Abstract
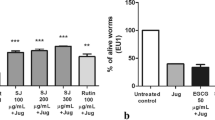
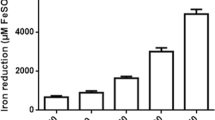
The development, at the experimental level, of therapeutic strategies based on natural products to attenuate neurological alterations in degenerative disorders has gained attention. Antioxidant molecules exhibit both anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Alpha-mangostin (α-Man) is a natural xanthonoid isolated from the mangosteen tree with demonstrated antioxidant and cytoprotective properties. In this study, we investigated the antioxidant and protective properties of α-Man, both ex vivo and in vivo. We assessed the mitochondrial reductant capacity and oxidative damage to lipids in rat cortical slices, and several endpoints characteristic of physiological stress in the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), upon exposure to the parkinsonian neurotoxin, 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). In rat cortical slices, α-Man (25 and 50 µM) reduced the 6-OHDA (100 µM)-induced oxidative damage to lipid levels, but failed to reverse loss in cell viability. In wild-type (N2) C. elegans, α-Man (5–100 µM) protected against 6-OHDA (25 mM)-induced decrease in survival when administered either as pre- or post-treatment. Protective effects of α-Man were also observed on survival in the VC1772 strain (skn-1 KO−) exposed to 6-OHDA, though the extent of the protection was lesser than in the wild-type N2 strain. However, α-Man (5–50 µM) failed to attenuate the 6-OHDA-induced motor alterations in the N2 strain. The loss of lifespan induced by 6-OHDA in the N2 strain was fully reversed by high concentrations of α-Man. In addition, while 6-OHDA decreased the expression of glutathione S-transferase in the CL2166 C. elegans strain, α-Man preserved and stimulated the expression of this protein. α-Man (25 µM) also prevented 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the BZ555 C. elegans strain. Altogether, our novel results suggest that α-Man affords partial protection against several, but not all, short-term toxic effects induced by 6-OHDA in cortical slices and in a skn-1-dependent manner in C. elegans.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An JH, Blackwell TK (2003) SKN-1 links C. elegans mesendodermal specification to a conserved oxidative stress response. Genes Develop 17:1882–1893
Blackwell TK, Steinbaugh MJ, Hourihan JM, Ewald CY, Isik M (2015) SKN-1/Nrf, stress responses, and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Free Radic Biol Med 88:290–301
Blandini F, Armentero MT (2012) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J 279:1156–1166
Chavan T, Muth A (2021) The diverse bioactivity of alpha-mangostin and its therapeutic implications. Future Med Chem 13:1679–1694
Colín-González AL, Luna-López A, Königsberg M, Ali SF, Pedraza-Chaverrí J, Santamaría A (2014) Early modulation of the transcription factor Nrf2 in rodent striatal slices by quinolinic acid, a toxic metabolite of the kynurenine pathway. Neuroscience 260:130–139
Colonnello A, Kotlar I, de Lima ME, Ortíz-Plata A, García-Contreras R, Antunes Soares FA, Aschner M, Santamaría A (2018) Comparing the effects of ferulic acid and sugarcane aqueous extract in in vitro and in vivo neurotoxic models. Neurotox Res 34:640–648
Do HTT, Cho J (2020) Mangosteen pericarp and its bioactive xanthones: potential therapeutic value in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and depression with pharmacokinetic and safety profiles. Int J Mol Sci 21:6211
Fang Y, Su T, Qiu X, Mao P, Xu Y, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Xie P, Liu Q (2016) Protective effect of alpha-mangostin against oxidative stress induced-retinal cell death. Sci Rep 6:21018
Fu T, Li H, Zhao Y, Cai E, Zhu H, Li P, Liu J (2018) Hepatoprotective effect of α-mangostin against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 106:896–901
Hao XM, Li LD, Duan CL, Li YJ (2017) Neuroprotective effect of alpha-mangostin on mitochondrial dysfunction and alpha-synuclein aggregation in rotenone-induced model of Parkinson’s disease in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res 19:833–845
He C-L, Tang Y, Wu J-M, Long T, Yu L, Teng J-F, Qiu W-Q, Pan R, Yu C-L, Qin D-L, Wu AG, Zhou X-G (2021) Chlorogenic acid delays the progression of Parkinson’s disease via autophagy induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutr Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2021.2009993
Hu Z, Wang W, Ling J, Jiang C (2016) α-Mangostin inhibits α-synuclein-induced microglial neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36:811–820
Ibrahim KA, Eleyan M, Khwanes SA, Mohamed RA, Ayesh BM (2021) Alpha-mangostin attenuates the apoptotic pathway of abamectin in the fetal rats’ brain by targeting pro-oxidant stimulus, catecholaminergic neurotransmitters, and transcriptional regulation of reelin and nestin. Drug Chem Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2021.1960856 (In press)
Jaisin Y, Ratanachamnong P, Kuanpradit C, Khumpum W, Suksamrarn S (2018) Protective effects of γ-mangostin on 6-OHDA-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Lett 5:229–235
Joshi G, Johnson JA (2012) The Nrf2-ARE pathway: a valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 7:218–229
Jung H, Su B, Keller W, Mehta R, Kinghorn A (2006) Antioxidant xanthones from the pericarp of Garcinia mangostana (Mangosteen). J Agric Food Chem 54:2077–2082
Khaw K, Ong YS, Goh BH (2020) A rapid method for the retrieval of bioactive xanthone from Garcinia mangostana: a case study of α-mangostin. Prog Drug Disc Biomed Sci 3:1–5
Kotlar I, Colonnello A, Aguilera-González MF, Avila DS, de Lima ME, García-Contreras R, Ortíz-Plata A, Soares FAA, Aschner M, Santamaría A (2018) Comparison of the toxic effects of quinolinic acid and 3-nitropropionic acid in C. elegans: involvement of the SKN-1 pathway. Neurotox Res 33:259–267
Markowickz J, Uram L, Sobich J, Mangiardi L, Maj P, Rode W (2019) Antitumor and anti-nematode activities of α-mangostin. Eur J Pharmacol 863:172678
Márquez-Valadez B, Lugo-Huitrón R, Valdivia-Cerda V, Miranda-Ramírez LR, Pérez-De La Cruz V, González-Cuahutencos O, Rivero-Cruz I, Mata R, Santamaría A, Pedraza-Chaverrí J (2009) The natural xanthone alpha-mangostin reduces oxidative damage in rat brain tissue. Nutr Neurosci 12:35–42
Márquez-Valadez B, Maldonado PD, Galván-Arzate S, Méndez-Cuesta LA, Pérez-De La Cruz V, Pedraza-Chaverrí J, Chánez-Cárdenas ME, Santamaría A (2012) Alpha-mangostin induces changes in glutathione levels associated with glutathione peroxidase activity in rat brain synaptosomes. Nutr Neurosci 15:13–19
Martínez A, Hernández-Marin E, Galano A (2012) Xanthones as antioxidants: a theoretical study on the thermodynamics and kinetics of the single electron transfer mechanism. Food Funct 3:442–450
Martínez-Finley EJ, Caito S, Slaughter JC, Aschner M (2013) The role of SKN-1 in methylmercury-induced latent dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neurochem Res 38:2650–2660
Nass R, Blakely RD (2003) The Caenorhabditis elegans dopaminergic system: opportunities for insights into dopamine transport and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:521–544
Nass R, Hall DH, Miller DM III, Blakely RD (2002) Neurotoxin-induced degeneration of dopamine neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:3264–3269
Nava Catorce M, Acero G, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Fragoso G, Govezensky T, Gevorkian G (2016) Alpha-mangostin attenuates brain inflammation induced by peripheral lipopolysaccharide administration in C57BL/6J mice. J Neuroimmunol 297:20–27
Ovalle-Magallanes B, Eugenio-Pérez D, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2017) Medicinal properties of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.): a comprehensive update. Food Chem Toxicol 109:102–122
Parkhe A, Parekh P, Nalla LV, Sharma N, Sharma M, Gadepalli A, Kate A, Khairnar A (2020) Protective effect of alpha mangostin on rotenone induced toxicity in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 716:134652
Pedraza-Chaverrí J, Reyes-Fermín LM, Nolasco-Amaya EG, Orozco-Ibarra M, Medina-Campos ON, González-Cuahutencos O, Rivero-Cruz I, Mata R (2009) ROS scavenging capacity and neuroprotective effect of alpha-mangostin against 3-nitropropionic acid in cerebellar granule neurons. Exp Toxicol Pathol 61:491–501
Powolny AA, Singh SV, Melov S, Hubbard A, Fisher AL (2011) The garlic constituent diallyl trisulfide increases the lifespan of C. elegans via skn-1 activation. Exp Gerontol 46:441–452
Salam S, Ansari A, Amon S, Rezai P, Selvaganapathy PR, Mishra RK, Gupta BP (2013) A microfluidic phenotype analysis system reveals function of sensory and dopaminergic neuron signaling in C. elegans electrotactic swimming behavior. Worm 2:e24558
Shashikumar S, Pradeepa H, Chinnu S, Rajini PS, Rajanikant GK (2015) Alpha-linolenic acid suppresses dopaminergic neurodegeneration induced by 6-OHDA in C. elegans. Physiol Behav 151:563–569
Staab TA, Griffen TC, Corcoran C, Evgrafov O, Knowles JA, Sieburth D (2013) The conserved SKN-1/Nrf2 stress response pathway regulates synaptic function in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet 9:e1003354
Strange K (2006) An overview of C. elegans biology. Methods Mol Biol 351:1–11
Thammawong N, Takahashi H, Sugawara T, Sakamoto K (2018) α-Mangostin promotes DAF-16-mediated thermotolerance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Nutr Sci 9:693–702
Thirugnanam T, Santhakumar K (2022) Chemically induced models of Parkinson’s disease. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109213
Wang F, Ma H, Liu Z, Huang W, Xu X, Zhang X (2017) α-Mangostin inhibits DMBA/TPA-induced skin cancer through inhibiting inflammation and promoting autophagy and apoptosis by regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 92:672–680
Xu Q, Ma J, Lei J, Duan W, Sheng L, Chen X, Hu A, Wang Z, Wu Z, Wu E, Ma Q, Li X (2014) α-Mangostin suppresses the viability and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biomed Res Int 2014:546353
Zhao L-X, Wang Y, Liu T, Wang Y-X, Chen H-Z, Xu J-R, Qiu Y (2017) α-Mangostin decreases β-amyloid peptides production via modulation of amyloidogenic pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 23:526–534
Funding
MA was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIEHS) grant numbers NIEHS R01ES07331 and R01ES10563.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Estrada-Valencia, R., Hurtado-Díaz, M.E., Rangel-López, E. et al. Alpha-Mangostin Alleviates the Short-term 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Damage in Rat Cortical Slices and in Caenorhabditis elegans. Neurotox Res 40, 573–584 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00493-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00493-8