siviera e dei carboni, La Metallurgia Italiana n.10/2016–ISSN 0026-0843 (2016)
Branca, T.A., Colla, V., Valentini, R.: A way to reduce environmental impact of ladle furnace slag. Ironmak. Steelmak. 36(8), 597–602 (2009)
Polanco, J.A., Manso, J.M., Setién, J., Gonzàlez, J.J.: Strenght and durability of concrete made with electric steelmaking slag. ACI Mater. J. 108(2), 196–203 (2011)
Manso, J.M., Gonzalez, J.J., Polanco, J.A.: Electric arc furnace slag in concrete. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 16(6), 639–645 (2004)
Manso, J.M., Polanco, J.A., Losanez, M., González, J.J.: Durability of concrete made with EAF slag as aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 28(6), 528–534 (2006)
Pellegrino, C., Gaddo, V.: Mechanical and durability characteristics of concrete containing EAF slag as aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 31(9), 663–671 (2009)
Papayianni, I., Anastasiou, E.: Production of high-strength concrete using high volume of industrial by-products. Constr. Build. Mater. 24(8), 1412–1417 (2010)
Al-Zaid, R.Z., Al-Sugair, F.H., Al-Negheimish, A.I.: Investigation of potential uses of electric-arc furnace dust (EAFD) in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 27(2), 267–278 (1997)
Beh, C.L., Chuah, T.G., Nourouzi, M.N., Choong, T.: Removal of heavy metals from steel making waste water by using electric arc furnace slag. J. Chem. 9(4), 2557–2564 (2012)
Claveau-Mallet, D., Wallace, S., Comeau, Y.: Removal of phosphorus, fluoride and metals from a gypsum mining leachate using steel slag filters. Water Res. 47(4), 1512–1520 (2013)
Matino, I., Colla, V., Baragiola, S.: A simulation assessment of modifications of the water network of an electric arc furnace steelworks to allow wastewater reuse. In: 3rd European steel technology and application days, ESTAD 2017, Vienna, Austria, 2017
Zhao, J.X., Li, X.M., Guo, J.L., Huang, M., Ma, J.: Study on LF slag recycling use for desulphurization. Steelmaking 4, 013 (2009)
Ning-ning, L., Jing-kun, Y.U., Chang, S.U.: The development of research on recycling of LF spent slag. China Metall. 10, 003 (2011)
Aminorroaya-Yamini, S., Edris, H., Tohidi, A., Parsi, J., Zamani, B.: Recycling of ladle furnace slags, Australian Institute for Innovative Materials—Papers (2004)
Matino, I., Colla, V., Romaniello, L., Rosito, F., Portulano, L.: Simulation techniques for an efficient use of resources: an overview for the steelmaking field. In: Proceedings of sustainable technologies (WCST) 2015 World Congress, IEEE, London, pp. 48–54, (2015)
Colla, V., Matino, I., Branca, T.A., Fornai, B., Romaniello, L., Rosito, F.: Efficient use of water resources in the steel industry. Water 9(11), 874 (2017)
Alcamisi, E., Matino, I., Colla, V., Maddaloni, A., Romaniello, L., Rosito, F.: Process integration solutions for water networks in integrated steel making plants. Chem. Eng. Trans. 45, 37–42 (2015)
Porzio, G.F., Colla, V., Fornai, B., Vannucci, M., Larsson, M., Stripple, H.: Process integration analysis and some economic-environmental implications for an innovative environmentally friendly recovery and pre-treatment of steel scrap. Appl. Energy 161, 656–672 (2016)
Matino, I., Colla, V.: Modelling of an ozonation process for cyanide removal from blast furnace gas-washing water and analyses of process behaviour in different scenarios. Chem. Eng. Trans. 61, 1447–1452 (2017)
Matino, I., Colla, V., Baragiola, S.: Electric energy consumption and environmental impact in unconventional EAF steelmaking scenarios. Energy Proc. 105, 3636–3641 (2017)
Matino, I., Colla, V., Baragiola, S.: Quantification of energy and environmental impacts in uncommon electric steelmaking scenarios to improve process sustainability. Appl. Energy 207, 543–552 (2017)
Colla, V., Cirilli, F., Kleimt, B., Unamuno, I., Tosato, S., Baragiola, S., Klung, J.-S., Quintero, B.P., De Miranda, U.: Monitoring the environmental and energy impacts of electric arc furnace steelmaking. Matér. Tech. 104(1), 102 (2016)
Matino, I., Colla, V., Cirilli, F., Kleimt, B., Iriondo, U., Tosato, I., Baragiola, S., Klung, S., Peña Quintero, J.-S., De Miranda, U.: Environmental impact evaluation for effective resource management in EAF steelmaking. La Metall. Ital. 10, 48–58 (2017)
Jones, J.A.T.: Electric arc furnace steelmaking, STEELWORKS—the online resource for steel. http://www.steel.org/making-steel/how-its-made/processes/processes-info/electric-arc-furnace-steelmaking.aspx. Accessed 01 May 2015
Borovsky, T., Kijac, J., Bulko, B., Domevec, M., Havran, J.: The influence of slag composition on the distribution of manganese between slag and metal in the electric arc furnace. Acta Metall. Slov. 18(1), 28–33 (2012)
Matino, I., Alcamisi, E., Colla, V., Baragiola, S., Moni, P.: Process modelling and simulation of electric arc furnace steelmaking to allow prognostic evaluations of process environmental and energy impacts. Matér. Tech. 104(1), 104 (2016)
Matino, I., Colla, V., Colucci, V., Lamia, P., Baragiola, S., Di Cecca, C.: Simulation of electric steelworks: a way to predict environmental impact. In: 11th European electric steelmaking conference EEC 2016, Venice, Italy, 25–27 May 2016
Matino, I., Colla, V., Colucci, V., Lamia, P., Baragiola, S., Di Cecca, C.: Improving sustainability of electric steelworks through process simulations. Chem. Eng. Trans. 52, 763–768 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The work described in the present paper was developed within the project entitled EIRES—Environmental Impact Evaluation and Effective Management of Resources in the EAF Steelmaking (Contract No. RFSR-CT-2013-00030), and received funding from the Research Fund for Coal and Steel of the European Union, which is gratefully acknowledged. The sole responsibility of the issues treated in the present paper lies with the authors; the Union is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information contained therein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matino, I., Colla, V. & Baragiola, S. Internal Slags Reuse in an Electric Steelmaking Route and Process Sustainability: Simulation of Different Scenarios Through the EIRES Monitoring Tool. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 2481–2491 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0264-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0264-3