Abstract
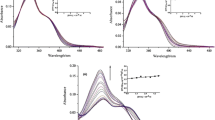
Nimustine, a chloroethyl nitrosourea derivative (CENU), is an antineoplastic agent, which is used for the treatment of various types of cancer. The present study focuses on the prediction and investigation of binding properties of nimustine with DNA using molecular modeling and UV–Visible spectroscopic technique. The docking study show that nimustine plausibly binds within the major groove of DNA. Further analysis of docking suggests direct interaction of nimustine with the moieties of heterocyclic nitrogenous bases of DNA. The free binding energy value of the best nimustine-DNA docked conformer is predicted as −4.31 kcal/mol using docking results.The molecular modeling study also reveals that the interaction between nimustine and DNA is majorly governed by van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions, whereas the contribution of electrostatic forces stands negligible. Further, UV–Visible spectra of free calf thymus DNA and its complexes with varying concentration of nimustine indicate the binding constant (K a ) value as 3.27 × 103 M−1, which suggests moderate interaction of nimustine with DNA. The spectroscopic results are further used to calculate the binding free energy of the complex using the relation ΔG = −RT ln (K a ). This accounts for a value of −4.79 kcal/mol. It corroborates well with the docking outcomes. The results of present study may help in designing and synthesis of new chloroethyl nitrosourea derivatives with improved efficacy and specificity for the target molecules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Palchaudhuri and P. J. Hergenrother, DNA as a target for anticancer compounds: methods to determine the mode of binding and the mechanism of action, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 18 (2007) 497–503.
A. Paul and S. Bhattacharya, Chemistry and biology of DNA-binding small molecules, Curr. Sci., 02 (2012) 212–231.
W. P. Roos and B. Kaina, DNA damage-induced cell death by apoptosis, Trends Mol. Med., 12 (2006) 440–450.
S. Agarwal, D. K. Jangir, R. Mehrotra, N. Lohani and M. R. Rajeswari, A structural insight into major groove directed binding of nitrosourea derivative nimustine with DNA: a spectroscopic study, PLoS One, 09 (2014) e104115.
J. Glasel, Validity of nucleic acid purities monitored by 260/280 nm absorbance ratios, Bio-techniques, 18 (1995) 62–63.
H. R. Drew, R. M. Wing, T. Takano, C. Broka, S. Tanaka, K. Itakura and R. E. Dickerson, Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer conformation and dynamics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 78 (1981) 2179–2183.
J. J. Irwin, T. Sterling, M. M. Mysinger, E. S. Bolstad and R.G. Coleman, ZINC: a free tool to discover chemistry for biology, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 52 (2012) 1757–1768.
N. M. O’Boyle, M. Banck, C. A. James, C. Morley, T. Vandermeersch and G. R. Hutchison, Open Babel: an open chemical toolbox, J. Cheminform., 3 (2011) 1–14.
G. M. Morris, R. Huey, W. Lindstrom, M. F. Sanner, R. K. Belew, D. S. Goodsell and A. J. Olson, AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility, J. Comput. Chem., 30 (2009) 2785–2791.
G. Morris, D. Goodsell, R. Halliday, R. Huey, W. Hart, R. Belew and A. Olson, Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function, J. Comput. Chem., 19 (1998) 1639–1662.
M. F. Sanner, Python: a programming language for software integration and development, J. Mol. Graph. Model., 17 (1999) 57–61.
K. A. Connors, Binding constants: the measurement of molecular complex stability, Wiley, New York, (1987).
S. Agarwal, D. K. Jangir and R. Mehrotra, Spectroscopic studies of the effects of anticancer drug mitoxantrone interaction with calf-thymus DNA, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 120 (2013) 177–182.
S. Agarwal, D. Chadha and R. Mehrotra, Molecular modeling and spectroscopic studies of semustine binding with DNA and its comparison with lomustine–DNA adduct formation, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn., 33 (2014) 1653–1668.
G. Tyagi, S. Agarwal and R. Mehrotra, tRNA binding with anti-cancer alkaloids–nature of interaction and comparison with DNA–alkaloids adducts, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 142 (2015) 250–256.
S. Agarwal, D. K. Jangir, P. Singh and R. Mehrotra, Spectroscopic analysis of the interaction of lomustine with calf thymus DNA, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 130 (2014) 281–286.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Director, CSIR-National Physical Laboratory, New Delhi, India, for granting the permission for publication of the work. S. A is thankful to Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi, India, for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chadha, D., Agarwal, S. & Mehrotra, R. Investigation of Anti-Cancer Drug Nimustine Interaction with Calf Thymus DNA. MAPAN 31, 169–175 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-016-0170-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-016-0170-8