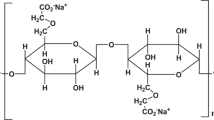
Abstract
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is an important industrial polymer with a wide range of applications in flocculation, drag reduction, detergents, textiles, paper, foods, drugs, and oil well drilling operation. The various properties of CMC depend upon three factors: molecular weight of the polymer, average number of carboxyl content per anhydroglucose unit (AGU) i.e. degree of substitution and also on the distribution of carboxyl substituent’s along the polymer chains. The cellulose extracted from corn cobic lignocellulosic waste biomass was converted to CMC by etherification process using sodium hydroxide and monochloroacetic acid (MCA) under heterogeneous condition. The carboxymethylation reaction was optimized against the NaOH concentration, monochloroacetic acid concentration, reaction temperature and time. The degree of substitution (DS) was analyzed with respect to the reaction conditions using chemical method. The produced CMC was characterized by using Fourier transform infrared spectra and X-ray diffractogram. The optimized conditions to yield CMC with high DS of 1.18 are; concentration of aqueous NaOH 3.25 mol/AGU, 25 % (w/v); concentration of MCA, 2.4 mol/AGU; reaction time, 3.0 h and temperature, 60 °C with isopropyl alcohol as the supporting solvent medium.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkalow, D.G., Young, R.A.: Cellulose derivatives derived from pulp and paper mill sludge. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 5, 293–312 (1985)
Klemm, D., Heublein, B., Fink, H.-P., Bohn, A.: Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. 44, 3358–3393 (2005)
Heinze, T., Koschella, A.: Carboxymethyl ethers of cellulose and starch-a review. Macromol. Symp. 223, 130–139 (2005)
Feddersen, R.L., Thorp, S.N.: Sodium carboxymethylcellulose. In: Whistler, R.L., BeMiller, J.N. (eds.) Industrial Gums and their Derivatives, pp. 537–578. Academic Press, New York (1993)
Sandford, P.A., Baird, J.: Industrial utilization of polysaccharides. In: Aspinall, G.O. (ed.) The Polysaccharides, pp. 411–490. Academic Press, Reading MA (1983)
Keller, J.D.: Sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC). In: Gliksman, M. (ed.) Food Hydrocolloids, Vol. 3, pp. 45–104. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press (1986)
Heinze, T., Pfeiffer, K.: Studies on the synthesis and characterization of carboxymethylcellulose. Die Angewandte Makromolekulare Chemie 266, 37–45 (1999)
Ho, F.F.-L., Klosiewicz, D.W.: Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry for determination of substituents and their distribution in carboxymethylcellulose. Anal. Chem. 52, 913–916 (1980)
Reuben, J., Conner, H.T.: Analysis of the carbon-13 NMR spectrum of hydrolyzed O-(carboxymethyl)cellulose: monomer composition and substitution patterns. Carbohydr. Res. 115, 1–13 (1983)
Barba, C., Montane, D., Rinaudo, M., Farriol, X.: Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethylcelluloses (CMC) from non-wood fibers I. Accessibility of cellulose fibers and CMC synthesis. Cellulose 9, 319–326 (2002)
Guo, Z., Xing, R., Liu, S., Zhong, Z., Li, P.: Synthesis and hydroxyl radicals scavenging activity of quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 73, 173–177 (2008)
He, X., Wu, S., Fua, D., Nia, J.: Preparation of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose from paper sludge. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 84, 427–434 (2009)
Togrul, H., Arslan, N.: Production of carboxymethyl cellulose from sugar beet pulp cellulose and rheological behaviour of carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 54, 73–82 (2003)
Ramos, L.A., Frollini, E., Heinze, Th.: Carboxymethylation of cellulose in the new solvent dimethyl sulfoxide/tetrabutylammonium fluoride. Carbohydr. Polym. 60, 259–267 (2005)
Kirk, R.E., Othmer, D.F.: Cellulose Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, Vol. 4, pp. 593–683. Wiley, New York (1997)
Methacanon, P., Chaikumpollert, O., Thavorniti, P., Suchiva, K.: Hemicellulosic polymer from Vetiver grass and its physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 54, 335–342 (2003)
Dolz, M., Jiménez, J., Hernández, M.J., Delegido, J., Casanovas, A.: Flow and thixotropy of non-contaminating oil drilling fluids formulated with bentonite and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 57, 294–302 (2007)
Fijan, R., Basile, M., Turk, S.S., Agar, Z.M., Zigon, M., Lapasin, R.: A study of rheological and molecular weight properties of recycled polysaccharides used as thickeners in textile printing. Carbohydr. Polym. 76, 8–16 (2009)
Mohanty, A.K., Simmons, C.R., Wiener, M.C.: Inhibition of tobacco etch virus protease activity by detergents. Protein Exp Purif 27, 109–114 (2003)
Amin, M.C.I., Soom, R.M., Ahmad, I., Lian, H.H.: Carboxymethyl cellulose from palm oil empty fruit bunch–their properties and use as a film coating agent. J Sains Kesihatan Malaysia 4, 53–62 (2007)
Vieira, M.C., Heinzel, Th., Antonio-Cruz, R., Mendoza-Martinez, A.M.: Cellulose derivatives from cellulosic material isolated from Agaveb lechuguilla and fourcroydesCellulose. Cellulose 9, 203–212 (2002)
Ruzene, D.S., Gonçalves, A.R., Teixeira, J.A., de Amorim, M.T.: Carboxymethylcellulose obtained by ethanol/water organosolv process under acid conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 137–140, 573–582 (2007)
Heydarzadeh, H.D., Najafpour, G.D., Nazari-Moghaddam, A.A.: Catalyst-free conversion of alkali cellulose to fine carboxymethyl cellulose at mild conditions. World Appl Sci J 6, 564–569 (2009)
Jahan, I.A., Sultana, F., Islam, M.N., Hossain, M.A., Abedin, J.: Studies on indigenous cotton linters for preparation of carboxymethyl cellulose. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 42, 29–36 (2007)
Varshney, V.K., Gupta, P.K., Naithani, S., Khullar, R., Bhatt, A., Soni, P.L.: Carboxymethylation of α-cellulose isolated from Lantana camara with respect to degree of substitution and rheological behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 63, 40–45 (2006)
Yasar, F., Togrul, H., Arslan, N.: Flow properties of cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose from orange peel. J. Food Eng. 81, 187–199 (2007)
Jahan, I.A., Rahman, A.H.M.M.: Studies on preparation of cobalt carboxymethyl cellulose from agricultural wastes. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 41, 159–166 (2006)
Pushpamalar, V., Langford, S.J., Ahmad, M., Lim, Y.Y.: Optimization of reaction conditions for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose from sago waste. Carbohydr. Polym. 64, 312–318 (2006)
Barai, B.K., Singhal, R.S., Kulkarni, P.R.: Optimization of a process for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose from water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes). Carbohydr. Polym. 32, 229–231 (1997)
Sakaguchi, Y., Tsutsumi, M., Kaji, A., Abe, S.: Structural changes in cellulose fibers treated with sodium hydroxide or liquid ammonia evaluated by relaxation behavior of solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Sen’i Gakkaishi (In Japanese) 58, 321–326 (2002)
Kumar, S., Upadhyaya, J.S., Negi, Y.S.: Preparation of nanoparticles from corn cobs by chemical treatment methods. BioResources 5, 1292–1300 (2010)
Colom, X., Carrillo, F., Nogues, F., Garriga, P.: Structural analysis of photodegraded wood by means of FTIR spectroscopy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 80, 543–549 (2003)
Adebajo, M.O., Frost, R.L.: Infrared and 13C MAS nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study of acetylation of cotton. Spectrochimica Acta Part A 60, 449–453 (2004)
Kondo, T.: The assignment of IR absorption bands due to free hydroxyl groups in cellulose. Cellulose 4, 281–292 (1997)
Ivanova, N.V., Korolenko, E.A., Korolik, E.V., Zhbankov, R.G.: IR spectrum of cellulose. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 51, 847–851 (1989)
Fengel, D., Wegener, G.: Wood: Chemistry, Ultrastructure, Reactions. Walter de Gruyter & Co, Berlin (1989)
Singh, R.K., Khatri, O.P.: A scanning electron microscope based new method for determining degree of substitution of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. J. Microsc. 246, 43–52 (2012)
Khalil, M.I., Hasem, A., Habeish, A.: Carboxymethylation of maize starch. Starch/Starke 42, 60–63 (1990)
Bhattacharyya, D., Singhal, R.S., Kulkarni, P.R.: A comparative account of conditions for synthesis of sodium carboxymethyl starch from corn and amaranth starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 27, 247–253 (1995)
Hebeish, A., Abou-Zied, N.Y., Waly, A., Higazy, A.: Chemical modification of flax cellulose via etherification, esterification, and crosslinking reactions. Cellulose Chem Technol 22, 591–605 (1984)
Tijsen, C.J., Kolk, H.J., Stamhuis, E.J., Beenackers, A.A.: An experimental study on the carboxymethylation of granular potato starch in non-aqueous media. Carbohydr. Polym. 45, 219–226 (2001)
Youssef, M.A.M., Nada, A.M.A., Ibrahem, A.A.: Effect of thermal treatment on the reactivity of cellulose towards carboxymethylation. Cellulose Chem Technol 23, 505–511 (1989)
Lin, X., Qu, T., Qi, S.: Kinetics of the carboxymethylation of cellulose in the isopropyl alcohol system. Acta Polym. 41, 220–222 (1990)
Acknowledgments
We kindly acknowledge the Director, IIP for his kind permission to publish these results. We thank the analytical division of Institute for providing analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R.K., Singh, A.K. Optimization of Reaction Conditions for Preparing Carboxymethyl Cellulose from Corn Cobic Agricultural Waste. Waste Biomass Valor 4, 129–137 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-012-9123-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-012-9123-9