Abstract
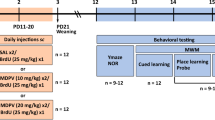
Exposure to cyanuric acid (CA) causes multiple organ failure accompanied by the involvement in kinds of target proteins, which are detectable and play central roles in the CNS. The hippocampus has been identified as a brain area which was especially vulnerable in developmental condition associated with cognitive dysfunction. No studies have examined the effects of CA on hippocampal function after in vitro or in vivo treatment. Here, we aimed to examine hippocampal synaptic function and adverse behavioral effects using a rat model administered CA intraperitoneally or intrahippocampally. We found that infusion of CA induced a depression in the frequency but not the amplitude of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs), miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs), or N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) of the CA1 neurons in dose-dependent pattern. Both intraperitoneal and intrahippocampal injections of CA suppressed hippocampal LTP from Schaffer collaterals to CA1 regions. Paired-pulse facilitation (PPF), a presynaptic phenomenon, was enhanced while the total and phosphorylated expression of NMDA-GluN1, NMDA-GluN2A, and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-GluA1 subunits were comparable between CA-treated and control groups. In Morris water maze test, both groups could effectively learn and retain spatial memory. Our studies provide the first evidence for the neurotoxic effect of CA and the insight into its potential mechanisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WC, Logan B, Greenwood JM, Dragunow M (2002) Induction and experience-dependent consolidation of stable long-term potentiation lasting months in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 22:9626–9634
An L, Fu J, Zhang T (2015) Reversible effects of vitamins C and E combination on cognitive deficits and oxidative stress in the hippocampus of melamine-exposed rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 132:152–159
An L, Li J, Luo L, Huang P, Liu P, Tang C, Sun W (2019) Prenatal melamine exposure impairs cognitive flexibility and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in adolescent and adult female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 186:172791
An L, Li X, Tang C, Xu N, Sun W (2018) Hippocampal proBDNF facilitates place learning strategy associated with neural activity in rats. Brain Struct Funct 223:4099–4113
An L, Li Z, Yang Z, Zhang T (2011) Cognitive deficits induced by melamine in rats. Toxicol Lett 206:276–280
An L, Li Z, Yang Z, Zhang T (2012a) Melamine induced cognitive impairment associated with oxidative damage in rat’s hippocampus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 102:196–202
An L, Li Z, Zhang T (2014) Reversible effects of vitamins C and E combination on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in melamine-treated PC12 cells. Free Radic Res 48:239-250
An L, Liu S, Yang Z, Zhang T (2012b) Cognitive impairment in rats induced by nano-CuO and its possible mechanisms. Toxicol Lett 213:220–227
An L, Sun W (2017a) A brief review of neurotoxicity induced by melamine. Neurotox Res 32:301–309
An L, Sun W (2017b) Prenatal melamine exposure impairs spatial cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity by presynaptic and postsynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic transmission in adolescent offspring. Toxicol Lett 269:55–64
An L, Sun W (2017c) Prenatal melamine exposure induces impairments of spatial cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in female adolescent rats. Neurotoxicology 62:56–63
An L, Sun W (2018) Acute melamine affects spatial memory consolidation via inhibiting hippocampal NMDAR-dependent LTD in rats. Toxicol Sci 163:385–396
An L, Yang Z, Zhang T (2013a) Imbalanced synaptic plasticity induced spatial cognition impairment in male offspring rats treated with chronic prenatal ethanol exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37:763–770
An L, Yang Z, Zhang T (2013b) Melamine induced spatial cognitive deficits associated with impairments of hippocampal long-term depression and cholinergic system in Wistar rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 100:18–24
An L, Zhang T (2013) Spatial cognition and sexually dimorphic synaptic plasticity balance impairment in rats with chronic prenatal ethanol exposure. Behav Brain Res 256:564–574
An L, Zhang T (2014a) Prenatal melamine exposure induces impairments of spatial cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in male adolescent rats. Reprod Toxicol 49:78–85
An L, Zhang T (2014b) Vitamins C and E reverse melamine-induced deficits in spatial cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in rats. Neurotoxicology 44:132–139
An L, Zhang T (2015) Prenatal ethanol exposure impairs spatial cognition and synaptic plasticity in female rats. Alcohol 49:581–588
An L, Zhang T (2016) Comparison impairments of spatial cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity between prenatal and postnatal melamine exposure in male adult rats. Neurotox Res 29:218–229
Anaeigoudari A et al (2015) The effects of L-arginine on spatial memory and synaptic plasticity impairments induced by lipopolysaccharide Adv. Biomed Res 4:202
Auger ML, Meccia J, Galea LAM, Floresco SB (2019) Disinhibition of the prefrontal cortex leads to brain-wide increases in neuronal activation that are modified by spatial learning. Brain Struct Funct 224:171–190
Baxter PS et al (2015) Synaptic NMDA receptor activity is coupled to the transcriptional control of the glutathione system. Nat Commun 6:6761
Berberich S, Jensen V, Hvalby O, Seeburg PH, Kohr G (2007) The role of NMDAR subtypes and charge transfer during hippocampal LTP induction. Neuropharmacology 52:77–86
Bi G, Poo M (1999) Distributed synaptic modification in neural networks induced by patterned stimulation. Nature 401:792–796
Blank T, Nijholt I, Spiess J (2004) Molecular determinants mediating effects of acute stress on hippocampus-dependent synaptic plasticity and learning. Mol Neurobiol 29:131–138
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39
Bondy SC, Campbell A (2005) Developmental neurotoxicology. J Neurosci Res 81:605–612
Braekevelt E, Lau BP, Feng S, Menard C, Tittlemier SA (2011) Determination of melamine, ammeline, ammelide and cyanuric acid in infant formula purchased in Canada by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 28:698-704
Busanello EN et al (2011) Neurochemical evidence that pristanic acid impairs energy production and inhibits synaptic Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in brain of young rats. Neurochem Res 36:1101-1107
Camera D et al (2016) Learning, memory and long-term potentiation are altered in Nedd4 heterozygous mice. Behav Brain Res 303:176-181
Cardoso BR, Hare DJ, Bush AI, Roberts BR (2017) Glutathione peroxidase 4: a new player in neurodegeneration? Mol Psychiatry 22:328–335
Chang L, Yue Z, She R, Sun Y, Zhu J (2015) The toxic effect of a mixture of melamine and cyanuric acid on the gastrointestinal tract and liver in mice. Res Vet Sci 102:234–237
Chen B, Liu X, Li S, Zhou Y, Jiang Q (2009) Melamine exposure assessment in children with nephrolithiasis. Pediatr Nephrol 24:2065–2067
Chen YT et al (2013) Effects of sodium citrate on melamine-cyanuric acid mixture-induced urolithiasis in rats. Clin Chim Acta 424:76–82
Cullen CL, Burne TH, Lavidis NA, Moritz KM (2014) Low dose prenatal alcohol exposure does not impair spatial learning and memory in two tests in adult and aged rats. PLoS One 9:e101482
de Lores Arnaiz GR, Ordieres MG (2014) Brain Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in aging and disease. Int J Biomed Sci 10:85-102
Dobson RL et al (2008) Identification and characterization of toxicity of contaminants in pet food leading to an outbreak of renal toxicity in cats and dogs. Toxicol Sci 106:251–262
Dorne JL et al (2013) Recent advances in the risk assessment of melamine and cyanuric acid in animal feed. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 270:218–229
Gao H, Han Z, Huang S, Bai R, Ge X, Chen F, Lei P (2017) Intermittent hypoxia caused cognitive dysfunction relate to miRNAs dysregulation in hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 335:80–87
Gilbert M, Kelly M, Samsam T, Goodman J (2005) Chronic developmental lead exposure reduces neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus but does not impair spatial learning. Toxicol Sci 86:365–374
Goldschmith A, Infante C, Leiva J, Motles E, Palestini M (2005) Interference of chronically ingested copper in long-term potentiation (LTP) of rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1056:176-182
Gonzalez J et al (2009) Nephrotoxicosis in Iberian piglets subsequent to exposure to melamine and derivatives in Spain between 2003 and 2006. J Vet Diagn Invest 21:558–563
Gustafsson B, Wigstrom H (1990) Long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region: its induction and early temporal development. Prog Brain Res 83:223-232
Han G, An L, Yang B, Si L, Zhang T (2014) Nicotine-induced impairments of spatial cognition and long-term potentiation in adolescent male rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 33:203–213
Han H, Peng Y, Dong Z (2015) D-Serine rescues the deficits of hippocampal long-term potentiation and learning and memory induced by sodium fluoroacetate. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 133:51–56
He C et al (2016) Superficial layer-specific histaminergic modulation of medial entorhinal cortex required for spatial learning. Cereb Cortex 26:1590–1608
Herry C, Garcia R (2003) Behavioral and paired-pulse facilitation analyses of long-lasting depression at excitatory synapses in the medial prefrontal cortex in mice. Behav Brain Res 146:89–96
Hoh T, Beiko J, Boon F, Weiss S, Cain DP (1999) Complex behavioral strategy and reversal learning in the water maze without NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 19:RC2
Hosseiny S, Pietri M, Petit-Paitel A, Zarif H, Heurteaux C, Chabry J, Guyon A (2015) Differential neuronal plasticity in mouse hippocampus associated with various periods of enriched environment during postnatal development. Brain Struct Funct 220:3435–3448
Huang CH, Moser T (2018) Ca(2+) Regulates the kinetics of synaptic vesicle fusion at the afferent inner hair cell synapse. Front Cell Neurosci 12:364
Hullinger R, O'Riordan K, Burger C (2015) Environmental enrichment improves learning and memory and long-term potentiation in young adult rats through a mechanism requiring mGluR5 signaling and sustained activation of p70s6k. Neurobiol Learn Mem 125:126-134
Jacob CC, Von Tungeln LS, Vanlandingham M, Beland FA, Gamboa da Costa G (2012) Pharmacokinetics of melamine and cyanuric acid and their combinations in F344 rats. Toxicol Sci 126:317-324
Klanker M, Post G, Joosten R, Feenstra M, Denys D (2013) Deep brain stimulation in the lateral orbitofrontal cortex impairs spatial reversal learning. Behav Brain Res 245:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.01.043
Lee IC et al (2016) Melamine and cyanuric acid co-exposure causes renal dysfunction and structural damage via MAPKs and mitochondrial signaling. Food Chem Toxicol 96:254–262
Leiva J, Palestini M, Infante C, Goldschmidt A, Motles E (2009) Copper suppresses hippocampus LTP in the rat, but does not alter learning or memory in the morris water maze. Brain Res 1256:69-75
Li C, Wang W, Kwon TH, Knepper MA, Nielsen S, Frokiaer J (2003) Altered expression of major renal Na transporters in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F155-166
Li C, Wang W, Norregaard R, Knepper MA, Nielsen S, Frokiaer J (2007) Altered expression of epithelial sodium channel in rats with bilateral or unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F333-341
Li X, Sun W, An L (2018a) Nano-CuO impairs spatial cognition associated with inhibiting hippocampal long-term potentiation via affecting glutamatergic neurotransmission in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 34:409–421
Li X, Sun W, An L (2018b) Nano-CuO impairs spatial cognition associated with inhibiting hippocampal LTP via affecting glutamatergic neurotransmission in rats. Toxicol Ind Health. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233718758233
Liang X et al (2019) Exercise improves depressive symptoms by increasing the number of excitatory synapses in the hippocampus of CUS-Induced depression model rats. Behav Brain Res 374:112115
Lv Y, Liu Z, Tian Y, Chen H (2013) Effect on morphology, oxidative stress and energy metabolism enzymes in the testes of mice after a 13-week oral administration of melamine and cyanuric acid combination. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 65:183-188
Ma C, Kang H, Liu Q, Zhu R, Cao Z (2011) Insight into potential toxicity mechanisms of melamine: an in silico study. Toxicology 283:96–100
Ma Z et al (2012) Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is the pore-forming subunit of an ion channel that mediates extracellular Ca2+ regulation of neuronal excitability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E1963-1971
Meiri N, Sun MK, Segal Z, Alkon DL (1998) Memory and long-term potentiation (LTP) dissociated: normal spatial memory despite CA1 LTP elimination with Kv1.4 antisense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15037-15042
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Morris RG, Garrud P, Rawlins JN, O’Keefe J (1982) Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297:681–683
Moura AP et al (2018) Glycine administration alters MAPK signaling pathways and causes neuronal damage in rat brain: putative mechanisms involved in the neurological dysfunction in nonketotic hyperglycinemia. Mol Neurobiol 55:741–750
Moura AP, Ribeiro CA, Zanatta A, Busanello EN, Tonin AM, Wajner M (2012) 3-Methylcrotonylglycine disrupts mitochondrial energy homeostasis and inhibits synaptic Na(+),K (+)-ATPase activity in brain of young rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:297-307
Muhammad A, Mychasiuk R, Hosain S, Nakahashi A, Carroll C, Gibb R, Kolb B (2013) Training on motor and visual spatial learning tasks in early adulthood produces large changes in dendritic organization of prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens in rats given nicotine prenatally. Neuroscience 252:178–189
Nilubol D, Pattanaseth T, Boonsri K, Pirarat N, Leepipatpiboon N (2009) Melamine- and cyanuric acid-associated renal failure in pigs in Thailand. Vet Pathol 46:1156–1159
O’Keefe J, Dostrovsky J (1971) The hippocampus as a spatial map preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res 34:171–175
Pacini N et al (2013) Antioxidant responses and renal crystal formation in rainbow trout treated with melamine administered individually or in combination with cyanuric acid. J Toxicol Environ Health A 76:491–508
Pang J et al (2013) Toxicokinetic study of melamine in the presence and absence of cyanuric acid in rats. J Appl Toxicol 33:444–450
Park D et al (2011) Increased nephrotoxicity after combined administration of melamine and cyanuric Acid in rats. Lab Anim Res 27:25–28
Puschner B, Poppenga RH, Lowenstine LJ, Filigenzi MS, Pesavento PA (2007) Assessment of melamine and cyanuric acid toxicity in cats. J Vet Diagn Invest 19:616–624
Reimschuessel R et al (2008) Evaluation of the renal effects of experimental feeding of melamine and cyanuric acid to fish and pigs. Am J Vet Res 69:1217–1228
Robillard JM, Gordon GR, Choi HB, Christie BR, MacVicar BA (2011) Glutathione restores the mechanism of synaptic plasticity in aged mice to that of the adult. PLoS One 6:e20676
Salazar-Weber NL, Smith JP (2011) Copper inhibits NMDA receptor-independent LTP and modulates the paired-pulse ratio after LTP in mouse hippocampal slices. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:864753
Sathyanarayana S et al (2019) Melamine and cyanuric acid exposure and kidney injury in US children. Environ Res 171:18–23
Schmajuk NA (1990) Role of the hippocampus in temporal and spatial navigation: an adaptive neural network. Behav Brain Res 39:205–229
Sedlak TW et al (2019) The glutathione cycle shapes synaptic glutamate activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:2701–2706
Sorrells SF, Munhoz CD, Manley NC, Yen S, Sapolsky RM (2014) Glucocorticoids increase excitotoxic injury and inflammation in the hippocampus of adult male rats. Neuroendocrinology 100:129–140
Sun H, Wang K, Wei H, Li Z, Zhao H (2016) Cytotoxicity, organ distribution and morphological effects of melamine and cyanuric acid in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 26:501-510
Sun T, Vasek MJ, Klein RS (2014) Congenitally acquired persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection reduces neuronal progenitor pools in the adult hippocampus and subventricular zone. PLoS One 9:e96442
Sun W, Che H, Li J, Tang D, Liu X, Liu W, An L (2020a) Dorsolateral striatal proBDNF Improves reversal learning by enhancing coordination of neural activity in rats. Mol Neurobiol
Sun W, Li J, Cui S, Luo L, Huang P, Tang C, An L (2019) Sleep deprivation disrupts acquisition of contextual fear extinction by affecting circadian oscillation of hippocampal-infralimbic proBDNF. eNeuro 6
Sun W, Li X, An L (2018a) Distinct roles of prelimbic and infralimbic proBDNF in extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropharmacology 131:11–19
Sun W, Li X, Tang C, An L (2018b) Acute low alcohol disrupts hippocampus-striatum neural correlate of learning strategy by inhibition of PKA/CREB pathway in rats. Front Pharmacol 9:1439
Sun W, Li X, Tang D, Wu Y, An L (2020b) Subacute melamine exposure disrupts task-based hippocampal information flow via inhibiting the subunits 2 and 3 of AMPA glutamate receptors expression. Hum Exp Toxicol:960327120975821
Sun W, Wu Y, Tang D, Li X, An L (2021) Melamine disrupts spatial reversal learning and learning strategy via inhibiting hippocampal BDNF-mediated neural activity. PLoS One 16:e0245326
Sweatt JD (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:311–317
Thibaudeau G, Potvin O, Allen K, Dore FY, Goulet S (2007) Dorsal, ventral, and complete excitotoxic lesions of the hippocampus in rats failed to impair appetitive trace conditioning. Behav Brain Res 185:9-20
Vivekanandarajah A, Aishah A, Waters KA, Machaalani R (2017) Intermittent hypercapnic hypoxia effects on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the developing piglet hippocampus and brainstem. Neurotoxicology 60:23–33
Wang C, Qin X, Huang B, He F, Zeng C (2010) Hemolysis of human erythrocytes induced by melamine-cyanurate complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402:773–777
Wang Y, Liu F, Wei Y, Liu D (2011) The effect of exogenous melamine on rat hippocampal neurons. Toxicol Ind Health 27:571–576
Yang J, An L, Yao Y, Yang Z, Zhang T (2011) Melamine impairs spatial cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity by presynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic transmission in infant rats. Toxicology 289:167–174
Yeganeh F, Nikbakht F, Rasouli H (2011) The effect of acute ethanol and gabapentin administration on spatial learning and memory. Basic Clin Neurosci 2:44–47
Yin RH et al (2017) The effects of melamine with or without cyanuric acid on immune function in ovalbumin-sensitized mice. Res Vet Sci 114:254–261
Yin RH et al (2019) iTRAQ-based proteomics analysis reveals the deregulated proteins related to liver toxicity induced by melamine with or without cyanuric acid in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:618-629
Yin RH et al (2016) The effects of melamine on humoral immunity with or without cyanuric acid in mice. Res Vet Sci 105:65–73
Zhang J et al (2013) Salidroside attenuates beta amyloid-induced cognitive deficits via modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in rat hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 244:70–81
Zhang Y et al (2016) Biphasic effects of copper on rat learning and memory in the Morris water maze. Ann Clin Lab Sci 46:346–352
Zucker RS, Regehr WG (2002) Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Physiol 64:355–405
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31700929) to LA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Yang, Y., Wu, Z. et al. Chronic Cyanuric Acid Exposure Depresses Hippocampal LTP but Does Not Disrupt Spatial Learning or Memory in the Morris Water Maze. Neurotox Res 39, 1148–1159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00355-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00355-9