Abstract
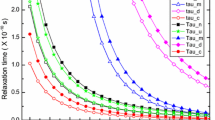
The built-in-polarization field at the interface of InxGa1-xN/GaN quantum well enhances the elastic constant, phonon velocity and Debye temperature of InxGa1-xN alloy and their respective bowing constants. As a result, the phonon scattering processes in InxGa1-xN are modified. The combined phonon relaxation time and phonon mean free path has been computed for with and without built-in-polarization field for different indium (In) contents at room temperature. Our result shows that the built-in-polarization field suppresses the scattering mechanisms and enhances the phonon relaxation time and mean free path. The result is used to determine the effect of built-in-polarization field on electrical and thermal properties of InxGa1-xN.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H Morkoc Nitride Semiconductor Devices (Germany: Wiley) (2013)
H Morkoc Handbook of Nitride Semiconductors and Devices (Germany: Wiley) (2008)
J Piprek Nitride Semiconductor Devices: Principles and simulation, (Germany: Wiley) (2007)
E F Schubert Light Emitting Diodes, (New York: Cambridge University Press) (2006)
J Wu J. Appl. Phys. 106 011101 (2009)
S Nakamura and G Fasol The Blue Laser Diode: The Complete Story (Berlin: Springer) (2000)
F K Yam and Z Hassan, Superlattices Microstructures 43 1 (2008)
Y Wu, Yih-Yin Lin, H Huang and J Singh J. Appl. Phys. 105 013117 (2009)
S Nakmura Science 281 956 (1998)
S Nakamura, M Senoh, and T Mukai Appl. Phys. Lett. 62 2390 (1993)
H Zhao et al. Optic Express 19 147902 (2011)
Shih-Wei Feng et al. Optical Mater Express 3 1777 (2013)
Shih-Wei Feng et al. J. Appl. Phys. 108 093118 (2010)
G F Brown et al. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 94 478 (2010)
H Zhang et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84 4644 (2004)
R Schmidt et al. 0-7803-7418-5/02/© 2002 IEEE (2002)
O Ambacher et al. J. Appl. Phys. 87 334(2000)
O Ambacher et al J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 14 3399 (2002)
C Wood and D Jena Polarization Effects in Semiconductors: From Ab InitioTheory to Device Applications (New York: Springer) (2000)
S De et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 121919 (2012)
E P Pokatilov, D L Nika and A A Balandin Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 112110 (2006)
E P Pokatilov, D L Nika and A A Balandin Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 113508 (2006)
F Bernardini, V Fiorentini and O Ambacher Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 1204 (2002)
F Bernardini and V Fiorentini Phys. Rev. B 64 08520 (2001)
J Yan, Y Zhang, P Kim and A Pinczuk Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 166802 (2007)
Z Q Li et al. Nature Physics 4 532(2008)
E H Hwang and S Das Sarma Phys. Rev. B 77 115449 (2008)
D A Siegel, C Hwang, A V Fedorov and A Lanzara New J. Phys. 14 95006 (2012)
S Tanaka, M Matsunami and S Kimura Scientific Reports 3 3031(2013)
G Verzellesi et al. J. Appl. Phys. 114 071101(2013)
W Liu and A A Balandin J. Appl .Phys. 97 123705 (2005)
A Sztein, J E Bowers, S P DenBaars and S Nakamura J. Appl. Phys. 113 183707 (2013)
A Sztein, J E Bowers, S P DenBaars and S Nakamura Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 183707 (2013)
A Sztein, J E Bowers, S P DenBaars and S Nakamura Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 042106 (2014)
M Balkanski and R F Wallis Semiconductor Physics and Application (New York: Oxford Univ Press) (2000)
B K Sahoo J. Mat. Sc. 47 2624 (2012)
S K Sahoo, B K Sahoo and S Sahoo J. Appl. Phys. 114 163501 (2013)
W Liu and A A Balandin J. Appl. Phys. 97 073710 (2005)
J Zou and A A Balandin J. Appl. Phys. 89 2932 (2001)
P G Klemen (Chem. and Phys. of Nanostructures and Related Non equilibrium materials) (Minerals, Metals, and Materials Society, Warrendale, PA) ed. E. Ma, B. Fultz, R. Shall, J. Morral, and P. Nash (1997)
D I Florescu, V M Asnin, F H Pollak, R J Molnar and C E C Wood J. Appl. Phys. 88 3295 (2000)
A Pansari, V Gedam and B K Sahoo Physica B 456 66 (2015)
V Gedam, A Pansari and B K Sahoo J. Electr. Mater. 44 1035 (2015)
A X Levander et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 012108 (2011)
D Kotchetkov, J Zou, A A Balandin, D I Florescu and F H Pollak Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 4316 (2001)
S Krukowski et al. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 59 289 (1998)
G A Slack, L J Schowalter, D Morelli and J A Freitas Jr. J. Cryst. Growth 246 287 (2002)
J Zou, D Kotchetkov, A A Balandin, D I Florescu, and F H Pollak J. Appl. Phys. 92 2534 (2002)
B N Pantha, R Dahal, J Li, J Y Lin, and H X Jiang, G Pomrenke Appl. Phys. Lett. 92 042112 (2008)
T Tong et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 121906 (2013)
C Shi, P M Asbeck and E T Yu Appl. Phys. Lett. 74 573 (1999)
J Piprek, R Farrell, S DenBaars and S Nakamura, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 18 1041 (2006)
Acknowledgments
V. G thanks University Grant Commission, New Delhi, India for providing financial support to carry out research work at National Institute of Technology, Raipur, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gedam, V., Pansari, A. & Sahoo, B.K. Effect of built-in-polarization field on relaxation time and mean free path of phonons in InxGa1-xN/GaN quantum well. Indian J Phys 90, 991–997 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-016-0836-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-016-0836-7
Keywords
- InxGa1-xN QW
- Built-in-polarization field
- Phonon relaxation time
- Mean free path
- Thermoelectric properties