Abstract
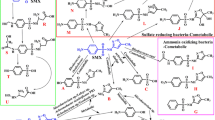
The goal of this study was to isolate and characterize a new bacterium capable of tolerating high concentrations of toxic organic solvents. The production of several extracellular secondary metabolites by Pseudomonas aeruginosa IBBPo16 cells was investigated using a combination of cultural, biochemical and molecular methods. A gram-negative bacterium, P. aeruginosa strain IBBPo16 (GenBank KT315654) was isolated from Poeni oily sludge by enrichment cultures method. Based on 16S rRNA gene sequence, isolated bacterium exhibited 100% similarity with other P. aeruginosa strains from nucleotide database. P. aeruginosa IBBPo16 was able to tolerate 100% cyclohexane, n-hexane, n-decane, styrene, 40% ethylbenzene, and 5% toluene. Toluene and ethylbenzene were more toxic for this bacterium, as compared with cyclohexane, n-hexane, n-decane, and styrene. In the genomic DNA extracted from P. aeruginosa IBBPo16 cells alkane hydroxylase (alkB1), xylene monooxygenase (xylM), naphthalene dioxygenase (ndoM), hydrophobic/amphiphilic efflux 1 (HAE1), and rhamnosyltransferase 1 (rhlAB) genes were detected. P. aeruginosa IBBPo16 produced some extracellular secondary metabolites, such as rhamnolipid surfactant, pyocyanin, pyorubin and pyoverdin pigments, which are well recognized for their numerous potential applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mawgoud, A.M., Aboulwafa, M.M., Hassouna, N.A.-H.: Characterization of rhamnolipid produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate Bs20. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 157, 329–345 (2009)
Ali, C.H., Qureshi, A.S., Mbadinga, S.M., Liu, J.-F., Yang, S.- Z., Mu, B.-Z.: Organic solvent tolerant lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa FW_SH-1: purification and characterization. JSM Enzym. Prot. Sci. 1, 1005 (2016)
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., Lipman, D.J.: Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410 (1990)
Das, K., Mukherjee, A.K.: Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a petroleum-oil contaminated soil from North-East India. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 1339–1345 (2007)
Das, N., Chandran, P.: Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants: an overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int. (2011). doi:10.4061/2011/941810
Déziel, E., Lépine, F., Milot, S., He, J., Mindrinos, M.N., Tompkins, R.G., Rahme, L.G.: Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) reveals a role for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 1339–1344 (2004)
El-Fouly, M.Z., Sharaf, A.M., Shahin, A.A.M., El-Bialy, H.A., Omara, A.M.A.: Biosynthesis of pyocyanin pigment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 8, 36–48 (2015)
Gao, Y., Dai, J., Peng, H., Liu, Y., Xu, T.: Isolation and characterization of a novel organic solventtolerant Anoxybacillus sp. PGDY12, a thermophilic Gram-positive bacterium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 110, 472–478 (2011)
Gaur, R., Khare, S.K.: Cellular response mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PseA during growth in organic solvents. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 49, 372–377 (2009)
Gesheva, V., Stackebrandt, E., Vasileva-Tonkova, E.: Biosurfactant production by halotolerant Rhodococcus fascians from Casey Station, Wilkes Land, Antarctica. Curr. Microbiol. 61, 112–117 (2010)
Heipieper, H.J., Diefenbac, R., Keweloh, H.: Conversion of cis unsaturated fatty acids to trans, a possible mechanism for the protection of phenol-degrading Pseudomonas putida P8 from substrate toxicity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 1847–1852 (1992)
Inoue, A., Horikoshi, K.: Estimation of solvent-tolerance of bacteria by the solvent parameter log P. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 71, 194–196 (1991)
Jain, P.K., Gupta, V.K., Gaur, R.K., Lowry, M., Jaroli, D.P., Chauhan, U.K.: Bioremediation of petroleum oil contaminated soil and water. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 5, 1–26 (2011)
Jensen, V., Löns, D., Zaoui, C., Bredenbruch, F., Meissner, A., Dieterich, G., Münch, R., Häussler, S.: RhlR expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is modulated by the Pseudomonas quinolone signal via PhoB-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Bacteriol. 188, 8601–8606 (2006)
Jimenez, P.N., Koch, G., Thompson, J.A., Xavier, K.B., Cool, R.H., Quax, W.J.: The multiple signaling systems regulating virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 76, 46–65 (2012)
Kalaiarasan, E., Narasimha, H.B.: Antimicrobial resistance patterns and prevalence of virulence factors among biofilm producing strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Biotechnol. Biosci. 4, 26–28 (2016)
King, E.O., Ward, M.K., Raney, D.E.: Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 44, 301–307 (1954)
Kohno, T., Sugimoto, Y., Sei, K., Mori, K.: Design of PCR primers and gene probes for general detection of alkane-degrading bacteria. Microbes Environ. 17, 114–121 (2002)
Marchesi, J.R., Sato, T., Weightman, A.J., Martin, T.A., Fry, J.C., Hiom, S.J., Wade, W.G.: Design and evaluation of useful bacterium-specific PCR primers that amplify genes coding for bacterial 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 795–799 (1998)
Márquez-Rocha, F.J., Olmos-Soto, J., Rosano-Hernández, M.C., Muriel-Garcia, M.: Determination of the hydrocarbon-degrading metabolic capabilities of tropical bacterial isolates. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 55, 17–23 (2005)
Medina, G., Juárez, K., Valderrama, B., Soberón-Chávez, G.: Mechanism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RhlR transcriptional regulation of the rhlAB promoter. J. Bacteriol. 185, 5976–5983 (2003)
Meguro, N., Kodama, Y., Gallegos, M.T., Watanabe, K.: Molecular characterization of resistance-nodulation-division transporters from solvent- and drug-resistant bacteria in petroleum-contaminated soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 580–586 (2005)
Mesarch, M.B., Nakatsu, C.H., Nies, L.: Development of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase-specific primers for monitoring bioremediation by competitive quantitative PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 678–683 (2000)
Mulet, M., David, Z., Nogales, B., Bosch, R., Lalucat, J., García-Valdés, E.: Pseudomonas diversity in crude-oil-contaminated intertidal sand samples obtained after the Prestige oil spill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 1076–1085 (2011)
Norman, R. S., Moeller, P., McDonald, T. J., Morris, P. J.: Effect of pyocyanin on a crude-oil-degrading microbial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 4004–4011 (2004)
Rikalović, M.G., Vrvić, M.M., Karadžić, I.M.: Rhamnolipid biosurfactant from Pseudomonas aeruginosa—from discovery to application in contemporary technology. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 80, 279–304 (2015)
Rocha, C.A., Pedregosa, A.M., Laborda, F.: Biosurfactant-mediated biodegradation of straight and methyl-branched alkanes by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 55925. AMB Express 1 (2011). doi:10.1186/2191-0855-1-9
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., Maniatis, T.: Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor (1989)
Segura, A., Molina, L., Fillet, S., Krell, T., Bernal, P., Muñoz-Rojas, J., Ramos, J.L.: Solvent tolerance in Gram-negative bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 23, 415–421 (2012)
Siegmund, I., Wagner, F.: New method for detecting rhamnolipids excreted by Pseudomonas species during growth on mineral agar. Biotechnol. Techn. 5, 265–268 (1991)
Stancu, M.M.: Response mechanisms in Serratia marcescens IBBPo15 during organic solvents exposure. Curr. Microbiol. 73, 755–765 (2016)
Stancu, M.M., Grifoll, M.: Multidrug resistance in hydrocarbon-tolerant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 57, 1–18 (2011)
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., Kumar, S.: MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725–2729 (2013)
Tang, X.Y., Pan, Y., Li, S., He, B.F.: Screening and isolation of an organic solvent-tolerant bacterium for high-yield production of organic solvent-stable protease. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 7388–7392 (2008)
Zhang, Z., Hou, Z., Yang, C., Ma, C., Tao, F., Xu, P.: Degradation of n-alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in petroleum by a newly isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa DQ8. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 4111–4116 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by Project No. RO1567-IBB05/2017 from the Institute of Biology Bucharest of Romanian Academy. The author is grateful to Ana Dinu for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stancu, M.M. Production of Some Extracellular Metabolites by a Solvent-Tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 1747–1755 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9967-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9967-0