Abstract
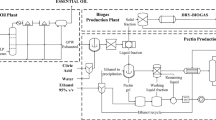
Citrus production generates a large quantities of residues which can be used in the production of intermediate compounds for the production of value added products which can be used in the synthesis of industrial fine chemicals, fragrances, flavorings, herbicides, pharmaceutical products among others. This work presents a study to increase the value added of essential oils obtained from orange peel producing p-cymene and pectin. Techno-economic and environmental assessments were developed demonstrating that computer-aided process engineering tools can be used to evaluate the feasibility of integrated processes. Two scenarios were evaluated (with and without electricity generation) obtaining 9.22 and 42.63 kg/h with purities of 97 and 81 % of p-cymene and pectin respectively. In the scenario with electricity generation, 99.81 kWh was obtained, covering all requirements in the process. The techno-economic analysis showed that the most appropriate scheme was that without electricity generation reaching a production cost of 5.27 and 3.53 USD/kg of p-cymene and pectin respectively. Environmental analysis reveals that the potential environmental impact was lowest for the scenario without electricity generation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
MinAgricultura: Anuario estadistico de frutas y hortalizas 2007–2011. http://www.agronet.gov.co (2012). Accessed 25 Aug 2013
Faostat: Crops production of oranges. http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=567#ancor (2014). Accessed 27 March 2014
Liu, Y., Shi, J., Langrish, T.A.G.: Water-based extraction of pectin from flavedo and albedo of orange peels. Chem. Eng. J. 120(3), 203–209 (2006)
Rojas, L.J.P., Perea, V.A., Stashenko, E.E.: Obtención de aceites esenciales y pectinas a partir de subproductos de jugos cítricos. Vitae 16(1), 110–115 (2009)
Bicu, I., Mustata, F.: Cellulose extraction from orange peel using sulfite digestion reagents. Bioresour. Technol. 102(21), 10013–10019 (2011)
Cerón, S.I., Cardona, A.C.: Evaluación del proceso integral para la obtención de aceite esencial y pectina a partir de cáscara de naranja. Ing. Ciencia 7, 65–86 (2011)
Lo Curto, R., Tripodo, M.M., Leuzzi, U., Giuffrè, D., Vaccarino, C.: Flavonoids recovery and SCP production from orange peel. Bioresour. Technol. 42(2), 83–87 (1992)
Luengo, E., Álvarez, I., Raso, J.: Improving the pressing extraction of polyphenols of orange peel by pulsed electric fields. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 17, 79–84 (2013)
Lagha, B.S., Madani, K.: Phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of orange varieties (Citrus sinensis L. and Citrus aurantium L.) cultivated in Algeria: peels and leaves. Ind. Crop Prod. 50, 723–730 (2013)
Allaf, T., Tomao, V., Besombes, C., Chemat, F.: Thermal and mechanical intensification of essential oil extraction from orange peel via instant autovaporization. Chem. Eng. Process. 72, 24–30 (2013)
Mira, B., Blasco, M., Subirats, S., Berna, A.: Supercritical CO2 extraction of essential oils from orange peel. J. Supercrit. Fluid 9(4), 238–243 (1996)
Rezzoug, S.A., Louka, N.: Thermomechanical process intensification for oil extraction from orange peels. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 10(4), 530–536 (2009)
Pourbafrani, M., Forgács, G., Horváth, I.S., Niklasson, C., Taherzadeh, M.J.: Production of biofuels, limonene and pectin from citrus wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 101(11), 4246–4250 (2010)
Grau, R.J., Zgolicz, P.D., Gutierrez, C., Taher, H.A.: Liquid phase hydrogenation, isomerization and dehydrogenation of limonene and derivatives with supported palladium catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 148(1–2), 203–214 (1999)
Gonçalves, J.A., Bueno, A.C., Gusevskaya, E.V.: Palladium-catalyzed oxidation of monoterpenes: highly selective syntheses of allylic ethers from limonene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 252(1–2), 5–11 (2006)
Mirata, M.A., Heerd, D., Schrader, J.: Integrated bioprocess for the oxidation of limonene to perillic acid with Pseudomonas putida DSM 12264. Process Biochem. 44(7), 764–771 (2009)
Martín, L.M.A., Yates, M., Martínez Domingo, M.J., Casal, B., Iglesias, M., Esteban, M., Ruiz-Hitzky, E.: Synthesis of p-cymene from limonene, a renewable feedstock. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 81(3–4), 218–224 (2008)
Martin, L.M.A., Yates, M., Rojo, E.S., Huerta Arribas, D., Aguilar, D., Ruiz Hitzky, E.: Sustainable p-cymene and hydrogen from limonene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 387(1–2), 141–146 (2010)
NIST: Base de Datos de Referencia Estándar del NIST Número 69. http://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ (2013). Accessed Nov 2012
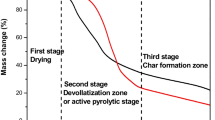
Aguiar, L., Márquez, M.F., Gonzalo, A., Sánchez, J.L., Arauzo, J.: Influence of temperature and particle size on the fixed bed pyrolysis of orange peel residues. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 83(1), 124–130 (2008)
Pandharipande, S., Makode, H.: Separation of oil and pectin from orange peel and study of effect of pH of extracting medium on the yield of pectin. J. Eng. Res. Stud. 3(2), 6–9 (2012)
Maldonado, C.Y., Salazar, O.S.M., Millones, C.C.E., Torres, M.E.V., Vásquez, C.E.R.: Extractión of pectin by acid hydrolysis method in fruit maushan (Vasconcellea weberbaueri (Harms) V.M. Badillo) from the district of San Miguel de Soloco, Amazon region. Aporte Santiaguino 3(2), 177–184 (2010)
NME: LyD considera arriesgado plantear desarrollo energético basado únicamente en shale gas. http://www.nuevamineria.com/revista/2013/05/27/lyd-considera-arriesgado-plantear-desarrollo-energetico-basado-unicamente-en-shale-gas/ (2013). Accessed 05 Aug 2013
ICIS: indicative chemical prices A–Z. http://www.icis.com/chemicals/channel-info-chemicals-a-z/ (2013). Accessed 25 July 2013
Alibaba: price of ethyl alcohol. http://www.alibaba.com/showroom/price-ethyl-alcohol.html (2013). Accessed 02 Sep 2012
Gregorini, V.A., Pasquevich, D., Laborde, M.: Price determination for hydrogen produced from bio-ethanol in Argentina. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 35(11), 5844–5848 (2010)
Zhang, Q-g, Bi, L-w, Zhao, Z-d, Chen, Y-p, Li, D-m, Gu, Y., Wang, J., Chen, Y-x, Bo, C-y, Liu, X-z: Application of ultrasonic spraying in preparation of p-cymene by industrial dipentene dehydrogenation. Chem. Eng. J. 159(1), 190–194 (2010)
Naghshineh, M., Olsen, K., Georgiou, C.A.: Sustainable production of pectin from lime peel by high hydrostatic pressure treatment. Food Chem. 136(2), 472–478 (2013)
Prakash, M.J., Sivakumar, V., Thirugnanasambandham, K., Sridhar, R.: Optimization of microwave assisted extraction of pectin from orange peel. Carbohyd. Polym. 97(2), 703–709 (2013)
Ma, E., Cervera, Q., Mejía, S.G.M.: Integrated utilization of orange peel. Bioresour. Technol. 44(1), 61–63 (1993)
Dasappa, S.: Potential of biomass energy for electricity generation in sub-Saharan Africa. Energy Sustain. Dev. 15(3), 203–213 (2011)
Labs, A.P.: Catalog personal scale power. http://gekgasifier.com/stage/wp-content/uploads/pdf/Catalog_053112_no_orderform.pdf (2013). Accessed 25 Aug 2013
Posada, J.A., Rincón, L.E., Cardona, C.A.: Design and analysis of biorefineries based on raw glycerol: addressing the glycerol problem. Bioresour. Technol. 111, 282–293 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dávila, J.A., Rosenberg, M. & Cardona, C.A. Techno-economic and Environmental Assessment of p-Cymene and Pectin Production from Orange Peel. Waste Biomass Valor 6, 253–261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-014-9339-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-014-9339-y