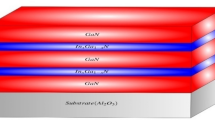
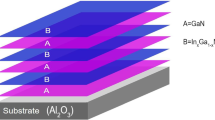
Abstract
A decrease in thermal conductivity (k) via electric field in superlattices (SL) is one of the recent attempts to get better thermoelectric efficiency. In this work, we report that interfacial electric (IFE) field of GaN/InxAl1−xN/GaN SL arising from crystal asymmetry and lattice mismatch strain can be used to decrease k of the SL. Theoretical results demonstrate that IFE field modifies acoustic phonon properties through elastic modulus and phonon velocity owing to inverse piezoelectric effect. High phonon velocity and size effect enhance interfacial phonon scattering, resulting into irregular change in specific heat at interfaces. This caused higher acoustic mismatch between layers and boosted thermal boundary resistance (TBR). Accordingly, k of SL is decreased, which can be controlled by IFE field engineering via indium composition and layer size. Room-temperature cross-plan thermal conductivities (kcp) in the presence (absence) of IFE field for GaN (12 nm)/InxAl1−xN(6 nm)/GaN SL (x = 0.1, 0.3 0.5, 0.7 and 0.9) are found to be 2.80 (3.46), 3.00 (3.42), 2.00 (4.10), 3.55 (3.98) and 3.99 (4.52) W/(mK), respectively, which demonstrates more than 20% decrease.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data can be available on reasonable request from corresponding author.
References
R Butte et al J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40 6328 (2007)
D Jena et al Japn. J. Appl. Phys. 58 SC0801 (2019)
E P Pokatilov, D L Nika and A A Balandin Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 113508 (2006)
A Sztein, J Haberstroh and J E Bowers J. Appl. Phys. 113 183707 (2013)
S Yamaguchi, R Izaki and N Kaiwa Phys. Lett. 84 5344 (2004)
A Sztein and J E Bowers J. Appl. Phys. 112 083716 (2012)
A Filatova-Zalewska et al. Nanotechnology 32 075707 (2021)
A Spindlberger, D Kysylychyn, L Thumfart, R Adhikari, A Rastelli and A Bonanni Appl. Phys. Lett. 118 062105 (2021)
Y K Koh, Y Cao, D G Cahill and D Jena Adv. Funct. Mater. 19 1 (2009)
Y Wang and C Liebig Phys. Lett. 97 083103 (2010)
R Cheaito et al Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 195901 (2012)
R P Chen, N A Katcho, J P Feser, W Li, M Glaser, O G Schmidt and D G Cahill Rev. Lett. 111 115901 (2013)
Q Zhang, Z Xiong and J Jiang J. Mater. Chem 21 12398 (2011)
J Zhang, H Tong and G Liu Phys. Lett. 109 053706 (2011)
H Tong, J Zhang, G Liu and J A Herbsommer Phys. Lett. 97 112105 (2010)
C Guthy, C Y Nam and J E Fischer J. Appl. Phys. 103 064319 (2008)
G Qin, Z Qin, S Yue, Q Yand and M Hu Nanoscale 9 7227 (2017)
Y Quan, S Y Yueand and B Liao Appl. Phys. Lett. 118 162110 (2021)
F Zhang et al. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11 519 (2016)
M Gladysiewicz, L Janicki, M Siekacz and G Cywinski Phys. Lett. 107 262107 (2015)
O Ambacher J. Phys. Condens. Matter 14 3399 (2002)
S K Sahoo, B K Sahoo and S Sahoo J. Appl. Phys. 114 163501 (2013)
J Zou, D Kotchetkov and A Balandin J. Appl. Phys. 92 2534 (2002)
J Callaway Phys. Rev. 113 1046 (1959)
S Mei and I Knezevic J Appl. Phys. 118 175101 (2015)
F X Alverez, J Alvarez-quintana and D Jou J. Appl. Phys. 107 084303 (2010)
M V Simkin and G D Mahan Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 927 (2000)
S S Sahu and B K Sahoo Thin Solid Films 684 59 (2019)
J W Pomeroy, M Kuball, H Lu and W J Schaff Phys. Lett. 86 223501 (2005)
N Domenech-Amador, R Cusco and L Artus Rev. B 83 245203 (2011)
C A Polanco and L Lindsay Phys. Rev. B 99 075202 (2019)
T L Bougher and L Yates Eng. 20 22 (2016)
S S Sahu and B K Sahoo Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136 1160 (2021)
S S Sahu and B K Sahoo J. Alloys and Comp. 898 162927 (2022)
W Kim, J Zide, A Gossard, D Klenov and S Stemmer Rev. Lett. 96 045901 (2006)
H K Lee and J S Yu Appl Phys. B 106 619 (2012)
J Ju et al. AIP Adv. 6 045216 (2016)
L Thumfart, J Carrete, B Vermeersch, N Ye, T Truglas, J Feser and H Groiss J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51 014001 (2018)
M S Vitiello Phys. Lett. 90 431 (2007)
M N Luckyanova et al. Nano Lett. 13 3973 (2013)
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (JM) acknowledges with thanks to NIT Raipur, Govt. of India, for an award of fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Equally contributed by authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mehra, J.K., Sahoo, B.K. Reduction of thermal conductivity in GaN/InxAl1−xN/GaN Superlattice under the influence of interfacial electric field. Indian J Phys 97, 3467–3481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02680-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02680-5