Abstract
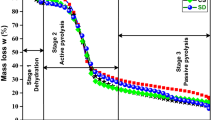
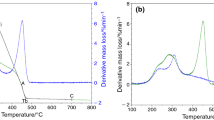
Lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose are the major components of biomass. The chemical reactivities of the biomass are affected by the difference in chemical structures making the knowledge of their composition, essential to predict the efficiency of the biomass conversion process for utilizing bio-energy, which is of immense importance for successful commercialization of these processes and thus to gain energy security. Despite the presence of accurate and robust Wet Chemical methods, it is very difficult to implement these techniques commercially. Therefore, in this study the chemical composition of biomass has been determined by a simpler physical technique—Thermogravimetric Analysis (TG). The values obtained were correlated with chemical methods and it was found that TG predicted the holocellulose content with a relatively high accuracy while it underestimated the lignin content by a huge margin. The kinetic parameters of degradation of five biomass samples have also been reported in this study. This study also compared the mass loss profiles of the biomass in TG with their mass loss profiles in a furnace.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Pre-exponential factor
- B, C, D :
-
Constants
- dw/dt :
-
Ratio of change in weight to change in time
- E :
-
Activation energy
- k :
-
Reaction constant
- n :
-
Order of the reaction
- R :
-
Universal gas constant
- R2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- t :
-
Time
- w :
-
Weight at any time
- w f :
-
Final weight at the end of the stage
- w o :
-
Initial weight at the start of the stage
- x :
-
Sample weight
- ASTM:
-
American Society for Testing and Materials
- DTG:
-
Derivative thermogravimetry
- H-NMR:
-
Hydrogen 1-nuclear magnetic resonance
- HR-TGA:
-
High-resolution thermogravimetric analysis
- MMT:
-
Million metric tonne
- PUT:
-
Pyrolytic unit thermographs
- TAPPI:
-
Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry
- TG:
-
Thermogravimetry
References
Klass, D.L.: Biomass for renewable energy, fuels, and chemicals, pp. 1–652. Academic Press, San Diego (1998)
Carrier, M., Loppinet-Serani, A., Denux, D., Lasnier, J.-M., Ham-Pichavant, F., Cansell, F., Aymonier, C.: Thermogravimetric analysis as a new method to determine the lignocellulosic composition of biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 35(1), 298–307 (2011)
Demirbas, A.: Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 157(2–3), 220–229 (2008)
Nelson, P., Hood, E., Powell, R.: The bioeconomy: a new era of products derived from renewable plant-based feedstocks. In: Hood, E., Nelson, P., Powell, R. (eds.) Plant Biomass Conversion, pp. 3–20. West Sussex, Wiley Blackwell (2011)
Yang, H., Yan, R., Chen, H., Lee, D.H., Zheng, C.: Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86, 1781–1788 (2007)
Demirbas, A.: Fuels from biomass. In: Demirbas, A. (ed.) Biohydrogen for Future Engine fuel Demands, pp. 43–59. Springer, London (2009)
Bledzki, A.K., Mamun, A.A., Volk, J.: Physical, chemical and surface properties of wheat husk, rye husk and soft wood and their polypropylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 41(4), 480–488 (2010)
Brinkmann, K., Blaschke, L., Polle, A.: Comparison of different methods for lignin determination as a basis for calibration of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy and implications of lignoproteins. J. Chem. Technol. 28(12), 2483–2501 (2002)
Saura-Calixto, F., Canellas, J., Garcia-Raso, J.: Determination of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin contents of dietary fibre and crude fibre of several seed hulls. data comparison. Z Leb. Unters Forsch 177, 200–202 (1983)
Ververis, C., Georghiou, K., Danielidis, D., Hatzinikolaou, D.G., Santas, P., Santas, R., Corleti, V.: Cellulose, hemicelluloses, lignin and ash content of some organic materials and their suitability for use as paper pulp supplements. Bioresour. Technol. 98(2), 296–301 (2007)
Singh, K, Das, K.C., Risse, M., Worley, J.: “Determination of composition of cellulose and lignin mixtures using thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA).In: 15th North American Waste to Energy Conference, pp. 219–226. (2007)
Cozzani, V., Lucchesi, A., Stoppato, G., Maschio, G.: A new method to determine the composition of biomass by thermogravimetric analysis. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 75(1), 127–133 (1997)
Freda, C., Zimbardi, F., Nanna, F., Viola, E.: Mathematical tool from corn stover TGA to determine its composition. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 167(8), 2283–2294 (2012)
Serapiglia, M.J., Cameron, K.D., Stipanovic, A.J., Smart, L.B.: High-resolution thermogravimetric analysis for rapid characterization of biomass composition and selection of shrub willow varieties. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 145(1–3), 3–11 (2008)
Serapiglia, M.J., Cameron, K.D., Stipanovic, A.J., Smart, L.B.: Analysis of biomass composition using high-resolution thermogravimetric analysis and percent bark content for the selection of shrub willow bioenergy crop varieties. BioEnergy Res. 2(1–2), 1–9 (2009)
Aghamohammadi, N., Sulaiman, N.M.N., Aroua, M.K.: Combustion characteristics of biomass in SouthEast Asia. Biomass Bioenergy 35(9), 3884–3890 (2011)
Kumar, A., Wang, L., Dzenis, Y.A., Jones, D.D., Hanna, M.A.: Thermogravimetric characterization of corn stover as gasification and pyrolysis feedstock. Biomass Bioenergy 32(5), 460–467 (2008)
Williams, P.T.: The pyrolysis of rice husks in a thermogravimetric analyser and static batch reactor. Fuel 72, 151–159 (1993)
Sheeba, K.N., Babu, J.S.C., Jaisankar, S.: The reaction kinetics for coir pith pyrolysis in thermogravimetric analyzer. Energy Sources Part A: Recovery, Util. Environ. Eff. 32(19), 1837–1850 (2010)
Barneto, A.G., Carmona, J.A., Galvez, A., Conesa, J.A.: Effects of the composting and the heating rate on biomass gasification. Energy Fuels 23(2), 951–957 (2008)
Weerachanchai, P., Tangsathitkulchai, C., Tangsathitkulchai, M.: Characterization of products from slow pyrolysis of palm kernel cake and cassava pulp residue. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 28(12), 2262–2274 (2011)
Abdullah, S.S., Yusup, S., Ahmad, M.M., Ramli, A., Ismail, L.: Thermogravimetry study on pyrolysis of various lignocellulosic biomass for potential hydrogen production. Int. J. Chem. Biol. Eng. 3(3), 137–141 (2010)
Weerachanchai, P., Tangsathitkulchai, C.: Comparison of pyrolysis kinetic models for thermogravimetric analysis of biomass. J. Sci. Technol. 17(4), 387–400 (2010)
Raveendran, K., Ganesh, A., Khilar, K.C.: Pyrolysis characteristics of biomass and biomass components. Fuel 75(8), 987–998 (1996)
Aradhey, A.: India sugar annual (2012)
Thomas, G.V., Palaniswami, C., Prabhu, S.R., Gopal, M., Gupta, A.: Co-composting of coconut coir pith with solid poultry manure. Curr. Sci. 104(2), 245–250 (2013)
Gidde, M.R., Jivani, A.P.: Waste to wealth—Potential of rice husk in India a literature review. In International Conference on Cleaner Technologies and Environment Management, pp. 586–590, (2007)
Biofuels: http://www.chhattisgarhbiofuels.com/introduction.html
Lin, L., Yan, R., Liu, Y., Jiang, W.: In-depth investigation of enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass wastes based on three major components : cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 101(21), 8217–8223 (2010)
Chen, Y.M., Wan, J.Q., Ma, Y.W.: Effect of noncellulosic constituents on physical properties and pore structure of recycled fiber. Appita 62(4), 290–302 (2009)
Naik, S., Goud, V.V., Rout, P.K., Jacobson, K., Dalai, A.K.: Characterization of Canadian biomass for alternative renewable biofuel. Renew. Energy 35(8), 1624–1631 (2010)
Song, C., Hu, H., Zhu, S., Wang, G., Chen, G.: Nonisothermal catalytic liquefaction of corn stalk in subcritical and supercritical water. Energy Fuels 18(1), 90–96 (2004)
Di Blasi, C., Signorelli, G., Di Russo, C., Rea, G.: Product distribution from pyrolysis of wood and agricultural residues. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 38(6), 2216–2224 (1999)
Mansaray, K.G., Ghaly, A.E.: Determination of reaction kinetics of rice husks in air using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Sources 21(10), 899–911 (1999)
Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R., Mora-diez, N., Vivier-bunge, A.: A quantum chemical and classical transition state theory explanation of negative activation energies in OH addition to substituted ethenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 3715–3720 (2000)
Çulcuoğlu, E., Ünay, E., Karaosm, F.: Thermogravimetric Analysis of the rapeseed cake. Energy Sources 23(10), 889–895 (2001)
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to ‘Department of Science and Technology, New-Delhi, India’ for financially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goenka, R., Parthasarathy, P., Gupta, N.K. et al. Kinetic Analysis of Biomass and Comparison of its Chemical Compositions by Thermogravimetry, Wet and Experimental Furnace Methods. Waste Biomass Valor 6, 989–1002 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9402-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9402-3