Abstract
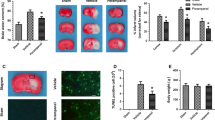
Edaravone has been widely used in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. However, there has been no oral preparation of edaravone in the clinic. In this study, we assessed the effect and possible mechanisms of oral edaravone on the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model in rats. Highly bioavailable form of novel edaravone formulation developed using self-nanomicellizing solid dispersion strategy which showed up to 16.1-fold improved oral bioavailability was considered oral edaravone. The male rats (n = 84) were randomly divided into sham; model; oral edaravone in low dose (10 mg/kg), medium dose (20 mg/kg), and high dose (30 mg/kg); and edaravone by intraperitoneal administration group (IP group, 10 mg/kg). Rats were treated with different drugs 5 h after the operation, twice a day for 7 days. The behavioral data were dose-dependently improved by oral edaravone and sensorimotor functions of the high dose group were similar to those of the edaravone by IP route group. Furthermore, oral edaravone significantly reduced cerebral infarction area and downregulated the levels of caspase-3, GFAP, Iba1, 3-NT, and 4-HNE, whereas upregulated those of Vamp-2 and Map-2 in a dose-dependent manner. Especially effect of the high dose on these molecules was equal to that of edaravone by IP administration. Taken together, our data suggest that the improvement of sensorimotor deficits by oral edaravone in high doses after ischemia is similar to that in edaravone by IP administration. Neuroprotection of oral edaravone is at least partial by minimizing oxidative stress, the overactivation of glial cells, and the levels of the apoptosis-associated proteins, and alleviating synaptic damage in a dose-dependent manner.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balkaya M, Kröber J, Gertz K, Peruzzaro S, Endres M (2013) Characterization of long-term functional outcome in a murine model of mild brain ischemia. J Neurosci Methods 213(2):179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.12.021
Bhandari R, Kuhad A, Kuhad A (2018) Edaravone: a new hope for deadly amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Drugs of today (Barcelona, Spain : 1998) 54(6):349–360. https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2018.54.6.2828189
Chen X, Sun Z, Wang J, Liang W, Zhao X, Wang Y, Wang Y (2020) Predicting the pharmacokinetic characteristics of edaravone intravenous injection and sublingual tablet through modeling and simulation. Clin Ther 42(3):428–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.01.006
Cruz DF, Fardilha M (2016) Relevance of peroxynitrite formation and 3-nitrotyrosine on spermatozoa physiology. Porto Biomed J 1(4):129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbj.2016.07.004
Enomoto A, Suzuki N, Morita A, Ito M, Liu CQ, Matsumoto Y, Yoshioka K, Shiba T, Hosoi Y (2003) Caspase-mediated cleavage of JNK during stress-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306(4):837–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(03)01050-7
Han J, Nepal P, Odelade A, Freely FD, Belton DM, Graves JL Jr, Maldonado-Devincci AM (2021) High-fat diet-induced weight gain, behavioral deficits, and dopamine changes in young C57BL/6J mice. Front Nutr 7:591161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.591161
Homma T, Kobayashi S, Sato H, Fujii J (2019) Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, protects against ferroptotic cell death in vitro. Exp Cell Res 384(1):111592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111592
Jiao L, Zhang J, Li Z, Liu H, Chen Y, Xu S (2011) Edaravone alleviates delayed neuronal death and long-dated cognitive dysfunction of hippocampus after transient focal ischemia in Wistar rat brains. Neuroscience 182:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.01.017
Kalinichenko SG, Korobtsov AV, Matveeva NY, Pushchin II (2020) Structural and chemical changes in glial cells in the rat neocortex induced by constant occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Acta Histochem 122(5):151573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151573
Kikuchi K, Kawahara K, Tancharoen S, Matsuda F, Morimoto Y, Ito T, Biswas KK, Takenouchi K, Miura N, Oyama Y, Nawa Y, Arimura N, Iwata M, Tajima Y, Kuramoto T, Nakayama K, Shigemori M, Yoshida Y, Hashiguchi T, Maruyama I (2009) The free radical scavenger edaravone rescues rats from cerebral infarction by attenuating the release of high-mobility group box-1 in neuronal cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329(3):865–874. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.149484
Léger CL, Torres-Rasgado E, Fouret G, Carbonneau MA (2008) First evidence for an LDL- and HDL-associated nitratase activity that denitrates albumin-bound nitrotyrosine–physiological consequences. IUBMB Life 60(1):73–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.14
Li Q, Qiu Z, Lu Y, Lu P, Wen J, Wang K, Zhao X, Li R, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Jia P, Fan P, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Lu H, Chen X, Liu Y, Zhang P (2019) Edaravone protects primary-cultured rat cortical neurons from ketamine-induced apoptosis via reducing oxidative stress and activating PI3K/Akt signal pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci 100:103399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2019.103399
Li X, Cheng S, Hu H, Zhang X, Xu J, Wang R, Zhang P (2020) Progranulin protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury by inhibiting necroptosis and oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 521(3):569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.111
Muralikrishna Adibhatla R, Hatcher JF (2006) Phospholipase A2, reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation in cerebral ischemia. Free Radical Biol Med 40(3):376–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.08.044
Parikh A, Kathawala K, Tan CC, Garg S, Zhou XF (2016) Development of a novel oral delivery system of edaravone for enhancing bioavailability. Int J Pharm 515(1–2):490–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.10.052
Parikh A, Kathawala K, Tan CC, Garg S, Zhou XF (2018) Self-nanomicellizing solid dispersion of edaravone: part I - oral bioavailability improvement. Drug Des Dev Ther 12:2051–2069. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S161940
Sekerdag E, Solaroglu I, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y (2018) Cell death mechanisms in stroke and novel molecular and cellular treatment options. Curr Neuropharmacol 16(9):1396–1415. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X16666180302115544
Sun JB, Li Y, Cai YF, Huang Y, Liu S, Yeung PK, Deng MZ, Sun GS, Zilundu PL, Hu QS, An RX, Zhou LH, Wang LX, Cheng X (2018) Scutellarin protects oxygen/glucose-deprived astrocytes and reduces focal cerebral ischemic injury. Neural Regen Res 13(8):1396–1407. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.235293
Sun Z, Xu Q, Gao G, Zhao M, Sun C (2019) Clinical observation in edaravone treatment for acute cerebral infarction. Niger J Clin Pract 22(10):1324–1327. https://doi.org/10.4103/njcp.njcp_367_18
Turnbull J (2018) Is edaravone harmful? (A placebo is not a control). Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis & Frontotemporal Degeneration 19(7–8):477–482. https://doi.org/10.1080/21678421.2018.1517179
Vaillant AR, Zanassi P, Walsh GS, Aumont A, Alonso A, Miller FD (2002) Signaling mechanisms underlying reversible, activity-dependent dendrite formation. Neuron 34(6):985–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00717-1
Wang J, Chen X, Yuan B, Wang W, Xu C, Zhao W, Zhao P, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wang Y (2018) Bioavailability of edaravone sublingual tablet versus intravenous infusion in healthy male volunteers. Clin Ther 40(10):1683–1691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.08.009
Yoshino H (2019) Edaravone for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Rev Neurother 19(3):185–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2019.1581610
Yuan Y, Zha H, Rangarajan P, Ling EA, Wu C (2014) Anti-inflammatory effects of edaravone and scutellarin in activated microglia in experimentally induced ischemia injury in rats and in BV-2 microglia. BMC Neurosci 15:125. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-014-0125-3
Zhao N, Xu X, Jiang Y, Gao J, Wang F, Xu X, Wen Z, Xie Y, Li J, Li R, Lv Q, Liu Q, Dai Q, Liu X, Xu G (2019) Lipocalin-2 may produce damaging effect after cerebral ischemia by inducing astrocytes classical activation. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):168. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1556-7
Zhang J, Shi Q, Yang P, Xu X, Chen X, Qi C, Zhang J, Lu H, Zhao B, Zheng P, Zhang P, Liu Y (2012) Neuroprotection of neurotrophin-3 against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury is regulated by hypoxia-responsive element in rats. Neuroscience 222:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.07.023
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (2019FA031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design: HY Luo and XF Zhou. Study conduct: Li-Qin Zhao, Ankit Parikh, and Y-Guo. Data collection: YX Xiong. Data analysis: QY Ye. Data interpretation: Li-Qin Zhao. Drafting manuscript: LQ Zhao and HY Luo. Revising manuscript content: XF Zhou. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, LQ., Parikh, A., Xiong, YX. et al. Neuroprotection of Oral Edaravone on Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats. Neurotox Res 40, 995–1006 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00520-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00520-8