Abstract
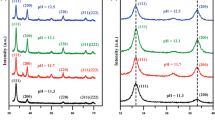
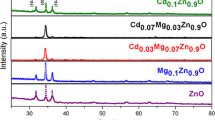
Nanostructured cadmium zinc sulphide films have been deposited onto cleaned glass substrates by chemical bath deposition method at room temperature using polyvinyl alcohol as capping agent. X-ray diffraction analysis confirms the formation of cubic-phase cadmium zinc sulphide films. Crystallite size obtained from the calculation of Scherrer’s formula and Williamson–Hall plot as well as size–strain plot is found to decrease with the increase in zinc concentration. The films have very high dislocation density of the order of 1016 m−2, whereas the strain is of the order of 10−3. Scanning electron microscopic image reveals that the particles are agglomerated to form nanoclusters and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis confirms that films are composed of cadmium, zinc and sulphur. High-resolution transmission electron microscopic image reveals that the shape of the particles is nearly spherical, uniformly distributed. Selected-area electron diffraction pattern supports the formation of cubic phase of the film. Optical absorption peaks of the films shift towards lower wavelength side and their optical band gap increases with the increase in zinc concentration. The increase in zinc concentration enhances the photoluminescence emission intensity, whose emission is in the green region of visible spectrum.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
G Mandal and T Ganguly Indian J. Phys. 85 1229 (2011)
S Sarmah and A Kumar Indian J. Phys. 85 713 (2011)
P Mallick, C Rath, R Biswal and N C Mishra Indian J. Phys. 83 517 (2009)
S N Alamri Indian J. Phys. 88 259 (2014)
Y P Zhang, W Liu, B D Liu and R M Wang Rare Met. 33 1 (2014)
T P Kumar and K Sankaranarayanan Chalcogenide Lett. 6 555 (2009)
B J Wu et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63 2935 (1993)
S Guha, B J Wu, H Cheng and J M De Puydt Appl. Phys. Lett. 63 2129 (1993)
M A Haase, J Qiu, J M De Puydt and H Cheng Appl. Phys. Lett. 59 1272 (1991)
H Geon et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 59 3619 (1991)
N Gaewdang and T Gaewdang Mater. Lett. 59 3577 (2005)
W Wang, I Germanenko and M S El-Shall Chem. Mater. 14 3028 (2002)
M C Baykul and N Orhan Thin Solid Films 518 1925 (2010)
M A Rafea, A A M Farag and N Roushdy J. Alloys Compounds 485 660 (2009)
S Ham et al. J. Korean Electrochemical Soc. 10 262 (2007)
P B Smith J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 10 897 (1992)
G Laukaitis et al. Appl. Surf. Sci. 161 396 (2000)
D Patidar, N S Saxena and T P Sharma J. Modern Optics 55 79 (2008)
S D Chavhan, S Senthilarasu and S H Lee Appl. Surf. Sci. 254 4539 (2008)
B Barman and K C Sarma Indian J. Phys. 86 703 (2012)
A Goswami Thin Film Fundamentals (New Delhi: New Age International Pvt. Ltd.) p 36 (1996)
K L Chopra Thin Film Phenomena (New York: McGraw-Hill Inc.) p 90 (1969)
J B Nelson and D P Riley Proc. Phys. Soc. (London) 57 160 (1945)
S Sen, S K Halder and S P Sengupta J. Phys. Soc. Jap. 38 1641 (1975)
J K Dongre, V Nogriya and M Ramrakhiani Appl. Sur. Sci. 255 6115 (2009)
G K Williamson and W H Hall Acta Metall. 1 22 (1953)
P K Mochahari and K C Sarma Indian J. Phys. 88 1265 (2014)
P Roy and S K Srivastava Thin Solid Films 496 293 (2006)
G B Williamson and R E Smallman Philos. Mag. 1 34 (1956)
N Choudhury and B K Sarma Thin Solid Films 519 2132 (2011)
A K Zak, W H A Majid, M E Abrishami and R Yousefi Solid State Sci. 13 251 (2011)
M A Tagliente and M Massaro Nucl. Instrum. Meths. Phys. Res. B 266 1055 (2008)
P Rajeswari and S Dhanuskodi Cryst. Res. Technol. 48 589 (2013)
J Tauc (ed.) Amorphous and liquid semiconductors (London and New York: Plenum press) Chapter 4, p 171 (1974)
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (PKM) is thankful to the University Grants Commission (UGC), India, for awarding him FDP fellowship. The authors thank IIT Gauhati, India, for providing XRD and HRTEM facilities. They are thankful to Instrumentation and USIC and Department of Chemistry, Gauhati University, India, for providing XRD facility and UV–visible as well as PL measurement, respectively. Sincere thanks go to Tezpur University, India, for providing SEM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochahari, P.K., Sarma, K.C. Study of structural and optical properties of chemically synthesized nanostructured cadmium zinc sulphide films for band gap tunability. Indian J Phys 90, 21–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0721-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0721-9