Abstract
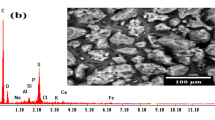
Biosorption of chemical oxygen demand (COD), manganese (Mn) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) onto an empty fruit bunch (EFB)–based powdered activated carbon (PAC) from a multicomponent system—biotreated palm oil mill effluent (BPOME)—were studied in a batch adsorption process. The experimental results were fitted to four isotherm models, and four kinetic models. Amongst the isotherm models (Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich) employed, Langmuir model showed the best conformity to the equilibrium data with R 2 values of 1.00 for COD and 0.9999 for both Mn and H2S. The Dubinin–Radushkevich model followed the conformity trend with R 2 values of 0.9984, 0.9948 and 0.9824 for COD, H2S, and Mn, respectively. Also, amongst the kinetic models (Pseudo-first order, Lagergren’s pseudo-second order, Elovich and Weber–Morris intra-particle diffusion) employed, only the pseudo-second order model could best describe the adsorption behaviours of all the three contaminants with R 2 values of 1.00 in all cases. The mechanistic uptake pathway was further examined by means of the Fourier transform infrared in studying the surface chemistry of the PAC. It was observed that the presence of functional groups like the aldehydes and ketones, carbonyl, mono-alkyl, amines, amongst others led to physicochemical interactions between PAC surface and the contaminants. Overall, the equilibrium, kinetics and surface chemistry analyses pointed towards the adsorption processes been largely driven by electrostatic sorption. Additionally, the EFB-based PAC was capable of reducing COD, Mn and H2S from POME, hence, could be utilized in developing a unit operation for integration into the current POME treatment.
Graphical Abstract
Percent uptake versus adsorption time plot for COD, Mn and H2S removal from biotreated POME.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suzuki, M.: Adsorption Engineering. Kodansha Ltd. and Elsevier Science Publishers B.V, Tokyo (1990)
Çeçen, F., Aktaş, Ö.: Activated carbon for water and wastewater treatment: Integration of adsorption and biological treatment. Wiley-VCH Verlag & Co. KGaA, Weinheim (2012)
Noble, R.D., Terry, P.A.: Principles of chemical separations with environmental applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Ignatowicz, K.: Low-cost sorbent for removing pesticides during water treatment. In: Stoytcheva, M. (ed.) Pesticides—Formulations, Effects, Fate. Intech, Rijeka (2011)
Dąbrowski, A.: Adsorption—from theory to practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 93(1), 135–224 (2001)
Crini, G., Badot, P.-M.: Sorption Processes and Pollution: Conventional and Non-conventional Sorbents for Pollutant Removal from Wastewaters. Presses universitaires de Franche, Comté (2010)
USEPA: Handbook for Sampling and Sample Preservation of Water and Wastewater-USEPA, vol. EPA-600/4-82-029. Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory Office of Research and Development, Cincinnati, Ohio (1982)
Phan, N.H., Rio, S., Faur, C., Le Coq, L., Le Cloirec, P., Nguyen, T.H.: Production of fibrous activated carbons from natural cellulose (jute, coconut) fibers for water treatment applications. Carbon 44(12), 2569–2577 (2006)
Koay, Y.S., Ahamad, I.S., Mohsen Nourouzi, M., Chuah, T.G.: Ion-exchange adsorption of reactive dye solution onto quaternized palm kernel shell. J. Appl. Sci. 14(12), 1314–1318 (2014). doi:10.3923/jas.2014.1314.1318.
Amosa, M.K., Jami, M.S., Alkhatib, M.F.R., Jimat, D.N., Muyibi, S.A.: A two-step optimization and statistical analysis of COD reduction from biotreated POME using empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon produced from pyrolysis. Water Qual Expo Health (2015). doi:10.1007/s12403-015-0176-4
El-Naas, M.H., Al-Zuhair, S., Alhaija, M.A.: Reduction of COD in refinery wastewater through adsorption on date-pit activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 173(1), 750–757 (2010)
Demiral, H., Gündüzoğlu, G.: Removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from sugar beet bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 101(6), 1675–1680 (2010)
Ho, Y.S., Porter, J.F., McKay, G.: Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: copper, nickel and lead single component systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 141(1–4), 1–33 (2002)
Richter, E., Wilfried, S., Myers, A.L.: Effect of adsorption equation on prediction of multicomponent adsorption equilibria by the ideal adsorbed solution theory. Chem. Eng. Sci. 44(8), 1609–1616 (1989)
Kamari, A., Ngah, W.S.: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of lead and copper uptake by H2SO4 modified chitosan. Colloids Surf. B 73(2), 257–266 (2009)
Langmuir, I.: The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40(9), 1361–1403 (1918)
Langmuir, I.: The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 38(11), 2221–2295 (1916)
Langmuir, I.: The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part II. Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 39(9), 1848–1906 (1917)
Amosa, M.K., Alkhatib, M.F.R., Jami, M.S., Jimat, D.N., Owolabi, R.U., Muyibi, S.A.: Morphological synthesis and environmental application of ZSM-5 zeolite crystals from combined low-water and fluoride syntheses routes. Adv. Environ. Biol. 8(3), 613–625 (2014)
Demiral, H., Demiral, İ., Tümsek, F., Karabacakoğlu, B.: Pore structure of activated carbon prepared from hazelnut bagasse by chemical activation. Surf. Interface Anal. 40(3–4), 616–619 (2008)
Lee, C.-H.: Adsorption science and technology. World Scientific Publishing Co. Re. Ltd, Singapore (2003)
Toth, J.: Adsorption: Theory, Modeling and Analysis. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York (2002)
Dada, A.O., Olalekan, A.P., Olatunya, A.M., Dada, O.: Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk IOSR. J. Appl. Chem. 3(1), 38–45 (2012)
Freundlich, H.M.F.: Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 57(385471), 1100–1107 (1906)
El-Naas, M., Al-Rub, F.A., Ashour, I., Al Marzouqi, M.: Effect of competitive interference on the biosorption of lead (II) by Chlorella vulgaris. Chem. Eng. Process. 46(12), 1391–1399 (2007)
Hameed, B., Daud, F.: Adsorption studies of basic dye on activated carbon derived from agricultural waste: Hevea brasiliensis seed coat. Chem. Eng. J. 139(1), 48–55 (2008)
Gómez, V., Larrechi, M.S., Callao, M.P.: Kinetic and adsorption study of acid dye removal using activated carbon. Chemosphere 69(7), 1151–1158 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.076
Radushkevich, L.: Potential theory of sorption and structure of carbons. Zh. Fiz. Khim. 23(12), 1410–1420 (1949)
Dubinin, M.: Modern state of the theory of volume filling of micropore adsorbents during adsorption of gases and steams on carbon adsorbents. Zh. Fiz. Khim. 39(19), 1305–1317 (1965)
Ho, Y.-S.: Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 136(3), 681–689 (2006)
Amin, N.K.: Removal of reactive dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbons prepared from sugarcane bagasse pith. Desalination 223(1), 152–161 (2008)
Ho, Y.-S.: Removal of copper ions from aqueous solution by tree fern. Water Res. 37(10), 2323–2330 (2003)
Robati, D.: Pseudo-second-order kinetic equations for modeling adsorption systems for removal of lead ions using multi-walled carbon nanotube. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 3(55), 1–6 (2013). doi:10.1186/2193-8865-3-55
Taffarel, S.R., Rubio, J.: On the removal of Mn2+ ions by adsorption onto natural and activated Chilean zeolites. Miner. Eng. 22(4), 336–343 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2008.09.007
Plazinski, W., Dziuba, J., Rudzinski, W.: Modeling of sorption kinetics: the pseudo-second order equation and the sorbate intraparticle diffusivity. Adsorption 19(5), 1055–1064 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10450-013-9529-0
Weber, W.J., Morris, J.C.: Advances in water pollution research: removal of biologically resistant pollutant from wastewater by adsorption. In: International Conference on Water Pollution Symposium, pp. 231–266. Pergamon, Oxford (1962)
Hameed, B.H., Tan, I.A.W., Ahmad, A.L.: Adsorption isotherm, kinetic modeling and mechanism of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on coconut husk-based activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 144, 235–244 (2008)
Plazinski, W., Rudzinski, W.: Kinetics of adsorption at solid/solution interfaces controlled by intraparticle diffusion: a theoretical analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 12495–12501 (2009)
Acharya, J., Sahu, J., Mohanty, C., Meikap, B.: Removal of lead (II) from wastewater by activated carbon developed from Tamarind wood by zinc chloride activation. Chem. Eng. J. 149(1–3), 249–262 (2009)
Alkhatib, M.F., Muyibi, S.A., Amode, J.O.: Optimization of activated carbon production from empty fruit bunch fibers in one-step steam pyrolysis for cadmium removal from aqueous solution. Environmentalist 31(4), 349–357 (2011)
Hameed, B., Tan, I., Ahmad, A.: Preparation of oil palm empty fruit bunch-based activated carbon for removal of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol: optimization using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 164(2), 1316–1324 (2009)
Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.: Effect of porosity and functionality of activated carbon in adsorption. In: Zhou, L. (ed.) Adsorption: Progress in Fundamental and Application Research. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Singapore (2007)
Amosa, M.K., Jami, M.S., Alkhatib, M.F.R., Jimat, D.N., Muyibi, S.A.: Comparative and optimization studies of adsorptive strengths of activated carbons produced from steam- and CO2-activation for BPOME treatment. Adv. Environ. Biol. 8(3), 603–612 (2014)
Linders, M., Van Den Broeke, L., Van Bokhoven, J., Duisterwinkel, A., Kapteijn, F., Moulijn, J.: Effect of the adsorption isotherm on one-and two-component diffusion in activated carbon. Carbon 35(9), 1415–1425 (1997)
Bansal, R.C., Goyal, M.: Activated carbon adsorption. Taylor and Francis Group, LLC, New York (2010)
Do Duong, D.: Adsorption Analysis: Equilibria and Kinetics, vol. 2. Imperial College Press, Singapore (1998)
Ferraro, J.R., Krishnan, K.: Practical Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Industrial and Laboratory Chemical Analysis. Academic Press Inc., San Diego (2012)
Nikolic, G.S.: Fourier Transforms—New Analytical Approaches and FTIR Strategies. InTech, Rijeka (2011)
Arunachalam, A.M.: Adsorption/absorption features of peat moss for water pollution control: feasibility studies for St. John’s harbour water pollution. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Igwe, J.C., Arukwe, U., Anioke, S.N.: Isotherm and kinetic studies of residual oil adsorption from palm oil mill effluent (POME) using boiler fly ash. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 12(3), 417–427 (2013)
Yang, R.T.: Adsorbents: Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley, Hoboken (2003)
Hassani, A., Vafaei, F., Karaca, S., Khataee, A.R.: Adsorption of a cationic dye from aqueous solution using Turkish lignite: kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic studies and neural network modeling. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(4), 2615–2624 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2013.10.049
Mohan, D., Sarswat, A., Ok, Y.S., Pittman Jr, C.U.: Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—a critical review. Bioresour. Technol. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.120
Emad, S.M.A.: Production of Powdered Activated Carbon from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch for Removal of Phenol and Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Final Effluent. International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur (2010)
Corbitt, R.A.: Standard Handbook of Environmental Engineering, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1999)
Malkoc, E., Nuhoglu, Y.: Determination of kinetic and equilibrium parameters of the batch adsorption of Cr(VI) onto waste acorn of Quercus ithaburensis. Chem. Eng. Process. 46(10), 1020–1029 (2007)
Itodo, A.U., Itodo, H.U.: Sorption energies estimation using Dubinin–Radushkevich and Temkin adsorption isotherms. Life Sci. J. 7(4), 31–39 (2010)
Hank, D., Azi, Z., Ait Hocine, S., Chaalal, O., Hellal, A.: Optimization of phenol adsorption onto bentonite by factorial design methodology. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(4), 2256–2263 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2013.09.058
Crosson, G.S., Sandmann, E.: Kinetic study of denatonium sorption to smectite clay minerals. Environ. Eng. Sci. 30(6), 311–316 (2013)
Motsi, T., Rowson, N.A., Simmons, M.J.H.: Adsorption of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by natural zeolite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 92(1–2), 42–48 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.minpro.2009.02.005
Kushwaha, S., Sudhakar, P.P.: Sorption of uranium from aqueous solutions using palm-shell-based adsorbents: a kinetic and equilibrium study. J. Environ. Radioact. 126, 115–124 (2013)
Inglezakis, V.J., Loizidou, M.D., Grigoropoulou, H.P.: Equilibrium and kinetic ion exchange studies of Pb2+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ on natural clinoptilolite. Water Res. 36, 2784–2792 (2002)
Kiurski, J., Adamovic, S., Krstic, J., Oros, I., Miloradov, M.V.: Adsorption efficiency of low-cost materials in the removal of Zn (II) ions from printing developer. Acta Technica Corviniensis 4, 61–66 (2011)
Cao, W., Dang, Z., Yuan, B.-L., Shen, C.-H., Kan, J., Xue, X.-L.: Sorption kinetics of sulphate ions on quaternary ammonium-modified rice straw. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(4), 2603–2609 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2013.10.047
Inglezakis, V., Poulopoulos, S.: Adsorption, Ion Exchange and Catalysis: Design of Operations and Environmental Applications, vol. 3. Elsevier B.V, Amsterdam (2006)
Štrkalj, A., Glavaš, Z., Brnardić, I.: Application of foundry waste for adsorption of hexavalent chromium. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 27(1), 15–19 (2013)
Ho, Y.-S., Chiang, T.-H., Hsueh, Y.-M.: Removal of basic dye from aqueous solution using tree fern as a biosorbent. Process Biochem. 40(1), 119–124 (2005)
Vázquez, G., Fernández-Bea, R., Freire, M.S., González-Álvarez, J., Antorrena, G.: Determination of equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of cadmium (II) onto Castanea sativa shell. In: European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6), Copenhagen, 16–20 Sept 2007
Alam, M.Z., Muyibi, S.A., Mansor, M.F., Wahid, R.: Removal of phenol by activated carbons prepared from palm oil mill effluent sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 18(3), 446–452 (2006)
Husin, N.I., Wahab, N.A.A., Isa, N., Boudville, R.: Sorption equilibrium and kinetics of oil from aqueous solution using banana pseudostem fibers. In: International Conference on Environment and Industrial Innovation (ICEII 2011). IACSIT Press (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) Malaysia, for partially financing the research project under the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS13-029-0270) and also to Sime Darby for their support in EFB and BPOME sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amosa, M.K., Jami, M.S. & Alkhatib, M.F.R. Electrostatic Biosorption of COD, Mn and H2S on EFB-Based Activated Carbon Produced through Steam Pyrolysis: An Analysis Based on Surface Chemistry, Equilibria and Kinetics. Waste Biomass Valor 7, 109–124 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9435-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9435-7