Abstract
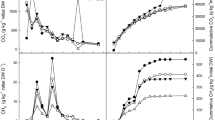
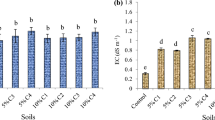
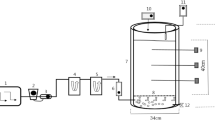
The application rate of poultry manure as organic fertilizer is restricted due to its low C/P and N/P ratio. This research was set up to find out optimal feedstock composition for composting chicken manure in order to create a soil improver with a higher value as organic fertilizer, and to assess the effects of this process on P availability in the end products. The research is based on two compost experiments with three treatments each, and the chicken manure composts were compared with the end products of green waste compost used as bedding material in chicken houses, centrally processed chicken manure and a stockpiled mixture of green waste compost and chicken manure. In the first compost trial, feedstock materials were compared for composting with fresh chicken manure. The chicken manure compost with 42.5 vol% bark in the feedstock had the highest quality as soil improver in terms of organic matter content, C/P ratio, C/N ratio and stability. Results of the second compost trial indicate that 10 vol% of fresh chicken manure is the upper limit in small-scale on-farm windrow composting above which nutrient losses become too high and the N/P ratio of the obtained fertilizer becomes too low. Stability of the product (expressed as oxygen uptake rate) had a major effect on P availability in the compost. Blending the chicken manure compost with biochar based on holm oak resulted in a more than proportional decrease in easily available P in the biochar-blended compost. P in poultry manure can be recycled through composting and be applied as an organic fertilizer with optimal nutrient ratio and organic matter content when appropriate feedstock materials are selected and the amount of fresh manure in the feedstock mixture is restricted.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Preusch, P.L., Adler, P.R., Sikora, L.J., Tworkoski, T.J.: Nitrogen and phosphorus availability in composted and uncomposted poultry litter. J. Environ. Qual. 31, 2051–2057 (2002)
Toor, G.S., Haggard, B.E.: Phosphorus and trace metal dynamics in soils amended with poultry litter and granulates. Soil Use Manage. 25, 409–418 (2009)
Leconte, M.C., Mazzarino, M.J., Satti, P., Crego, M.P.: Nitrogen and phosphorus release from poultry manure composts: the role of carbonaceous bulking agents and compost particle sizes. Biol. Fert. Soils 47, 897–906 (2011)
Ranatunga, T.D., Seshadri, S.R., Taylor, R.W.: Phosphorus distribution in soil aggregate size fractions in a poultry litter applied soil and potential environmental impacts. Geoderma 192, 446–452 (2013)
Larney, F.J., Olson, A.F., Miller, J.J., DeMaere, P.R., Zvomuya, F., McAllister, T.A.: Physical and chemical changes during composting of wood chip-bedded and straw-bedded beef cattle feedlot manure. J. Environ. Qual. 37, 725–735 (2008)
Dias, B.O., Silva, C.A., Higashikawa, F.S., Roig, A., Sanchez-Monedero, M.A.: Use of biochar as bulking agent for the composting of poultry manure: effect on organic matter degradation and humification. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 1239–1246 (2010)
Jindo, K., Suto, K., Matsumoto, K., Garcia, C., Sonoki, T., Sanchez-Monedero, M.A.: Chemical and biochemical characterisation of biochar-blended composts prepared from poultry manure. Bioresour. Technol. 110, 396–404 (2012)
Hass, A., Gonzalez, J.M., Lima, I.M., Godwin, H.W., Halvorson, J.J., Boyer, D.G.: Chicken manure biochar as liming and nutrient source for acid Appalachian soil. J. Environ. Qual. 41, 1096–1106 (2012)
Mishra, A., Cabrera, M.L., Rema, J.A.: Phosphorus fractions in poultry litter as affected by flue-gas desulphurization gypsum and litter stacking. Soil Use Manage. 28, 27–34 (2012)
Brennan, R.B., Fenton, O., Rodgers, M., Healy, M.G.: Evaluation of chemical amendments to control phosphorus losses from dairy slurry. Soil Use Manage. 27, 238–246 (2011)
Bustamante, M.A., Alburquerque, J.A., Restrepo, A.P., de la Fuente, C., Paredes, C., Moral, R., Bernal, M.P.: Co-composting of the solid fraction of anaerobic digestates, to obtain added-value materials for use in agriculture. Biomass Bioenerg. 43, 26–35 (2012)
Felton, G.K., Carr, L.E., Prigge, C.E., Bouwkamp, J.C.: Nitrogen and phosphorous dynamics in cocomposted yard trimmings and broiler litter. Compost Sci. Util. 12, 349–355 (2004)
Boxall, A.B., Johnson, P., Smith, E.J., Sinclair, C.J., Stutt, E., Levy, L.S.: Uptake of veterinary medicines from soils into plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 2288–2297 (2006)
Jones-Lepp, T.L., Sanchez, C.A., Moy, T., Kazemi, R.: Method development and application to determine potential plant uptake of antibiotics and other drugs in irrigated crop production systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010(58), 11568–11573 (2010)
Dolliver, H., Kumar, K., Gupta, S.: Sulfamethazine uptake by plants from manure-amended soil. J. Environ. Qual. 36, 1224–1230 (2007)
Broekaert, N., Daeseleire, E., Delezie, E., Vandecasteele, B., De Beer, T., Van Poucke, C.: Can the use of coccidiostats in poultry breeding lead to residues in vegetables? An experimental study. J. Agric. Food Chem. doi:10.1021/jf304149d
Dolliver, H., Gupta, S., Noll, S.: Antibiotic degradation during manure composting. J. Environ. Qual. 37, 1245–1253 (2008)
Ramaswamy, J., Prasher, S.O., Patel, R.M., Hussain, S.A., Barrington, S.F.: The effect of composting on the degradation of a veterinary pharmaceutical. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 2294–2299 (2010)
Steel, H., Vandecasteele, B., Willekens, K., Sabbe, K., Moens, T., Bert, W.: Nematode communities and macronutrients in composts and compost-amended soils as affected by feedstock composition. Appl. Soil Ecol. 61, 100–112 (2012)
Frederickson, J., Howell, G., Hobson, A.M.: Effect of pre-composting and vermicomposting on compost characteristics. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 43, S320–S326 (2007)
Tognetti, C., Mazzarino, M.J., Laos, F.: Compost of municipal organic waste: effects of different management practices on degradability and nutrient release capacity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 40, 2290–2296 (2008)
Leconte, M.C., Mazzarino, M.J., Satti, P., Iglesias, M.C., Laos, F.: Co-composting rice hulls and/or sawdust with poultry manure in NE Argentina. Waste Manage. 29, 2446–2453 (2009)
Gabrielle, B., Da-Silveira, J., Houot, S., Francou, C.: Simulating urban waste compost effects on carbon and nitrogen dynamics using a biochemical index. J. Environ. Qual. 33, 2333–2342 (2004)
Francou, C., Linères, M., Derenne, S., Villio-Poitrenaud, M.L., Houot, S.: Influence of green waste, biowaste and paper-cardboard initial ratios on organic matter transformations during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 8926–8934 (2008)
Lashermes, G., Barriuso, E., Le Villio-Poitrenaud, M., Houot, S.: Composting in small laboratory pilots: performance and reproducibility. Waste Manage. 32, 271–277 (2012)
Paradelo, R., Moldes, A.B., Barral, M.T.: Evolution of organic matter during the mesophilic composting of lignocellulosic winery wastes. J. Environ. Manage. 116, 18–26 (2013)
Blanco, M.-J., Almendros, G.: Chemical transformation, phytotoxicity and nutrient availability in progressive composting stages of wheat straw. Plant Soil 196, 15–25 (1997)
Chalhoub, M., Garnier, P., Coquet, Y., Mary, B., Lafolie, F., Houot, S.: Increased nitrogen availability in soil after repeated compost applications: use of the PASTIS model to separate short and long-term effects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 65, 144–157 (2013)
Borchard, N., Prost, K., Kautz, T., Moeller, A., Siemens, J.: Sorption of copper (II) and sulphate to different biochars before and after composting with farmyard manure. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 63, 399–409 (2012)
Van Soest, P.J., Robertson, J.B., Lewis, B.A.: Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 74, 3583–3597 (1991)
Grigatti, M., Dios Perez, M., Blok, W., Ciavatta, C., Veeken, A.: A standardized method for the determination of the intrinsic carbon and nitrogen mineralization capacity of natural organic matter sources. Soil Biol. Biochem. 39, 1493–1503 (2007)
Vandecasteele, B., Willekens, K., Zwertvaegher, A., Degrande, L., Tack, F.M.G., Du Laing, G.: Effect of composting on the Cd, Zn and Mn content and fractionation in feedstock mixtures with wood chips from a short-rotation coppice and bark. Waste Manage. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2013.06.014
Gagnon, B., Demers, I., Ziadi, N., Chantigny, M.H., Parent, L.-E., Forge, T.A., Larney, F.J., Buckley, K.E.: Forms of phosphorus in composts and in compost-amended soils following incubation. Can. J. Soil Sci. 92, 711–721 (2012)
Garcia-Albacete, M., Martin, A., Cartagena, M.C.: Fractionation of phosphorus biowastes: characterisation and environmental risk. Waste Manage. 32, 1061–1068 (2012)
Du Laing, G., Bontinck, A., Samson, R., Vandecasteele, B., Vanthuyne, D.R.J., Meers, E., Lesage, E., Tack, F.M.G., Verloo, M.G.: Effect of decomposing litter on the mobility and availability of metals in the soil of a recently created floodplain. Geoderma 147, 34–46 (2008)
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the lab and field technicians of ILVO for their help during the composting trials, and for executing the chemical analyses. This research was partly financially supported by the Flemish Government - Sustainable Agricultural Development Division (ADLO), and partly executed within the FERTIPLUS project. The project FERTIPLUS (Grant Agreement No 289853) is co-funded by the European Commission, Directorate General for Research and Innovation, within the 7th Framework Programme of RTD, Theme 2—Biotechnologies, Agriculture & Food. The views and opinions expressed in this paper are purely those of the writers and may not in any circumstances be regarded as stating an official position of the European Commission. We are grateful to Jos Arits and the Op de Beeck group for their logistic support, and to Antonio Quero Alba from PROININSO S.A. for providing the biochar based on holm oak.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vandecasteele, B., Reubens, B., Willekens, K. et al. Composting for Increasing the Fertilizer Value of Chicken Manure: Effects of Feedstock on P Availability. Waste Biomass Valor 5, 491–503 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-013-9264-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-013-9264-5