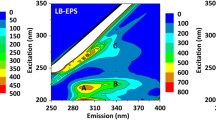
Abstract
Extracellular polymeric substance (EPS), a high molecular weight biological polymer that can bind to a large amount of organic matter and moisture, plays a vital role in the process of sludge formation and structural stability, affecting sedimentation and dewatering performance of sludge. The aim of this study was to observe the changes in the key components of EPS extracted from mechanical dewatered sludge before and after enzyme and thermal pressure treatment. The results showed that the soluble protein content increased by 160 and 110% and the polysaccharide content increased by 180 and 200% after adding 0.03 g/g TSS neutral protease and alpha-amylase, respectively. The effect of compound enzyme treatment was better than that of single enzyme treatment. Furthermore, three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy indicated the presence of tryptophan and aromatic-like proteins, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy showed that the types of functional groups exhibited a sharp decrease in the loosely bound-EPS layer after thermal pressure treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saveyn, H., Pauwels, G., Timmerman, R., Van der Meeren, P.: Effect of polyelectrolyte conditioning on the enhanced dewatering of activated sludge by application of an electric field during the expression phase. Water Res. 39(13), 3012–3020 (2005)
Yuan, H.P., Zhu, N.W., Song, F.Y.: Dewaterability characteristics of sludge conditioned with surfactants pretreatment by electrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 102(3), 2308–2315 (2011)
Luo, K., Yang, Q., L, X.M.., al, e: Enhanced hydrolysis of excess sludge by external enzymes. Environ. Sci. 31, 763–767 (2010)
Liu, Y., Fang, H.H.: Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on flocculation, settling, and dewatering of activated sludge. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 33(3), 237–273 (2003)
Silva A F, Carvalho G, Soares R, et al. Step-by-step strategy for protein enrichment and proteome characterisation of extracellular polymeric substances in wastewater treatment systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 95(3), 767–776(2012).
Froslashlund, B., Palmgren, R., Keiding, K., et al.: Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 30(8), 1749–1758 (1996)
Block, J.C., Manem, J., Urbain, V.: Bioflocculation in activated sludge: an analytic approach. Water Res. 27(5), 829–838 (1993)
Lin, Y.M., Sharma, P.K., van Loosdrecht, M.C.M: The chemical and mechanical differences between alginate-like exopolysaccharides isolated from aerobic flocculent sludge and aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 47(1), 57–65 (2013)
Dignac, M.-F., Urbain, V., Ryback, D., et al.: Chemical description of extracellular polymers: implication on activated sludge floc structure. Water Sci. Technol. 38(8), 45–53 (1998)
Houghton, J.I., Stephenson, T.: Effect of influent organic content on digested sludge extracellular polymer content and dewaterability. Water Res. 36(14), 3620–3628 (2002)
Jiang, J.Q., Zhao, Q.L., Wei, L.L., et al.: Extracellular biological organic matters in microbial fuel cell using sewage sludge as fuel. Water Res. 44(7), 2163–2170 (2010)
Neyens, E., Baeyens, J., Dewil, R.: Advanced sludge treatment affects extracellular polymeric substances to improve activated sludge dewatering. J. Hazard. Mat. 106(2), 83–92 (2004)
Jin, B., Wilén, B., Lant, P.: Impacts of morphological, physical and chemical properties of sludge flocs on dewaterability of activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 98(1), 115–126 (2004)
Higgins, M. J., Novak, J. T.: Characterization of exocellular protein and its role in bioflocculation. J. Environ. Eng. 123(5), 479–485 (1997)
Adav, S. S., Lee, D. J., Tay, J. H.: Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule. Water Res. 42(6–7), 1644–1650 (2008)
Frolund, B., Griebe, T., Nielsen, P.H.: Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 43, 755–761 (1995)
Poxon, T.L., Darby, J.L.: Extracellular polyanions in digested sludge: measurement and relationship to sludge dewaterability. Water Res. 31, 749–758 (1997)
Yu, G.H., He, P.J., Shao, L.M.: Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) fractions from excess sludges and their effects on bioflocculability. Bioresour. Technol. 100(13), 3193–3198 (2009)
Liu, H., Fang, H.H.: Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J. Biotechnol. 95(3), 249–256 (2002)
Zhang, W.J., Cao, B.D., Wang, D.S.: Influence of wastewater sludge treatment using combined peroxyacetic acid oxidation and inorganic coagulants re-flocculation on characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Water Res. 88, 728–739 (2016)
Higuchi, Y., Ohashi, A., Imachi, H., et al.: Hydrolytic activity of alpha-amylase in anaerobic digested sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 52(1–2), 259–266 (2005)
Boczar, B.A., Begley, W.M., Larson, R.J.: Characterization of enzyme activity in activated sludge using rapid analyses for specific hydrolases. Water Environ. Res. 64(6), 792–797 (1992)
Goel, R., Mino, T., Satoh, H., et al.: Enzyme activities under anaerobic and aerobic conditions in activated sludge sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 32(7), 2081–2088 (1998)
Wang, W., Liu, W., Wang, L.: Characteristics and distribution research on extracellular polymer substance extracted from sewage sludge. J. Environ. Biol. 37(2), 305–312 (2016)
Li, J.B., Zeng, Y.F., Liu, W.W., et al.: Effect of methanogenesis of residue from thermal pre-treatment sludge by anaerobic fermentative hydrogen production. Proc. Environ Sci. 31, 318–324 (2016)
Adav, S.S., Lee, D.J., Lai, J.Y.: Potential cause of aerobic granular sludge breakdown at high organic loading rates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85(5), 1601–1610 (2010)
Bramhachari, P.V., Kishor, P.B., Ramadevi, R., et al.: Isolation and characterization of mucous exopolysaccharide (EPS) produced by Vibrio furnissii strain VB0S3. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17, 14–51 (2007)
Badireddy, A.R., Chellam, S., Gassman, P.L., et al.: Role of extracellular polymeric substances in bioflocculation of activated sludge microorganisms under glucose-controlled conditions. Water Res. 44(15), 4505–4516 (2010)
Gary, W.S.: Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. Vib. Spectrosc. 4(1), 123–124 (1992)
Barth, A., Zscherp, C.: What vibrations tell us about proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 35(4), 369–430 (2002)
Raszka, A., Chorvatova, M., Wanner, J.: The role and significance of extracellular polymers in activated sludge. Part I: literature review. Acta Hydrochim. Et Hydrobiol. 34(5), 411–424 (2006).
He, C., Giannis, A., Wang, J.Y.: Conversion of sewage sludge to clean solid fuel using hydrothermal carbonization. Appl. Energy. 111, 257–266 (2013)
Orem, W.H., Neuzil, S.G., Lerch, H.E., Cecil, C.B.: Experimental early-stage coalification of a peat sample and a peatified wood sample from Indonesia. Org. Geochem. 24(2), 111–125 (1996)
Henderson, R.K., Baker, A., Murphy, K.R., Hamblya, A., Stuetz, R.M., Khan, S.J.: Fluorescence as a potential monitoring tool for recycled water systems: a review. Water Res. 43(4), 863–881 (2009)
Chen, W., Westerhoff, P., Leenheer, J.A., Booksh, K.: Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37(24), 5701–5710 (2003)
Wei, D., Wang, Y.F., Wang, X.D., Li, M.T., et al.: Toxicity assessment of 4-chlorophenol to aerobic granular sludge and its interaction with extracellular polymeric substances. J. Hazard. Mater. 289, 101–107 (2015)
Wang, Z., Gao, M., Wang, Z., et al.: Effect of salinity on extracellular polymeric substances of activated sludge from an anoxic-aerobic sequencing batch reactor. Chemosphere. 93(11), 2789–2795 (2013)
Ng, T.C.A., Ng, H.Y.: Characterization of initial fouling in aerobic submerged membrane bioreactors in relation to physico-chemical characteristics under different flux conditions. Water Res. 44(7), 2336–2348 (2010)
Li, W.H., Sheng, G.P., Liu, X.W., et al.: Characterizing the extracellular and intracellular fluorescent products of activated sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 42(12), 3173–3181 (2008)
Yu, G.H., He, P.J., Shao, L.M.: Novel insights into sludge dewaterability by fluorescence excitation-emission matrix combined with parallel factor analysis. Water Res. 44(3), 797–806 (2010)
Li, X. Y., Yang, S. F.: Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res. 41(5), 1022–1030 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51308349) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51276119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Wang, L., Gao, X. et al. Distribution Characteristics of Extracellular Polymeric Substance Extracted from Dewatered Sludge Treated with Enzymes and Thermal Pressure. Waste Biomass Valor 9, 1523–1533 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9941-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9941-x