Abstract
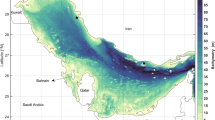
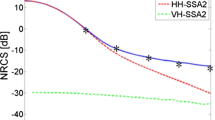
The brightness temperature is the principle parameter detected by passive microwave radiometers. The radio frequency interference at L-band radiometers (e.g., SMOS, Aquarius and SMAP) impacts the quality of brightness temperature detection in many parts of the world such as the Middle East and the Persian Gulf. In the present work, vertical and horizontal polarizations of brightness temperature over flat surface water of Persian Gulf at L-band were calculated by using physical computations and an empirical model. For this purpose, Rayleigh–Jeans radiation law and Fresnel reflection equations were used and complex permittivity was calculated by Blanch and Aguasca model. Input data for the model calculations are temperature and salinity that were provided from World Ocean Atlas 2013. The calculations showed that the brightness temperature distribution in the Persian Gulf experiences significant spatial and seasonal variations. At nadir incidence angle, the vertical and horizontal components of brightness temperature over the Persian Gulf vary in the range 90.5–96.5 °k and 85.5–90.2 °k, respectively. At off-nadir incidence angle, the temporal variability pattern of brightness temperature horizontal polarization is similar to its vertical counterpart but the difference between them significantly increases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
F Jianqing, Z Yonglio, B Wei, Z Yongchun, L Chin J. Geochem.29 204 (2010)
D Kumar Sarma, M Konwar, S Sharma Indian J. Radio Space Phys.35 (2006) 259 (2006)
Y Soldo, D M Le Vine, P de Matthaeis, P Richaume IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.55 7 (2017)
P N Mohammed, M Aksoy, J R Piepmeier, J T Johnson, A Bringer IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 54 10 (2016)
D M Le Vine, P De Matthaeis IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 11 10 (2014).
R Oliva, E Daganzo, Y H Kerr, S Mecklenburg, S Nieto, P Richaume, C Gruhier IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 50 5 (2012).
L A Klein, C T Swift IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag.25 104 (1977)
S Blanch, A Aguasca Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 04): Proc. 2 p 1362 (2004)
W J Ellison et al. Radio Sci.33 639 (1998)
J P Hollinger IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron9 165 (1971)
A Stogryn J. Geophys. Res.77 1658 (1972)
T Wilheit IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron.17 244 (1979)
F J Wentz J. Geophys. Res.88 1892 (1983)
A Guissard, P Sobieski Int. J. Remote Sens.8 1607 (1987)
C L Rufenach, R A Shuchman Int. J. Remote Sens.13 957 (1992)
L Shubo, J Yanxia, Q Zhen, W Enbo J. Ocean Univ. China14 38 (2015)
S Hassanzadeh, F hosseinibalam, A Rezaei-Latifi Appl. Math. Model.35 1512 (2011)
F Hosseinibalam, S Hassanzadeh, A Rezaei-Latifi Appl. Math. Model.35 5884 (2011)
S A Swift, A S Bower J. Geophys. Res.108 (2003)
F Wentz J. Geophys. Res.80 3441 (1975)
W Nordberg, J Conaway, D B Ross, T Wilheit J. Atmos. Sci.,38 429 (1971)
P G Thoppil, P J Hogan Deep-Sea Res. I 57 (2010) 946–955
R A Locarnini et al. World Ocean Atlas 2013, Temperature 1 (eds.) S Levitus and A Mishonov NOAA Atlas NESDIS 73, p 40 (2013)
M M Zweng World Ocean Atlas 2013 Salinity. 1 (eds.) S Levitus and A Mishonov NOAA Atlas NESDIS 74, p 39 (2013)
R.Michael Reynolds Mar. Pollut. Bull.27 35 (1993)
A Rezaei-Latifi Appl. Math. Model.40 1069 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to Dr. Ali Reza Nafarzadegan and Dr. Mohsen Ebrahimi-Khusfi for their valuable advices and keen insights.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei-Latifi, A. Computation of the vertical and horizontal polarizations of brightness temperature of flat surface water over the Persian Gulf at the L-Band. Indian J Phys 94, 293–301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01464-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01464-0