Abstract
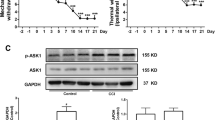
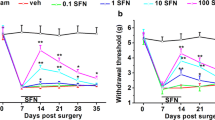
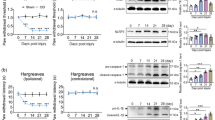
Neuropathic pain (NP) is a common disorder among individuals worldwide, but there is still no effective treatment for NP. The EGFR pathway promotes NP nociceptive sensitization and represents a potential therapeutic target. Geniposide is abundant in natural plants and has various pharmacological activities, such as analgesia and anti-inflammation properties, which can improve NP, but the specific mechanisms have not been elucidated. The present study first predicted and molecularly docked geniposide targets, suggesting that geniposide may play a role in improving NP by targeting EGFR. This study further clarified that geniposide alleviates NP and improves the inflammatory response using a chronic constriction injury (CCI) model, whereas the administration of an EGFR agonist weakens the above effects of geniposide. Analysis of transcriptome data further suggests that geniposide not only improves CCI symptoms by reducing EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway activity but also may exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the Ca2+ signaling pathway. The above results affirm the potential value of geniposide in the treatment of NP and lay the foundation for further clinical application.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borges JP, Mekhail K, Fairn GD, Antonescu CN, Steinberg BE (2021) Modulation of Pathological Pain by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Front Pharmacol 12:642820
Buteau J, Foisy S, Joly E, Prentki M (2003) Glucagon-like peptide 1 induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation via transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Diabetes 52:124–132
Cai L, Mu YR, Liu MM, Tang WJ, Li R (2020) Antidepressant-like effects of penta-acetyl geniposide in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression rat model: Involvement of inhibiting neuroinflammation in prefrontal cortex and regulating hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal axis. Int Immunopharmacol 80:106182
Cavalli E, Mammana S, Nicoletti F, Bramanti P, Mazzon E (2019) The neuropathic pain: An overview of the current treatment and future therapeutic approaches. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 33:2058738419838383
Chang DS, Hsu E, Hottinger DG, Cohen SP (2016) Anti-nerve growth factor in pain management: current evidence. J Pain Res 9:373–383
Chen P, Lin D, Wang C, Song C, Wang W, Qu J, Wu Z (2021) Proteomic Analysis of Emodin Treatment in Neuropathic Pain Reveals Dysfunction of the Calcium Signaling Pathway. J Pain Res 14:613–622
Chen Y, Shou K, Gong C, Yang H, Yang Y, Bao T (2018) Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Osteoarthritis by Suppressing the Activation of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int 2018:8384576
Dan XU, Yu-Xiang D, Feng W, Hong-Yan GE, You-Tian LI, Jiang Y, Li-Jie W (2013) Extraction of Geniposide and Its Application in Anesthesiology. Chem Res Chin Univ 29:724–729
Dreyling M, Jurczak W, Jerkeman M, Silva RS, Rusconi C, Trneny M, Offner F, Caballero D, Joao C, Witzens-Harig M et al (2016) Ibrutinib versus temsirolimus in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma: an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 387:770–778
Esposito MF, Malayil R, Hanes M, Deer T (2019) Unique Characteristics of the Dorsal Root Ganglion as a Target for Neuromodulation. Pain Med 20:S23–S30
Finnerup NB, Kuner R, Jensen TS (2021) Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol Rev 101:259–301
Gao Y, Sun N, Wang L, Wu Y, Ma L, Hong J, Ren J, Zhu B, Yu L, Yan M (2018) Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies p53 as a Candidate Prognostic Biomarker for Neuropathic Pain. Front Genet 9:320
Ghaly RF, Plesca A, Rana S, Candido KD, Knezevic NN (2018) Gabapentin-related suicide: Myth or fact. Surg Neurol Int 9:210
Gong N, Fan H, Ma AN, Xiao Q, Wang YX (2014) Geniposide and its iridoid analogs exhibit antinociception by acting at the spinal GLP-1 receptors. Neuropharmacology 84:31–45
Jackson NM, Ceresa BP (2017) EGFR-mediated apoptosis via STAT3. Exp Cell Res 356:93–103
Kersten C, Cameron MG, Laird B, Mjåland S (2015) Epidermal growth factor receptor-inhibition (EGFR-I) in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth 115:761–767
Lacagnina MJ, Watkins LR, Grace PM (2018) Toll-like receptors and their role in persistent pain. Pharmacol Ther 184:145–158
Leinders M, Koehrn FJ, Bartok B, Boyle DL, Shubayev V, Kalcheva I, Yu NK, Park J, Kaang BK, Hefferan MP et al (2014) Differential distribution of PI3K isoforms in spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia: potential roles in acute inflammatory pain. Pain 155:1150–1160
Liu W, Lv Y, Ren F (2018) PI3K/Akt Pathway is Required for Spinal Central Sensitization in Neuropathic Pain. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38:747–755
Martin LJ, Smith SB, Khoutorsky A, Magnussen CA, Samoshkin A, Sorge RE, Cho C, Yosefpour N, Sivaselvachandran S, Tohyama S et al (2017) Epiregulin and EGFR interactions are involved in pain processing. J Clin Invest 127:3353–3366
Pan T, Shi X, Chen H, Chen R, Wu D, Lin Z, Zhang J, Pan J (2018) Geniposide Suppresses Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Rat Chondrocytes via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 41:390–399
Ran D, Hong W, Yan W, Mengdie W (2021) Properties and molecular mechanisms underlying geniposide-mediated therapeutic effects in chronic inflammatory diseases. J Ethnopharmacol 273:113958
Rayiti RK, Munnangi SR, Bandarupalli R, Chakka V, Nimmagadda SL, Sk LS, Uppalapati S, Bolla R, Challa SR (2020) Effect of Chrysin on Mechanical Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constriction Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rat Model. Int J Appl Basic Med Res 10:189–193
Wang S, Liu S, Xu L, Zhu X, Liu W, Tian L, Chen Y, Wang Y, Nagendra B, Jia S et al (2019) The upregulation of EGFR in the dorsal root ganglion contributes to chronic compression of dorsal root ganglions-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Mol Pain 15:1744806919857297
Xiao H, Ma K, Huang D, Liu XG, Liu TH, Liu Q, Liu GZ, Song T, Tao W, Wu DS et al (2021) Expert consensus of the Chinese Association for the Study of Pain on ion channel drugs for neuropathic pain. World J Clin Cases 9:2100–2109
Xu D, Dong Y, Feng W, Ge H, Li Y, Jiang Y, Wang L, Song D (2013) Extraction of geniposide and its application in anesthesiology. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities 29
Zhang T, Zhang N, Zhang R, Zhao W, Chen Y, Wang Z, Xu B, Zhang M, Shi X, Zhang Q et al (2018) Preemptive intrathecal administration of endomorphins relieves inflammatory pain in male mice via inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling and regulation of inflammatory cytokines. J Neuroinflammation 15:320
Zhou L, Bao L, Wang Y, Chen M, Zhang Y, Geng Z, Zhao R, Sun J, Bao Y, Shi Y et al (2021) An Integrated Analysis Reveals Geniposide Extracted From Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis Regulates Calcium Signaling Pathway Essential for Influenza A Virus Replication. Front Pharmacol 12:755796
Funding
This study was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Fund Project (No.: 2017ZB082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DD Z and L Y designed the study. DD Z was responsible for animal and pathology and immunohistochemical experiments. QQ C was responsible for western blotting and statistical analysis. L Y obtained the funding and drafted the original manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The animal study conformed to the regulations on the administration of experimental animals of the Animal Ethics Committee of Ningbo University (Authorization number: NBU20210055).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Dd., Chen, Qq. & Yao, L. Geniposide Alleviates Neuropathic Pain in CCI Rats by Inhibiting the EGFR/PI3K/AKT Pathway And Ca2+ Channels. Neurotox Res 40, 1057–1069 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00531-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00531-5