Abstract
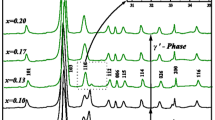
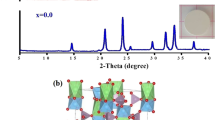
Synthesis and characterization of Bi2V1−xTixO5.5−(x/2)−δ (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.150) was done. For the present system, the lower limit of Ti required for near-complete tetragonal phase stabilization has been found to be x = 0.125. The optimum values of ionic conductivity were obtained for the compositions; Bi2V0.875Ti0.125O5.4375 and Bi2V0.9Ti0.1O5.45 at 300 °C and 600 °C, respectively. Interestingly, two peaks have been observed in frequency versus dielectric loss spectra for parent compound, which is in \(\alpha\)-orthorhombic phase, as well as for tetragonal phase stabilized specimens with compositions x ≥ 0.125 at temperatures below 300 °C. No such peaks have been found in \(\beta\)-orthorhombic (x = 0.085) as well as in mixed tetragonal and orthorhombic (x = 0.1 and 0.1125) phases. Thus, we propose that frequency-dependent dielectric loss spectra can be used to qualitatively distinguish \(\alpha\) and \(\gamma\)-phases from \(\beta\)-phase in BITIVOX system and it is the central result of this work.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
B Singh, S Ghosh, S Aich and B Roy J. Power Sources 339 103 (2017).
D S Khaerudini, G Guan, P Zhang, X Hao and A Abudula Rev. Chem. Eng. 30 539 (2014).
S Lazure, Ch Vernochet, R N Vannier, G Nowogrocki and G Mairesse Solid State Ionics 90 117 (1996).
F Krok, I Abrahams, M Malys, W Bogusz, J R Dygas, J A G Nelstrop and A J Bush Solid State Ionics 136–137 119 (2000).
J Chmielowiec, G Pa´Sciak and P Bujło J. Alloys Compd. 451 676 (2008).
F Krok, I Abrahams, D J Bangobango, W Bogusz and J A G Nelstrop Solid State Ionics 86–88 261 (1996).
L F Brum Malta and M E Medeiro J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 87 883 (2007).
S Beg, S Hafeez and N A S Al-Areqi Philos. Mag. 90 4579 (2010).
S Beg and N A S Al-Areqi Mater. Chem. Phys. 118 15 (2009).
E P Kharitonova and V I Voronkova Inorg. Mater. 43 55 (2007).
S Beg, S Hafeez and N A S Al-Areqi Defect Diffus. Forum 316–317 7 (2011).
M H Paydar, A M Hadian and G Fafilek J. Mater. Sci. 39 1357 (2004).
J Yan and M Greenblatt Solid State Ionics 81 225 (1995).
V Sharma, A K Shukla and J Gopalakrishnan Solid State Ion. 58 359 (1992).
S Beg and S Haneef Phase Transit. 87 821 (2014).
H Putz, Gbr Brandenburg and Kreuzherrenstr. Match! – Phase Identification from Powder Diffraction—Version 3, Crystal Impact, 102, 53227 Bonn, Germany, http://www.crystalimpact.com/match.
K Sooryanarayana, T N Guru Row and K B R Varma Mater. Res. Bull. 34 425 (1999).
C Muller, M Anne and M Bacmann Solid State Ionics 111 27 (1998).
L Zhang, F Liu, K Brinkman, K L Reifsnider and Virkar J. Power Sources 247 947 (2014).
D Tripathy and A Pandey J. Alloys Compd. 737 136 (2018).
A S Bondarenko and G A Ragoish In Progress in Chemometrics Research, Pomerantsev A. L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, 2005, pp. 89–102 http://www.abc.chemistry.bsu.by/vi/analyser/.
R Kant, K Singh and O P Pandey Ionics 16 277 (2010).
S Bag and B Behera J. Sci. Adv. Mate. Devices 1 512 (2016).
R Kant, K Singh and O P Pandey Ceram. Int. 35 221 (2009).
E S Buyanova, M V Morozova, Ju V Emelyanova, S A Petrova, R G Zakharov, N V Tarakina and V M Zhukovskiy Solid State Ion. 243 8 (2013).
W J Bowman, J Zhu, R Sharma and P A Crozier Solid State Ionics 272 9 (2015).
S Beg, N A S Al-Areqi, S Hafeez and A Al–Alas Ionics 21 421 (2015).
A KezˇIonis, W Bogusz, F Krok, J Dygas, A Orliukas, I Abrahams and W Gebicki Solid State Ionics 119 145 (1999).
I Abrahams, F Krok, M Malys and W Wrobel Solid State Ionics 176 2053 (2005).
F Abraham, M F Debreuille-Gresse, G Mairesse and G Nowogrocki Solid State Ionics 28–30 529 (1988).
A Dutta and T P Sinha J. Phys. Chem. Solids 67 1484 (2006).
S Bag and B Behera Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 5 (2015).
M Roy, S Sahu, A M Awasthi and S Bharadwaj J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 115 1265 (2014).
T V Kumar, A S Chary, S Bhardwaj, A M Awasthi and S N Reddy Int. J. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2 173 (2013).
K Shantha and K B R Varma Solid State Ionics 99 225 (1997).
T Badapanda, R K Harichandan, S S Nayak, A Mishra and S Anwar Process. Appl. Ceram. 8 145 (2014).
N Pandey, A K Thakur and R N P Choudhary Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 15 191 (2008).
N Shukla, A K Thakur, A Shukla and D T Marx Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7 7644 (2014).
G Mairesse, P Roussel, R N Vannier, M Anneb and G Nowogrocki Solid State Sci. 5 861 (2003).
D L Sidebottom, P F Green and R K Brow J. Non-Cryst. Solids 183 151 (1995).
L Borah, B Paik, S A Hashmi and A Pandey Ionics 18 747 (2012).
R B Belgacem, M Chaari, A F Brana, B J Garcia and A Matoussi J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100 2045 (2017).
Y B Taher, N Moutia, A Oueslati and M Gargouri RSC Adv. 6 39750 (2016).
N K Mohanty, R N Pradhan, S K Satpathy, A K Behera, B Behera and P Nayak J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25 117 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to DST, New Delhi, for providing the FIST facility (Sanction Order Number SB/52/CMP-093/2013) in the Physics department for XRD and impedance studies. One of the authors (AJS) gratefully acknowledges DST, New Delhi, for INSPIRE fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathy, D., Saikia, A., Tado, G.T. et al. Dielectric study of Ti-doped Bi2VO5.5 solid electrolyte. Indian J Phys 93, 845–859 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-018-1356-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-018-1356-4