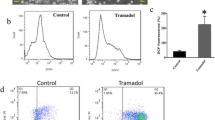
Abstract
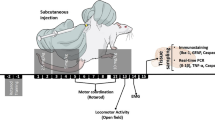
Tramadol is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic and SNRI (serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake-inhibitor) that structurally resembles codeine and morphine. Given the tramadol neurotoxic effect and the body of studies on the effect of tramadol on the cerebellum, this study aims to provide deeper insights into molecular and histological alterations in the cerebellar cortex related to tramadol administration. In this study, twenty-four adult male albino rats were randomly and equally divided into two groups: control and tramadol groups. The tramadol group received 50 mg/kg of tramadol daily for 3 weeks via oral gavage. The functional and structural change of the cerebellum under chronic exposure of tramadol were measured. Our data revealed that treating rats with tramadol not only lead to cerebellum atrophy but also resulted in the actuation of microgliosis, neuroinflammatoin, and apoptotic biomarkers. Our results illustrated a significant drop in VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) level in the tramadol group. Additionally, tramadol impaired motor coordination and neuromuscular activity. We also identified several signaling cascades chiefly related to neurodegenerative disease and energy metabolism that considerably deregulated in the cerebellum of tramadol-treated rats. Overall, the outcomes of this study suggest that tramadol administration has a neurodegeneration effect on the cerebellar cortex via several pathways consisting of microgliosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and neuroinflammatoin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Rahman MS, ELwasei, F. M. (2011) Protective effect of Nigella sativa oil against tramadol-induced tolerance and dependence in mice: role of nitric oxide and oxidative stress. Neurotoxicology 32(6):725–733
Aboulhoda BE, Hassan SS (2018) Effect of prenatal tramadol on postnatal cerebellar development: role of oxidative stress. J Chem Neuroanat 94:102–118
Aghajanpour F, Boroujeni ME, Jahanian A, Soltani R, Ezi S, Khatmi A, Aliaghaei A (2020) Tramadol: a potential neurotoxic agent affecting prefrontal cortices in adult male rats and PC-12 cell line. Neurotox Res
Airaksinen MS, Saarma M (2002) The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:383–394
Atici S, Cinel I, Cinel L, Doruk N, Eskandari G, Oral U (2005) Liver and kidney toxicity in chronic use of opioids: an experimental long term treatment model. J Biosci 30(2):245–252
Atici S, Cinel L, Cinel I, Doruk N, Aktekin M, Akca A, Oral U (2004) Opioid neurotoxicity: comparison of morphine and tramadol in an experimental rat model. Int J Neurosci 114(8):1001–1011
Awadalla EA, Salah-Eldin A-E (2016) Molecular and histological changes in cerebral cortex and lung tissues under the effect of tramadol treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 82:269–280
Baghishani F, Mohammadipour A, Hosseinzadeh H, Hosseini M, Ebrahimzadeh-Bideskan A (2018) The effects of tramadol administration on hippocampal cell apoptosis, learning and memory in adult rats and neuroprotective effects of crocin. Metab Brain Dis 33(3):907–916
Bameri B, Shaki F, Ahangar N, Ataee R, Samadi M, Mohammadi H (2018) Evidence for the involvement of the dopaminergic system in seizure and oxidative damage induced by tramadol. Int J Toxicol 37(2):164–170
Barsotti CE, Mycyk MB, Reyes J (2003) Withdrawal syndrome from tramadol hydrochloride. Am J Emerg Med 21(1):87–88
Bilbo SD, Wieseler JL, Barrientos RM, Tsang V, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2010) Neonatal bacterial infection alters fever to live and simulated infections in adulthood. Psychoneuroendocrinology 35(3):369–381
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong J-S (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(1):57–69
Bonizzi G, Karin M (2004) The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol 25(6):280–288
Boroujeni ME, Gardaneh M, Shahriari MH, Aliaghaei A, Hasani S (2017) Synergy between choroid plexus epithelial cell-conditioned medium and knockout serum replacement converts human adipose-derived stem cells to dopamine-secreting neurons. Rejuvenation Res 20(4):309–319
Bostan AC, Strick PL (2018) The basal ganglia and the cerebellum: nodes in an integrated network. Nat Rev Neurosci 19(6):338–350
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Briston T, Hicks AR (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative proteinopathies: mechanisms and prospects for therapeutic intervention. Biochem Soc Trans 46(4):829–842
Cendelin J (2014) From mice to men: lessons from mutant ataxic mice. Cerebellum & ataxias 1(1):1–21
Chen L-W, Dong M-H, Kuang F, Liu J-T, Zhang J-Q et al (2018) GDNF-expressing macrophages mitigate loss of dopamine neurons and improve Parkinsonian symptoms in MitoPark mice. Scientific Reports 8:5460
Chen Z, Jalabi W, Shpargel KB, Farabaugh KT, Dutta R, Yin X, Trapp BD (2012) Lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation and neuroprotection against experimental brain injury is independent of hematogenous TLR4. J Neurosci 32(34):11706–11715
Costa I, Oliveira A, Guedes de Pinho P, Teixeira HM, Moreira R, Carvalho F, Jorge Dinis-Oliveira R (2013) Postmortem redistribution of tramadol and O-desmethyltramadol. J Anal Toxicol 37(9):670–675
Dhuriya YK, Sharma D (2018) Necroptosis: a regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):199
El-Baky A, Hafez M (2017) NOS expression in oxidative stress, neurodegeneration and male infertility induced by the abuse of tramadol. Biochem Pharmacol (Los Angel), 6(223), 2167–0501.1000223
El-Bermawy MI, Salem MF (2015) Histological changes of the albino rat cerebellar cortex under the effect of different doses of tramadol administration. The Egyptian Journal of Histology 38(1):143–155
Eskandarian Boroujeni M, Peirouvi T, Shaerzadeh F, Ahmadiani A, Abdollahifar MA, Aliaghaei A (2020) Differential gene expression and stereological analyses of the cerebellum following methamphetamine exposure. Addict Biol 25(1):e12707
Ezzeldin E, Souror WA, El-Nahhas T, Soudi ANM, Shahat AA (2014) Biochemical and neurotransmitters changes associated with tramadol in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. BioMed Res Int
Ghoneim FM, Khalaf HA, Elsamanoudy AZ, Helaly AN (2014) Effect of chronic usage of tramadol on motor cerebral cortex and testicular tissues of adult male albino rats and the effect of its withdrawal: histological, immunohistochemical and biochemical study. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(11):7323
Glezer I, Simard A, Rivest S (2007) Neuroprotective role of the innate immune system by microglia. Neuroscience 147(4):867–883
Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Bolay H, Saribas O, Dalkara T (2000) Role of endothelial nitric oxide generation and peroxynitrite formation in reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 31(8):1974–1980
Hallett M, Shahani BT, Young RR (1975) EMG analysis of patients with cerebellar deficits. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38(12):1163–1169
Hanisch U-K, Kettenmann H (2007) Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1387–1394
Hashimoto M, Nitta A, Fukumitsu H, Nomoto H, Shen L, Furukawa S (2005) Involvement of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in activation processes of rodent macrophages. J Neurosci Res 79:476–487
Honda S, Nakajima K, Nakamura Y, Imai Y, Kohsaka S (1999) Rat primary cultured microglia express glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor receptors. Neurosci Lett 275:203–206
Hoogland IC, Houbolt C, van Westerloo DJ, van Gool WA, van de Beek D (2015) Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: systematic review of animal experiments. J Neuroinflammation 12(1):114
Hopkins D, Shipton E, Potgieter D, Van Der Merwe C, Boon J, De Wet C, Murphy J (1998) Comparison of tramadol and morphine via subcutaneous PCA following major orthopaedic surgery. Can J Anaesth 45(5):435–442
Jin K, Mao X, Batteur S, McEachron E, Leahy A, Greenberg D (2001) Caspase-3 and the regulation of hypoxic neuronal death by vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuroscience 108(2):351–358
Kaya D, Gürsoy-Özdemir Y, Yemisci M, Tuncer N, Aktan S, Dalkara T (2005) VEGF protects brain against focal ischemia without increasing blood–brain permeability when administered intracerebroventricularly. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(9):1111–1118
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2015) HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12(4):357–360
Langley PC, Patkar AD, Boswell KA, Benson CJ, Schein JR (2010) Adverse event profile of tramadol in recent clinical studies of chronic osteoarthritis pain. Curr Med Res Opin 26(1):239–251
Lanier RK, Lofwall MR, Mintzer MZ, Bigelow GE, Strain EC (2010) Physical dependence potential of daily tramadol dosing in humans. Psychopharmacology 211(4):457–466
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W (2014) featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30(7):923–930
Liu L-W, Lu J, Wang X-H, Fu S-K, Li Q, Lin F-Q (2013) Neuronal apoptosis in morphine addiction and its molecular mechanism. Int J Clin Exp Med 6(7):540
Manto M, Bower JM, Conforto AB, Delgado-García JM, Da Guarda SNF, Gerwig M, Mariën P (2012) Consensus paper: roles of the cerebellum in motor control—the diversity of ideas on cerebellar involvement in movement. The Cerebellum 11(2):457–487
Mattia C, Coluzzi F (2005) Tramadol. Focus on musculoskeletal and neuropathic pain. Minerva Anestesiol 71(10), 565–584
McQuown SC, Wood MA (2010) Epigenetic regulation in substance use disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep 12(2):145–153
Moehle MS, West AB (2015) M1 and M2 immune activation in Parkinson’s disease: foe and ally? Neuroscience 302:59–73
Mohamed HM, Mahmoud AM (2019) Chronic exposure to the opioid tramadol induces oxidative damage, inflammation and apoptosis, and alters cerebral monoamine neurotransmitters in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 110:239–247
Mohamed TM, Ghaffar HMA, El Husseiny RM (2015) Effects of tramadol, clonazepam, and their combination on brain mitochondrial complexes. Toxicol Ind Health 31(12):1325–1333
Nafea OE, ElKhishin IA, Awad OA, Mohamed DA (2016) A study of the neurotoxic effects of tramadol and cannabis in adolescent male albino rats. Sci Rep 2:143–154
Narasimhan P, Liu J, Song YS, Massengale JL, Chan PH (2009) VEGF Stimulates the ERK 1/2 signaling pathway and apoptosis in cerebral endothelial cells after ischemic conditions. Stroke 40(4):1467–1473
Nestler EJ, Lüscher C (2019) The molecular basis of drug addiction: linking epigenetic to synaptic and circuit mechanisms. Neuron 102(1):48–59
Neureither F, Ziegler K, Pitzer C, Frings S, Möhrlen F (2017) Impaired motor coordination and learning in mice lacking anoctamin 2 calcium-gated chloride channels. The Cerebellum 16(5–6):929–937
Nguyen MD, D’Aigle T, Gowing G, Julien J-P, Rivest S (2004) Exacerbation of motor neuron disease by chronic stimulation of innate immunity in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 24(6):1340–1349
Pidgeon GP, Barr MP, Harmey JH, Foley DA, Bouchier-Hayes DJ (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) upregulates BCL-2 and inhibits apoptosis in human and murine mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 85(2):273–278
Pocock JM, Liddle AC (2001) Microglial signalling cascades in neurodegenerative disease. Prog Brain Res 132:555–565
Quan N, Banks WA (2007) Brain-immune communication pathways. Brain Behav Immun 21(6):727–735
Raffa R (2006) Pharmacological aspects of successful long-term analgesia. Clin Rheumatol 25(1):9–15
Raffa RB, Friderichs E, Reimann W, Shank RP, Codd EE, Vaught JL (1992) Opioid and nonopioid components independently contribute to the mechanism of action of tramadol, an’atypical’opioid analgesic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260(1):275–285
Raudvere U, Kolberg L, Kuzmin I, Arak T, Adler P, Peterson H, Vilo J (2019) g: Profiler: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W191–W198
Renthal W, Nestler EJ (2008) Epigenetic mechanisms in drug addiction. Trends Mol Med 14(8):341–350
Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (2011) Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(11):623–637
Rocha SM, Cristovao AC, Campos FL, Fonseca CP, Baltazar G (2012) Astrocyte-derived GDNF is a potent inhibitor of microglial activation. Neurobiol Dis 47:407–415
Sarhan NR, Taalab YM (2018) Oxidative stress/PERK/apoptotic pathways interaction contribute to tramadol neurotoxicity in rat cerebral and cerebellar cortex and thyme enhances the antioxidant defense system: histological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Int J 4(6):124
Simard AR, Rivest S (2007) Neuroprotective effects of resident microglia following acute brain injury. J Comp Neurol 504(6):716–729
Soltani R, Boroujeni ME, Aghajanpour F, Khatmi A, Ezi S, Mirbehbahani SH, Heidari M-H (2020) Tramadol exposure upregulated apoptosis, inflammation and autophagy in PC12 cells and rat’s striatum: an in vitro- in vivo approach. J Chem Neuroanat 109:101820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101820
Steinhorn R, McPherson C, Anderson PJ, Neil J, Doyle LW, Inder T (2015) Neonatal morphine exposure in very preterm infants—cerebral development and outcomes. J Pediatr 166(5), 1200–1207. e1204
Tang Y, Le W (2016) Differential roles of M1 and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 53(2):1181–1194
Tarazona S, García-Alcalde F, Dopazo J, Ferrer A, Conesa A (2011) Differential expression in RNA-seq: a matter of depth. Genome Res 21(12):2213–2223
Thomasy SM, Moeller BC, Stanley SD (2007) Comparison of opioid receptor binding in horse, guinea pig, and rat cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Veterinary Anaesth Analg 34(5):351–358
Thompson BL, Levitt P, Stanwood GD (2009) Prenatal exposure to drugs: effects on brain development and implications for policy and education. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(4):303–312
van der Vaart T, Van Woerden G, Elgersma Y, De Zeeuw C, Schonewille M (2011) Motor deficits in neurofibromatosis type 1 mice: the role of the cerebellum. Genes Brain Behav 10(4):404–409
Veloz MFV, Zhou K, Bosman LW, Potters J-W, Negrello M, Seepers RM, De Zeeuw CI (2015) Cerebellar control of gait and interlimb coordination. Brain Struct Funct 220(6):3513–3536
Walhovd KB, Moe V, Slinning K, Siqveland T, Fjell AM, Bjørnebekk A, Smith L (2009) Effects of prenatal opiate exposure on brain development—a call for attention. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(5):390–390
Zhang YT, Zheng QS, Pan J, Zheng RL (2004) Oxidative damage of biomolecules in mouse liver induced by morphine and protected by antioxidants. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 95(2):53–58
Zhang Z, Chopp M (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins in focal cerebral ischemia. Trends Cardiovasc Med 12(2):62–66
Zwicker JG, Miller SP, Grunau RE, Chau V, Brant R, Studholme C, Stiver ML (2016) Smaller cerebellar growth and poorer neurodevelopmental outcomes in very preterm infants exposed to neonatal morphine. J Pediatr 172(81–87):e82
Acknowledgements
This article has been extracted from the Ph.D. thesis written by Ms. Samira Ezi. We also thank Netsaai group for providing us computational infrastructure.
Funding
We received funding from Hearing Disorders Research Center, Loghman Hakim Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Registration No: 23846). The present article is financially supported by School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezi, S., Boroujeni, M.E., Khatmi, A. et al. Chronic Exposure to Tramadol Induces Neurodegeneration in the Cerebellum of Adult Male Rats. Neurotox Res 39, 1134–1147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00354-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00354-w