Abstract
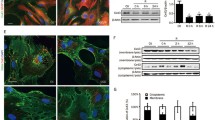
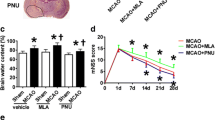
We aimed to test the effects of connexin43 (Cx43) on ischemic neurogenesis and examined whether it was dependent on aquaporin-4 (AQP4). We detected the expression of Cx43 and AQP4 in the ipsilateral subventricular zone (SVZ) and peri-infarct cortex after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Also, we examined neurogenesis in the above regions via co-labeling of 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU)/neuronal nuclear antigen (NeuN) and BrdU/doublecortin (DCX). The effects of Cx43 and AQP4 were investigated by using two transgenic animals: heterozygous Cx43 (Cx43±) mice and AQP4 knockout (AQP4−/−) mice, and connexin mimetic peptide (CMP), a selective Cx43 blocker. We demonstrated AQP4 and Cx43 were co-expressed in the astrocytes after MCAO and the expression was highly increased in ipsilateral SVZ and peri-infarct cortex. Cx43± mice had larger infarction volumes and worse neurological function. Both BrdU/NeuN and BrdU/DCX co-labeled cells in the two regions were reduced in Cx43± and AQP4−/− mice compared to wild-type (WT) mice, suggesting Cx43 and AQP4 participated in neurogenesis of neural stem cells. Moreover, CMP decreased AQP4 expression and inhibited neurogenesis in WT mice, while the latter failed to be observed in AQP4−/− mice. Besides, higher levels of IL-1β and TNF-α were detected in the SVZ and peri-infarct cortex of AQP4−/− and Cx43± mice than those in WT mice. In conclusion, our data suggest that Cx43 elicits neuroprotective effects after cerebral ischemia through promoting neurogenesis in the SVZ to regenerate the injured neurons, which is AQP4 dependent and associated with down-regulation of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets collected and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
30 April 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-024-00701-7
References
Aranarochana A, Kaewngam S, Anosri T, Sirichoat A, Pannangrong W, Wigmore P et al (2021) Hesperidin reduces memory impairment associated with adult rat hippocampal neurogenesis triggered by valproic acid. Nutrients 13:4364
Belayev L, Hong SH, Menghani H, Marcell SJ, Obenaus A, Freitas RS et al (2018) Docosanoids promote neurogenesis and angiogenesis, blood-brain barrier integrity, penumbra protection, and neurobehavioral recovery after experimental ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 55:7090–7106
Ceanga M, Dahab M, Witte OW, Keiner S (2021) Adult neurogenesis and stroke: a tale of two neurogenic niches. Front Neurosci 15:700297
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Lu D, Lu M et al (2001) Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 32:1005–1011
Chen G, Park CK, Xie RG, Berta T, Nedergaard M, Ji RR (2014) Connexin-43 induces chemokine release from spinal cord astrocytes to maintain late-phase neuropathic pain in mice. Brain 137:2193–2209
Chen Z, Hu Q, Xie Q, Wu S, Pang Q, Liu M et al (2019a) Effects of treadmill exercise on motor and cognitive function recovery of MCAO mice through the Caveolin-1/VEGF signaling pathway in ischemic penumbra. Neurochem Res 44:930–946
Chen B, Yang L, Chen J, Chen Y, Zhang L, Wang L et al (2019b) Inhibition of Connexin43 hemichannels with Gap19 protects cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in mice. Brain Res Bull 146:124–135
Cheng X, Hou Z, Sun J, Huang Y, Wang L, Zhou Z et al (2017) Protective effects of Tongxinluo on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury related to Connexin 43/Calpain II/Bax/caspase-3 pathway in rat. J Ethnopharmacol 198:148–157
Chu H, Tang Y, Dong Q (2013) Protection of vascular endothelial growth factor to brain edema following intracerebral hemorrhage and its involved mechanisms: effect of aquaporin-4. PLoS ONE 8:e66051
Chu H, Tang Y, Dong Q (2014a) Protection of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to hemorrhagic brain injuries and its involved mechanisms: effects of vascular endothelial growth factor and aquaporin-4. Neuroscience 260:59–72
Chu H, Ding H, Tang Y, Dong Q (2014b) Erythropoietin protects against hemorrhagic blood-brain barrier disruption through the effects of aquaporin-4. Lab Invest 94:1042–1053
Chu H, Xiang J, Wu P, Su J, Ding H, Tang Y et al (2014c) The role of aquaporin 4 in apoptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation 11:184
Chu H, Huang C, Ding H, Dong J, Gao Z, Yang X et al (2016) Aquaproin-4 and cerebrovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci 17:1249
Chu H, Huang C, Gao Z, Dong J, Tang Y, Dong Q (2017a) Reduction of ischemic brain edema by combined use of paeoniflorin and astragaloside IV via down-regulating Connexin 43. Phytother Res 31:1410–1418
Chu H, Yang X, Huang C, Gao Z, Tang Y, Dong Q (2017b) Apelin-13 protects against ischemic blood-brain barrier injury through the effects of aquaporin-4. Cerebrovasc Dis 44:10–25
Chu H, Gao Z, Huang C, Dong J, Tang Y, Dong Q (2020) The relationship between hematoma expansion induced by hypertension and hyperglycemia and blood-brain barrier disruption and its possible mechanism: role of aquaporin-4 and connexin43. Neurosci Bull 36:1369–1380
Cibelli A, Stout R, Timmermann A, de Menezes L, Guo P, Maass K et al (2021) Cx43 carboxyl terminal domain determines AQP4 and Cx30 endfoot organization and blood brain barrier permeability. Sci Rep 11:24334
Cuartero MI, García-Culebras A, Torres-López C, Medina V, Fraga E, Vázquez-Reyes S et al (2021) Post-stroke neurogenesis: friend or foe? Front Cell Dev Biol 9:657846
Davidson JO, Green CR, Nicholson LF, O’Carroll SJ, Fraser M, Bennet L et al (2012) Connexin hemichannel blockade improves outcomes in a model of fetal ischemia. Ann Neurol 71:121–132
Elbadawy HM, Mirabelli P, Xeroudaki M, Parekh M, Bertolin M, Breda C et al (2016) Effect of connexin 43 inhibition by the mimetic peptide Gap27 on corneal wound healing, inflammation and neovascularization. Br J Pharmacol 173:2880–2893
Fan Y, Zhang J, Sun XL, Gao L, Zeng XN, Ding JH et al (2005) Sex- and region-specific alterations of basal amino acid and monoamine metabolism in the brain of aquaporin-4 knockout mice. J Neurosci Res 82:458–464
Fang X, Wang H, Zhuo Z, Tian P, Chen Z, Wang Y et al (2021) miR-141-3p inhibits the activation of astrocytes and the release of inflammatory cytokines in bacterial meningitis through down-regulating HMGB1. Brain Res 1770:147611
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators (2021) Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol 20:795–820
Gonçalves JT, Schafer ST, Gage FH (2016) Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus: from stem cells to behavior. Cell 167:897–914
Guan ZF, Zhou XL, Zhang XM, Zhang Y, Wang YM, Guo QL et al (2016) Beclin-1- mediated autophagy may be involved in the elderly cognitive and affective disorders in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Transl Neurodegener 5:22
Guarnieri G, Sarchielli E, Comeglio P, Herrera-Puerta E, Piaceri I, Nacmias B et al (2020) Tumor necrosis factor α influences phenotypic plasticity and promotes epigenetic changes in human basal forebrain cholinergic neuroblasts. Int J Mol Sci 21:6128
Huang C, Dai C, Gong K, Zuo H, Chu H (2016) Apelin-13 protects neurovascular unit against ischemic injuries through the effects of vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuropeptides 60:67–74
Ishikawa S, Kuno A, Tanno M, Miki T, Kouzu H, Itoh T et al (2012) Role of connexin-43 in protective PI3K-Akt-GSK-3 signaling in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H2536–H2544
Jurkowski MP, Bettio L, K Woo E, Patten A, Yau SY, Gil-Mohapel J (2020) Beyond the hippocampus and the SVZ: adult neurogenesis throughout the brain. Front Cell Neurosci 14:576444
Kong H, Fan Y, Xie J, Ding J, Sha L, Shi X et al (2008) AQP4 knockout impairs proliferation, migration and neuronal differentiation of adult neural stem cells. J Cell Sci 121:4029–4036
Li Y, Xu QQ, Shan CS, Shi YH, Wang Y, Zheng GQ (2018) Combined use of emodin and ginsenoside Rb1 exerts synergistic neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Front Pharmacol 9:943
Liang R, Yong S, Huang X, Kong H, Hu G, Fan Y (2016) Aquaporin-4 mediates the suppressive effect of lipopolysaccharide on hippocampal neurogenesis. NeuroImmunoModulation 23:309–317
Liu X, Wu G, Tang N, Li L, Liu C, Wang F et al (2021) Glymphatic drainage blocking aggravates brain edema, neuroinflammation via modulating TNF-α, IL-10, and AQP4 after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Front Cell Neurosci 15:784154
Nakase T, Fushiki S, Naus CC (2003) Astrocytic gap junctions composed of connexin 43 reduce apoptotic neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia. Stroke 34:1987–1993
Niger C, Buo AM, Hebert C, Duggan BT, Williams MS, Stains JP (2012) ERK acts in parallel to PKC delta to mediate the connexin43-dependent potentiation of Runx2 activity by FGF2 in MC3T3 osteoblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302:C1035–C1044
Okada M, Oka T, Nakamoto M, Fukuyama K, Shiroyama T (2020) Astroglial Connexin43 as a potential target for a mood stabiliser. Int J Mol Sci 22:339
Price GW, Chadjichristos CE, Kavvadas P, Tang SCW, Yiu WH, Green CR et al (2020) Blocking Connexin-43 mediated hemichannel activity protects against early tubular injury in experimental chronic kidney disease. Cell Commun Signal 18:79
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G, Savalos RA, Davidson C, Sharp FR (1990) A semiautomated method for measuring brain infarct volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:290–293
Valls-Lacalle L, Consegal M, Ruiz-Meana M, Benito B, Inserte J, Barba I et al (2020) Connexin 43 deficiency is associated with reduced myocardial scar size and attenuated TGFβ1 signaling after transient coronary occlusion in conditional knock-out mice. Biomolecules 10:651
Wang X, Feng L, Xin M, Hao Y, Wang X, Shang P et al (2020) Mechanisms underlying astrocytic connexin-43 autophagy degradation during cerebral ischemia injury and the effect on neuroinflammation and cell apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother 127:110125
Wang Y, Huang C, Guo Q, Chu H (2022) Aquaporin-4 and cognitive disorders. Aging Dis 13:61–72
Wojtowicz JM, Kee N (2006) BrdU assay for neurogenesis in rodents. Nat Protoc 1:1399–1405
Wu LY, Yu XL, Feng LY (2015) Connexin 43 stabilizes astrocytes in a stroke-like milieu to facilitate neuronal recovery. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36:928–938
Xie M, Yi C, Luo X, Xu S, Yu Z, Tang Y et al (2011) Glial gap junctional communication involvement in hippocampal damage after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Ann Neurol 70:121–132
Yao D, Zhang R, Xie M, Ding F, Wang M, Wang W (2022) Updated understanding of the glial-vascular unit in central nervous system disorders. Neurosci Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-022-00977-9
Yu W, Jin H, Sun W, Nan D, Deng J, Jia J et al (2021) Connexin43 promotes angiogenesis through activating the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway under chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 41:2656–2675
Zaben M, Haan N, Sharouf F, Ahmed A, Sundstrom LE, Gray WP (2021) IL-1β and HMGB1 are anti-neurogenic to endogenous neural stem cells in the sclerotic epileptic human hippocampus. J Neuroinflammation 18:218
Zhang J, Griemsmann S, Wu Z, Dobrowolski R, Willecke K, Theis M et al (2018) Connexin43, but not connexin30, contributes to adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Brain Res Bull 136:91–100
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81500998, 81901102, and 82071472).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HC and JD: study design, experiment performance, and analysis and drafting of the manuscript. YT, CH, and QG: conception and design and revision and approval of the manuscript. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Our animal studies and protocol were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Fudan University.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, H., Dong, J., Tang, Y. et al. Connexin 43 Promotes Neurogenesis via Regulating Aquaporin-4 after Cerebral Ischemia. Neurotox Res 41, 349–361 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-023-00646-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-023-00646-3