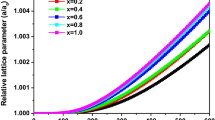
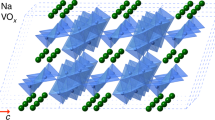
Abstract
We present here an unexpected relationship to predict the structural phase transition directly and unambiguously from the Bragg angle versus ionization energy plot. We first expose the changes to the F-band optical absorption energy peak in alkali halides so as to justify why the Bragg angle (2\(\theta\)) versus ionization energy plots for both anions and cations can be used to detect structural phase transition during substitutional doping or systematic changes to chemical composition. In principle, this plot can be extended to predict structural phase transition for all types of solid via doping, which includes cuprates, manganites, topological insulators and cathode materials used in lithium-ion batteries, but, unfortunately, not Fermi metals. The said plot can be implemented in all X-ray diffractometers as an additional feature to predict structural phase transition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A D Arulsamy Ionization Energy Theory: Formalism (Seattle : CreateSpace) (2016)
A D Arulsamy Ionization Energy Theory II: Interdisciplinary Science (Seattle : CreateSpace) (2017)
W L Bragg Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 17 43 (1913)
A H Compton Phys. Rev. 21 483 (1923)
C V Raman Indian J. Phys. 2 387 (1928)
C V Raman and K S Krishnan Indian J. Phys. 2 399 (1928)
C V Raman and K S Krishnan Nature 121 501 (1928)
C V Raman Nature 121 619 (1928)
A D Arulsamy Indian J. Phys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01394-x (2019)
A D Arulsamy Phys. Scr. 94 055803 (2019)
S Pancharatnam Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A 44 247 (1956)
A D Arulsamy Optik https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.11.061 (2019)
J Rout and R N P Choudhary Indian J. Phys. 92 575 (2018)
R V K Mangalam and A Sundaresan J. Chem. Sci. 99 118 (2006)
U Farid, H U Khan, M Avdeev, S Injac, J. Solid State Chem. 258 118 (2018)
A Jafari, S F Shayesteh, Indian J. Phys. 89 551 (2015)
W B Aribia, M Abdelmouleh, J. Chem. Sci. 124 403 (2012)
S Raju and E Mohandas J. Chem. Sci. 122 83 (2010)
R M Sebastian and E M Mohammed Indian J. Phys. 90 1397 (2016)
D S V Thampi, J. Solid State Chem. 255 121 (2017)
C Xing, J Li, H Chen, H Qiao, J Yang, H Dong, H Sun, J Wang, X Yin, Z M Qi and F Shi RSC Adv. 7 35305 (2017)
H Qiao, H Sun, J Li, H Chen, C Xing, J Yang, H Dong, J Wang, X Yin, Z M Qi and F Shi Scientific Rep. 7 13336 (2017)
D Roy, S Mandal, C K De, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 13336 (2018)
W B H Othmen, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 52 46 (2016)
W Li, X Wu, J Chen, Y Gong, Sens. Actuat. B 253 144 (2017)
B Sambandam, T Muthukumar, S Arumugam, P L Paulose and P T Manoharan RSC Adv. 4 22141 (2014)
A N Radhakrishnan, P P Rao, S K Mahesh, Inorg. Chem. 51 2409 (2012)
B Sambandam, S E Muthu, S Arumugam and P T Manoharan RSC Adv. 3 5184 (2013)
D S V Thampi, P P Rao and A N Radhakrishnan RSC Adv. 4 12321 (2014)
S Kaniyankandy, J. Mater. Chem. C1 2755 (2013)
A Ricci, N Poccia, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 24 1201 (2011)
S Margadonna, Y Takabayashi, M T McDonald, M Brunelli, G Wu, R H Liu, Phys. Rev. B79 014503 (2009)
M Calamiotou, D Lampakis, N D Zhigadlo, S Katrych, J Karpinski, A Fitch, P Tsiaklagkanos and E Liarokapis, Phys. C: Supercond. Appl.527 55 (2015)
N V Chandra Shekar, V Kathirvel and P Ch Sahu Indian J. Phys. 84 485 (2010)
F Oumelaz, O Nemiri, A Boumaza, S Ghemid, H Meradji, Indian J. Phys. 92 705 (2017)
R A Cowley and S M Shapiro J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.75 111001 (2006)
F Jona and G Shirane Ferroelectric Crystals (Oxford : Pergamon Press) (1962)
G Shirane Rev. Mod. Phys. 45 437 (1974)
M Fujimoto The Physics of Structural Phase Transitions (Berlin : Springer) (2005)
D Saritha J. Chem. Sci. 130 7 (2018)
S R S Prabaharan, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 7 A416 (2004)
K M Begam, M S Michael, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 7 A242 (2004)
K M Begam and S R S Prabaharan J. Power Sources 159 319 (2006)
A Manthiram and J B Goodenough J. Power Sources 26 403 (1989)
S R S Prabaharan, M S Michael, J. Electroanal. Chem. 570 107 (2004)
C Kittel Introduction to Solid State Physics (New York : Wiley) (1976)
J H Schulman and W D Compton Color Centers in Solids (Oxford : Pergamon) (1962)
A I Popov, Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 268 3084 (2010)
M P Tosi Solid State Phys. 16 1 (1964)
L Frevel Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 14 687 (1942)
R K Dowson and D Poole Phys. Status Solidi 35 95 (1969)
E A Kotomin and A I Popov Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 141 1998 (1998)
R Pandey, J. Mater. Res. 3 1362 (1988)
N Gemechu and T Abebe Ukr. J. Phys. 63 182 (2018)
P Sritowong, Ukr. J. Phys. 63 276 (2018)
Y Wang, J Xiao, H Zhu, Y Li, Y Alsaid, K Y Fong, Y Zhou, S Wang, W Shi, Y Wang, A Zettl, E J Reed and X Zhang Nature 550 487 (2017)
D B Sirdeshmukh, L Sirdeshmukh and K G Subhadra Alkali Halides: A Handbook of Physical Properties (Berlin : Springer) (2001)
A D Arulsamy RSC Adv. 6 109259 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Sebastiammal Savarimuthu and the late Arulsamy Innasimuthu (1941–2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arulsamy, A.D. Structural phase transition determined from the Bragg angle versus ionization energy plot. Indian J Phys 94, 391–396 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01454-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01454-2