Abstract
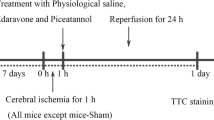
Permanent cerebral ischemia is a consequence of prolonged cerebral artery occlusion that results in severe brain damage. Neurotoxicity occurring after ischemia can induce brain tissue damage by destroying cell organelles and their function. Neferine is a natural compound isolated from the seed embryos of the lotus plant and has broad pharmacological effects, including blockading of the calcium channels, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-apoptosis. This study investigated the ability of neferine to reduce brain injury after permanent cerebral occlusion. Permanent cerebral ischemia in rats was induced by instigation of occlusion of the middle cerebral artery for 24 h. The rats were divided into 6 groups: sham, permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO), pMCAO with neferine and nimodipine treatment. To investigate the severity of the injury, the neurological deficit score and morphological alterations were investigated. After 24 h, the rats were evaluated to assess neurological deficit, infarct volume, morphological change, and the number of apoptotic cell deaths. In addition, the brain tissues were examined by western blot analysis to calculate the expression of proteins related to oxidative stress and apoptosis. The data showed that the neurological deficit scores and the infarct volume were significantly reduced in the neferine-treated rats compared to the vehicle group. Treatment with neferine significantly reduced oxidative stress with a measurable decrease in 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), nitric oxide (NO), neuronal nitric oxide (nNOS), and calcium levels and an upregulation of Hsp70 expression. Neferine treatment also significantly decreased apoptosis, with a decrease in Bax and cleaved caspase-3 and an increase in Bcl-2. This study suggested that neferine had a neuroprotective effect on permanent cerebral ischemia in rats by diminishing oxidative stress and apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All data are available on request from authors.
References
Balogi Z, Multhoff G, Jensen TK, Lloyd-Evans E, Yamashima T et al (2019) Hsp70 interactions with membrane lipids regulate cellular functions in health and disease. Prog Lipid Res 74:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2019.01.004
Baskaran R, Poornima P, Priya LB, Huang CY, Padma VV (2016) Neferine prevents autophagy induced by hypoxia through activation of Akt/mTOR pathway and Nrf2 in muscle cells. Biomed Pharmacother 83:1407–1413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.08.063
Baskaran R, Priya LB, Kalaiselvi P, Poornima P, Huang CY et al (2017) Neferine from Nelumbo nucifera modulates oxidative stress and cytokines production during hypoxia in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Biomed Pharmacother 93:730–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.003
Belov Kirdajova D, Kriska J, Tureckova J, Anderova M (2020) Ischemia-triggered glutamate excitotoxicity from the perspective of glial cells. Front Cell Neurosci 14:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00051
Carlson AP, Hänggi D, Macdonald RL, Shuttleworth CW (2020) Nimodipine reappraised: an old drug with a future. Curr Neuropharmacol 18:65–82. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X17666190927113021
Chaichompoo W, Chokchaisiri R, Apiratikul N, Chairoungdua A, Yingyongnarongkul B et al (2018) Cytotoxic alkaloids against human colon adenocarcinoma cell line (HT-29) from the seed embryos of Nelumbo nucifera. Med Chem Res 27:939–943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2115-3
Chaitanya GV, Babu PP (2008) Activation of calpain, cathepsin-b and caspase-3 during transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat model. Neurochem Res 33:2178–2186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9567-7
Chen H (2009) The role of NADPH oxidase in brain ischemia. JESTM 2:41–45
Chen J, Qi J, Chen F, Liu JH, Wang T, Yang J et al (2007) Relaxation mechanisms of neferine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro. Asian J Androl 9:795–800. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7262.2007.00321.x
Chen MS, Zhang JH, Wang JL, Gao L, Chen XX et al (2015) Anti-fibrotic effects of neferine on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice. Am J Chin Med 43:231–240. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X15500159
Cheng CY, Kao ST, Lee YC (2019) Ferulic acid exerts anti-apoptotic effects against ischemic injury by activating HSP70/Bcl-2- and HSP70/autophagy-mediated signaling after permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Am J Chin Med 47:39–61. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X19500034
Chiang T, Messing RO, Chou WH (2011) Mouse model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Vis Exp 48:2761. https://doi.org/10.3791/2761
Craig EA (2018) Hsp70 at the membrane: driving protein translocation. BMC Biol 16:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-017-0474-3
Dalleau S, Baradat M, Guѐraud F, Huc L (2013) Cell death and diseases related to oxidative stress: 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) in the balance. Cell Death Differ 20:1615–1630. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.138
Dong ZX, Zhao X, Gu DF, Shi YQ, Zhang J et al (2012) Comparative effects of liensinine and neferine on the human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channel and pharmacological activity analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem 29:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1159/000338497
Hori M, Nakamachi T, Shibato J, Rakwal R, Tsuchida M et al (2014) PACAP38 differentially effects genes and CRMP2 protein expression in ischemic core and penumbra regions of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion model mice brain. Int J Mol Sci 15:17017–17034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150917014
Jung HA, Jin SE, Choi RJ, Kim DH, Kim YS et al (2010) Anti-amnesic activity of neferine with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, as well as inhibition of ChEs and BACE1. Life Sci 87:420–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2010.08.005
Jurcau A, Ardelean AI (2022) Oxidative stress in ischemia/reperfusion injuries following acute ischemic stroke. Biomedicines 10:574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030574
Kim JY, Barua S, Huang MY, Park J, Yenari MA et al (2020) Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) induction: chaperon therapy for neuroprotection after brain injury. Cells 9:2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092020
Kim JY, Han Y, Lee JE, Yenari MA (2018) The 70-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp70) as a therapeutic target for stroke. Expert Opin Ther Targets 22:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2018.1439477
Kim JY, Kim N, Zheng Z, Lee JE, Yenari MA (2016) 70-kDa heat shock protein downregulates dynamin in experimental stroke a new therapeutic target? Stroke 47:2103–2111. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.012763
Kirkegaard T, Roth AG, Petersen NHT, Mahalka AK, Olsen OD et al (2010) Hsp70 stabilizes lysosomes and reverts Niemann-Pick disease-associated lysosomal pathology. Nature 463:549–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08710
Koriyama Y, Furukawa A (2016) HSP70 cleavage-induced photoreceptor cell death caused by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Neural Regen Res 11:1758–1759. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.194721
Kuriakose D, Xiao Z (2020) Pathophysiology and treatment of stroke: present status and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 21:7609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207609
Lai TW, Zhang S, Wang YT (2014) Excitotoxicity and stroke: identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 115:157–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.006
Lee SH, Kim M, Yoon BW, Kim YJ, Ma SJ et al (2001) Targeted hsp70.1 disruption increases infarction volume after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke 32:2905–2912. https://doi.org/10.1161/hs1201.099604
Lee WC, Wong HY, Chai YY, Shi CW, Amino N et al (2012) Lipid peroxidation dysregulation in ischemic stroke: plasma 4-HNE as a potential biomarker? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 425:842–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.002
Li J, McCullough LD (2010) Effects of AMP-activated protein kinase in cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:480–492. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2009.255
Li W, Yang S et al (2016) Targeting oxidative stress for the treatment of ischemic stroke: upstream and downstream therapeutic strategies. Brain Circ 2:153–163. https://doi.org/10.4103/2394-8108.195279
Liu F, McCullough LD (2011) Middle cerebral artery occlusion model in rodents: methods and potential pitfalls. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:464701. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/464701
Liu Y, Wang XC, Hu D, Huang SR, Li QS (2016) Heat shock protein 70 protects PC12 cells against ischemia-hypoxia/reoxygenation by maintaining intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis. Neural Regen Res 11:1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.187051
Mayer MP, Bukau B (2005) Hsp70 chaperones: cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:670–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4464-6
Moghadam SE, Tameh AA, Vahidinia Z, Atlasi MA, Bafrani HH et al (2018) Neuroprotective effects of oxytocin hormone after an experimental stroke model and the possible role of calpain-1. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 27:724–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.10.020
Neumar RW, Meng FH, Mills AM, Xu YA, Zhang C et al (2001) Calpain activity in the rat brain after transient forebrain ischemia. Exp Neurol 170:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.2001.7708
Nishimura K, Horii S, Tanahashi T, Sugimoto Y, Yamada J (2013) Synthesis and pharmacological activity of alkaloids from embryo of lotus, Nelumbo nucifera. Chem Pharm Bull (tokyo) 61:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c12-00820
Nishizawa Y (2001) Glutamate release and neuronal damage in ischemia. Life Sci 69:369–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(01)01142-0
Popp A, Jaenisch N, Witte OW, Frahm C (2009) Identification of ischemic regions in a rat model of stroke. PLoS ONE 4:e4764. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004764
Rami A, Bechmann I, Stehle JH (2008) Exploiting endogenous anti-apoptotic proteins for novel therapeutic strategies in cerebral ischemia. Prog Neurobiol 85:273–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.04.003
Rowland MJ, Ezra M, Winkler A, Garry P, Lamb C et al (2019) Calcium channel blockade with nimodipine reverses MRI evidence of cerebral oedema following acute hypoxia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 39:285–301. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17726624
Rozenzweig R, Nillegoda NB, Mayer MP, Bukau B (2019) The Hsp70 chaperone network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:665–680. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0133-3
Sahara S, Yamashima T (2010) Calpain-mediated Hsp70.1 cleavage in hippocampal CA1 neuronal death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:806–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.087
Sekerdag E, Solaroglu I, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y (2018) Cell death mechanisms in stroke and novel molecular and cellular treatment options. Curr Neuropharmacol 16:1396–1415. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X16666180302115544
Sengking J, Oka C, Wicha P, Yawoot N, Tocharus J et al (2021) Neferine protects against brain damage in permanent cerebral ischemic rat associated with autophagy suppression and AMPK/mTOR regulation. Mol Neurobiol 58:6304–6315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02554-z
Sharma D, Masison DC (2009) Hsp70 Structure, function, regulation and influence on yeast prions. Protein Pept Let 16:571–581. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986609788490230
Sugimoto Y, Furutani S, Itoh A, Tanahashi T, Nakajima H et al (2008) Effects of extracts and neferine from the embryo of Nelumbo nucifera seeds on the central nervous system. Phytomedicine 15:1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2008.09.005
Terasaki Y, Liu Y, Hayakawa K, Pham LD, Lo EH et al (2014) Mechanisms of neurovascular dysfunction in acute ischemic brain. Curr Med Chem 21:2035–2042. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666131228223400
Tomassoni D, Lanari A, Silvestrelli G, Traini E, Amenta F (2008) Nimodipine and its use in cerebrovascular disease: evidence from recent preclinical and controlled clinical studies. Clin Exp Hypertens 30:44–766. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641960802580232
Wang J, Kan Q, Li J, Zhang X, Qi Y (2011) Effect of neferine on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplant Proc 43:2536–2539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.04.013
Wang T, Duan S, Wang H, Sun S, Han B et al (2016) Neurological function following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion is improved by the Ruyi Zhenbao pill in a rats. Biomed Rep 4:161–166. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2016.568
Weinstein PR, Hong S, Sharp FR (2004) Molecular identification of the ischemic penumbra. Stroke 35:2666–2670. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000144052.10644.ed
Wen YD, Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Zhang X et al (2008) Neuronal injury in rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia is associated with activation of autophagic and lysosomal pathways. Autophagy 4:762–769. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.6412
Wicha P, Onsa-Ard A, Chaichompoo W, Suksamrarn A, Tocharus C (2020) Vasorelaxant and antihypertensive effects of neferine in rats: an in vitro and in vivo study. Planta Med 86:496–504. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1123-7852
Wierońska JM, Cieślik P, Kalinowski L (2021) Nitric oxide-dependent pathways as critical factors in the consequences and recovery after brain ischemic hypoxia. Biomolecules 11:1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081097
Yamashima T (2012) Hsp70.1 and related lysosomal factors for necrotic neuronal death. J Neurochem 120:477–494. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07596.x
Yamashima T, Mathivanan A, Dazortsava MY, Sakai S (2014) Calpain-mediated hsp70.1 cleavage in monkey CA1 after ischemia induces similar ‘lysosomal vesiculosis’ to Alzheimer neurons. JADP 4:139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.087
Yuan Q, Yuan Y, Zheng Y, Sheng R, Liu L et al (2021) Anti-cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury of polysaccharides: a review of the mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother 137:111303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111303
Zhou L, Li F, Xu HB, Luo CX, Wu HY et al (2010) Treatment of cerebral ischemia by disrupting ischemia-induced interaction of nNOS with PSD-95. Nat Med 16:1439–1443. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2245
Funding
This research was supported by the Faculty of Medicine Research Fund (grant no. 062–2563), Center for Research and Development of Natural Products for Health, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand. We also gratefully acknowledge support from the Thailand Research Fund (DBG6180030) and the Center of Excellence for Innovation in Chemistry, Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation. Jirakhamon Sengking acknowledges the teaching assistant/research assistant financial support from the Graduate School, Chiang Mai University; the Faculty of Medicine Graduate Scholarship, Chiang Mai University; a 2018 scholarship for graduate students from The King Prajadhipok and Queen Rambhai Barni Memorial Foundation; and a 2020 graduate scholarship from the National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conducting of methodology, data analysis, writing original draft, and revising of the manuscript were by J.S. The data analysis and writing review editing were contributed by J.T., C.O., and A.S. Participation in methodology was by N.Y. and W.C. Conceptualization, validation, formal analysis, writing review editing, and project administration were conducted by C.T. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All authors confirm that all experiments were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. All experiments in this study were conducted in compliance with the Animal Ethics Committee in accordance with the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals, as prepared by the Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sengking, J., Oka, C., Yawoot, N. et al. Protective Effect of Neferine in Permanent Cerebral Ischemic Rats via Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms. Neurotox Res 40, 1348–1359 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00568-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00568-6