Abstract
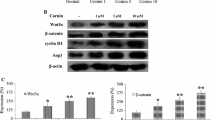
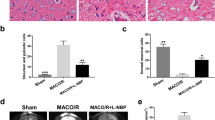
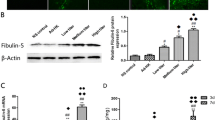
Cerebral damage following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury affects the neurological deficits and motor impairment of stroke patients in the long-term period. Angiogenesis, the essential process for restoration of cerebral blood flow (CBF) in the ischemic brain, promotes the recovery of neurological function following ischemia. The aim of this study was to investigate the long-term effects of morin on angiogenesis and functional outcomes in a middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and reperfusion model. Male Wistar rats were subjected to MCAO, and they were administered 30 mg/kg of morin at reperfusion via i.p. injection daily for 14 days. Fourteen days after I/R injury, the rats were evaluated for the brain damage, and angiogenic factors involved in Ang1/Tie-2 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In addition, at 1, 7, and 14 days after reperfusion, rotarod and pole tests were performed to investigate the functional recovery. We found morin significantly reduced the infarct size, blood–brain barrier (BBB) leakage, and apoptotic cells at 14 days after I/R injury. It also promoted angiogenesis via boosting the expression of angiogenic proteins, such as angiopoietin 1 (Ang1), Tie-2, Wnt3α, β-catenin, and cyclin D1. Morin-mediated angiogenesis was confirmed by a significant increase in microvessel’s density in the penumbra area and an increase in von Willebrand factor (vWF) protein expression of the morin-treated rats. Moreover, the rotarod and pole tests also demonstrated morin increased functional recovery in the morin-treated rats compared to the vehicle rats. Therefore, our data exposed that morin promotes angiogenesis and improves functional outcomes in MCAO and reperfusion rats.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Data available on request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- Ang1:
-
Angiopoietin 1
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
- I/R:
-
Ischemia/reperfusion
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- NRP-1:
-
Neuropilin-1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- t-PA:
-
Tissue-plasminogen activator
- TTC:
-
2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- vWF:
-
Von Willebrand factor
References
Ansari S, Azani H, McConnell DJ, Afzal A, Mocco J (2011) Intraluminal middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model for ischemic stroke with laser doppler flowmetry guidance in mice. JoVE 8:2879. https://doi.org/10.3791/2879
Ashwal S, Tone B, Tian HR, Cole DJ, Liwnicz BH et al (1999) Core and penumbral nitric oxide synthase activity during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in the rat pup. Pediatr Res 46:390–400. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199910000-00006
Beck H, Acker T, Wiessner C, Allegrini PR, Plate KH (2000) Expression of angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, and Tie receptors after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Am J Pathol 157:1473–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64786-4
Chen J, Cui X, Zacharek A, Chopp M (2009) Increasing Ang1/Tie-2 expression by simvastatin treatment induces vascular stabilization and neuroblast migration after stroke. J Cell Mol Med 13:1348–1357. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00380.x
Chen JY, Yu Y, Yuan Y, Zhang YJ, Fan XP et al (2017) Enriched housing promotes post-stroke functional recovery through astrocytic HMGB1-IL-6-mediated angiogenesis. Cell Death Dis 3:17054. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2017.54
Croll SD, Wiegand SJ (2001) Vascular growth factors in cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 23:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:23:2-3:121
Donnan GA, Fischer M, Maeleod M, Davis SM (2008) Stroke Lancet 371:1612–1623. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(08)60694-7
Gandin C, Widemann C, Lazdunski M, Heruteaux C (2016) MLC901 favors angiogenesis and associated recovery after ischemic stroke in mice. Cerebrovasc Dis 42:139–154. https://doi.org/10.1159/000444810
Hayashi T, Noshita N, Sugawara T, Chan PH (2003) Temporal profile of angiogenesis and expression of related genes in the brain after ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:166–180. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.WCB.0000041283.53351.CB
Janyou A, Wicha P, Jittiwat J, Suksamrarn A, Tocharus C et al (2017) Dihydrocapsaicin attenuates blood brain barrier and cerebral damage in focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via oxidative stress and inflammatory. Sci Rep 7:10556. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11181-5
Janyou A, Wicha P, Seechamnanturakit V, Bumroongkit K, Tocharus C et al (2020) Dihydrocapsaicin-induced angiogenesis and improved functional recovery after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in a rat model. J Pharmacol Sci 143:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2020.02.001
Johnston SC, Mendis S, Mathers CD (2009) Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: estimates from monitoring, surveillance, and modeling. Lancet Neurol 8:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70023-7
Khamchai S, Chumboatong W, Hata J, Tocharus C, Suksamran A et al (2020) Morin protects the blood-brain barrier integrity against cerebral ischemia reperfusion through anti-inflammatory actions in rats. Sci Rep 10:13379. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70214-8
Kim HK, Cheon BS, Kim YH, Kim SY, Kim HP (1999) Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure-activity relationships. Biochem Pharmacol 58:759–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00160-4
Krupinski J, Kaluza J, Kumar P, Kumar S, Wang JM (2007) Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 9:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.25.9.1794
Lee HS, Jung KH, Hong SW, Park IS, Lee C et al (2008) Morin protects acute liver damage by carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)) in rat. Arch Pharm Res 31:1160–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1283-5
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Commin R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.20.1.84
Marti HJ, Bernaudin M, Bellail A, Schoch H, Euler M et al (2000) Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression precedes neovascularization after cerebral ischemia. Am J Pathol 156:965–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64964-4
Martowicz A, Trusohamn M, Jensen N, Wisniewska-Kruk J, Corada M et al (2019) Endothelial β-catenin signaling supports postnatal brain and retinal angiogenesis by promoting sprouting, tip cell formation, and VEGFR (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor) 2 expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 39:2273–2288. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312749
Mey L, Hormann M, Schleicher N, Reuter P, Donges S (2013) Neuropilin-1 modulates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced poly (ADP ribose)-polymerase leading to reduced cerebrovascular apoptosis. Neurobiol Dis 59:111–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2013.06.009
Moss A (2013) The angiopoietin: Tie 2 interaction: a potential target for future therapies in human vascular disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 24:579–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.05.009
Oh WK, Lee CH, Lee MS, Bae EY, Sohn CB et al (2004) Antidiabetic effects of extracts from Psidium guajava. J Ethnopharmacol 96:411–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2004.09.041
Pettersson A, Nagy JA, Brown LF (2000) Heterogeneity of the angiogenic response induced in different normal adult tissues by vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor. Lab Invest 80:99–115. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.3780013
Pundik S, Xu K, Sundararajan S (2012) Reperfusion brain injury: focus on cellular bioenergetics. Neurology 79:44–51
Talwar T, Srivastava MV (2014) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor and other growth factors in post-stroke recovery. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 17:1–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-2327.128519
Uyar Z, Boke N, Turkay E, Koz O, Yasa I et al (2006) Flavonoid glycosides and methylinositol from Ebenus haussknechtii. Nat Prod Res 20:999–1007. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786410600921516
Widgerow AD (2014) Ischemia-reperfusion injury: influencing the microcirculatory and cellular environment. Ann Plast Surg 72:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.013e31852c089c
Wong KS, Chen C, Ng PW, Tsoi TH, Li HL et al (2007) Low-molecular-weight heparin compared with aspirin for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke in Asian patients with large artery occlusive disease: a randomized study. Lancet Neurol 6:407–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70079-0
Xu Y, Zhang G, Kang Z, Xu Y, Jiang W et al (2016) Cornin increases angiogenesis and improves functional recovery after stroke via the Ang1/Tie2 axis and the Wnt/b-catenin pathway. Arch Pharm Res 39:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0652-1
Yang Y, Rosenberg GA (2011) Blood-brain barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 42:3323–3328. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.608257
Zhang R, Kang KA, Piao MJ, Maeng YH, Lee KH et al (2008) Cellular protection of morin against the oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Chem Biol Interact 177:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2008.08.009
Zhang Z, Chop M (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoeitins in focal cerebral ischemia. Tradit Chin Med 12:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1050-1738(01)00149-9
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Chiang Mai University, Center for Research and Development of Natural Products for Health, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University grant no. 39/2564, The Thailand Research Fund (DBG6180030), the Center of Excellence for Innovation in Chemistry, Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation, and the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Program (PHD/0011/2558 SK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Satchakorn Khamchai, Jiraporn Tocharus; Methodology: Satchakorn Khamchai, Wijitra Chumboatong, Janejira Hata, Chainarong Tocharus, Apichart Suksamrarn; Formal analysis and investigation: Satchakorn Khamchai, Jiraporn Tocharus; Writing-original draft preparation: Satchakorn Khamchai; Writing-review and editing: Jiraporn Tocharus, Apichart Suksamrarn; Funding acquisition: Jiraporn Tocharus, Apichart Suksamrarn; Supervision: Jiraporn Tocharus.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khamchai, S., Chumboatong, W., Hata, J. et al. Morin Attenuated Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Promoting Angiogenesis Mediated by Angiopoietin-1-Tie-2 Axis and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Neurotox Res 40, 14–25 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00470-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00470-7