Abstract
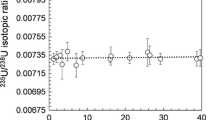
Actinides have widely entered the environment as a result of nuclear accidents and atmospheric weapon testing. These radionuclides, especially uranium, are outstanding radioactive pollutants, due to their high radiotoxicity and long half-lives. In addition to this, since depleted uranium (DU) has been used in the Balkan conflict in 1999, there has been a concern about the possible consequences of its use for the people and environment. Therefore, accurate, precise and simple determination methods are necessary in order to evaluate the human dose and the concentration and effects of these nuclides in the environment. The principal isotopes of uranium e.g. 235U and 238U are of primordial origin and 234U present in radioactive equilibrium with 238U. 236U occurs in nature at ultra trace concentrations with a 236U: 238U atom ratio of 10−14. Concentrations of uranium in soil samples were determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and isotope ratios of uranium were measured using a thermal ionisation mass spectrometer. Radioactive dis-equilibrium of 234/238U, depletion of 235/238U and significant evidence of 236U/238U were noticed in soil samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNSCEAR Sources and effects of Ionizing Radiation, Report to the General Assembly, Vol. I. (New York: United Nations) (2000)
S R Taylor and S M McLennan Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution (London, U K: Blackwell Scientific Publishers) (1985)
W Burkart Handbook on the Toxicity of the Inorganic Compounds (eds) H Sigel and H G Seiler (New York: M Dekker) p805 (1988)
C R Cothern and W L Lappenbusch Health Phys. 45 89(1983)
M I Litaor J. Environ. Qual. 24 314 (1995)
M E Ketterer, W C Wetzel, R R Layman, G Matisoff and E C Bonniwell Environ. Sci. Technol. 54 966 (2000)
A Bleise, P R Dansei and W Burkart J. Environ. Radioactivity 64 93 (2003)
M Ivanovich and R S Harmon Uranium Series Disequilibrium: Applications to Earth, Marine and Environmental Sciences (Oxford: Clarendon Press) (1992)
S F Boulyga, J S Baker, J L Matusevitch and H J Dietze Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 203 143 (2000)
M Yamamoto, K Shiraishi, K Komura, and K Ueno J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 185 183 (1994)
O J Marsden, F R Livens, J P Day, L K Fifield and P S Goodall Analyst 126 633 (2001)
T C Chu and J J Wang Appl. Radiat. Isotopes 48 3619 (1997)
J H Chen and G J Wasserburg Anal. Chem. 53 2060 (1981)
A S Cohen, N S Belshaw and R K O’Nions Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 116 71 (1992)
K L Ramakumar, S Jeykumar, R M Rao, L Gnanayyan and H C Jain J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 190 121 (1995)
X Luo, M Rehkamper, D C Lee and A Haliday Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 171 105 (1997)
S Ritcher, A Alonso, W De Bolle, R Wellum and P D P Taylor Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 193 9 (1999)
S K Sahoo and A Masuda Proc. Jpn. Acad. 76 151 (2000)
S K Sahoo, H Yonehara, K Kurotaki, K Shiraishi, V Ramzaev and A Barkovski J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 247 341 (2001)
R N Taylor, I W Croudace, P E Warwick and S J Dee Chem. Geol. 144 73 (1998)
P Goodall and C Lythgoe Analyst 124 263 (1999)
Z A Palacz, P A Freedman and A J Walder Chem. Geol. 101 157 (1992)
K H Wedepohl Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59 1217 (1995)
J P McLaughlin, L L Vintro, K J Smith, P I Mitchell and Z S Zunic J. Environ. Radioactivity 64 155 (2003)
P R Danesi, A Bleise, W Burkart, T Cabianca, M J Campbell, M Makarewicz, J Moreno, C Tuniz and M Hotchkis J. Environ. Radioactivity 64 121 (2003)
S K Sahoo, K Fujimoto, I Celikovic, P Ujic and Z S Zunic Nucl. Technol. Radiat. Prot. 19 26 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, S.K. Measurement of uranium and its isotopes at trace levels in environmental samples using mass spectrometry. Indian J Phys 83, 787–797 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-009-0046-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-009-0046-7