Abstract
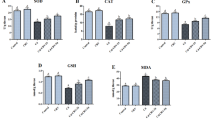
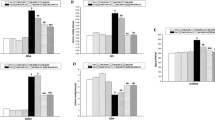
Cadmium (Cd) is a heavy metal of considerable toxicity, inducing a number of hazardous effects to humans and animals including neurotoxicity. This experiment was aimed to investigate the potential effect of kaempferol (KPF) against Cd-induced cortical injury. Thirty-two adult Sprague-Dawley rats were divided equally into four groups. The control rats intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with physiological saline (0.9% NaCl), the cadmium chloride (CdCl2)-treated rats were i.p. injected with 4.5 mg/kg of CdCl2, the KPF-treated rats were orally gavaged with 50 mg/kg of KPF, and the KPF + CdCl2-treated rats were administered orally 50 mg/kg of KPF 120 min before receiving i.p. injection of 4.5 mg/kg CdCl2. CdCl2 exposure for 30 days led to the accumulation of Cd in the cortical tissue, accompanied by a reduction in the content of monoamines and acetylcholinesterase activity. Additionally, CdCl2 induced a state of oxidative stress as evidenced by the elevation of lipid peroxidation and nitrate/nitrite levels, while glutathione content and the activities of glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase were decreased. Moreover, CdCl2 mediated inflammatory events in the cortical tissue through increasing tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta levels and upregulating the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Furthermore, pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax and caspase-3) were elevated, while Bcl-2, the anti-apoptotic protein, was decreased. Also, histological alterations were observed obviously following CdCl2. However, KPF pretreatment restored significantly the examined markers to be near the normal values. Hence, the obtained data provide evidences that KPF pretreatment has the protective effect to preserve the cortical tissues in CdCl2-exposed rats by restraining oxidative stress, inflammatory response, apoptosis, neurochemical modulation, and improving the histological changes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper.
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- CdCl2 :
-
Cadmium chloride
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- KPF:
-
Kaempferol
References
Abdel Moneim AE, Bauomy AA, Diab MM, Shata MT, Al-Olayan EM, El-Khadragy MF (2014) The protective effect of Physalis peruviana L. against cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 160(3):392–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0066-9
Abdullah A, Ravanan P (2018) Kaempferol mitigates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced cell death by targeting caspase 3/7. Scientific Reports 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20499-7
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C et al (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16(25):2766–2778. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161210793176572
Al Olayan EM, Aloufi AS, AlAmri OD, El-Habit OH, Abdel Moneim AE et al (2020) Protocatechuic acid mitigates cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats: Role of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Sci Total Environ:137969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137969
Al Omairi NE, Radwan OK, Alzahrani YA, Kassab RB (2018) Neuroprotective efficiency of Mangifera indica leaves extract on cadmium-induced cortical damage in rats. Metab Brain Dis 33(4):1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0222-6
Alkhalidy H, Moore W, Wang A, Luo J, McMillan RP, Wang Y, Zhen W, Hulver MW, Liu D et al (2018) Kaempferol ameliorates hyperglycemia through suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis and enhancing hepatic insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. J Nutr Biochem 58:90–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.04.014
Almeer RS, Alarifi S, Alkahtani S, Ibrahim SR, Ali D, Moneim A (2018) The potential hepatoprotective effect of royal jelly against cadmium chloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice is mediated by suppression of oxidative stress and upregulation of Nrf2 expression. Biomed Pharmacother 106:1490–1498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.089
Almeer RS, Kassab RB, AlBasher GI, Alarifi S, Alkahtani S, Ali D, Abdel Moneim AE et al (2018) Royal jelly mitigates cadmium-induced neuronal damage in mouse cortex. Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4451-x
Alnahdi HS, Sharaf IA (2019) Possible prophylactic effect of omega-3 fatty acids on cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats’ brains. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(30):31254–31262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06259-810.1007/s11356-019-06259-8[pii]
Amuno S, Shekh K, Kodzhahinchev V, Niyogi S et al (2019) Neuropathological changes in wild muskrats (Ondatra zibethicus) and red squirrels (Tamiasciurus hudsonicus) breeding in arsenic endemic areas of Yellowknife, Northwest Territories (Canada): Arsenic and cadmium accumulation in the brain and biomarkers of oxidative stress. Sci Total Environ:135426. doi:S0048–9697(19)35419–1 [pii] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135426
Andersson H, Petersson-Grawe K, Lindqvist E, Luthman J, Oskarsson A, Olson L et al (1997) Low-level cadmium exposure of lactating rats causes alterations in brain serotonin levels in the offspring. Neurotoxicol Teratol 19(2):105–115
Annunziato L, Amoroso S, Pannaccione A, Cataldi M, Pignataro G, D’Alessio A, Sirabella R, Secondo A, Sibaud L, Di Renzo GF et al (2003) Apoptosis induced in neuronal cells by oxidative stress: role played by caspases and intracellular calcium ions. Toxicol Lett 139(2–3):125–133
Ashok A, Rai NK, Tripathi S, Bandyopadhyay S et al (2015) Exposure to As-, Cd-, and Pb-mixture induces Abeta, amyloidogenic APP processing and cognitive impairments via oxidative stress-dependent neuroinflammation in young rats. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 143(1):64–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfu208
Ayaz M, Sadiq A, Junaid M, Ullah F, Ovais M, Ullah I, Ahmed J, Shahid M et al (2019) Flavonoids as Prospective Neuroprotectants and Their Therapeutic Propensity in Aging Associated Neurological Disorders. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 11 (155). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00155
Barnham KJ, Bush AI (2008) Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12(2):222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.02.019
Branca JJV, Morucci G, Becatti M, Carrino D, Ghelardini C, Gulisano M, Di Cesare Mannelli L, Pacini A et al (2019) Cannabidiol protects dopaminergic neuronal cells from cadmium. International journal of environmental research and public health 16(22):4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224420
Carageorgiou H, Tzotzes V, Pantos C, Mourouzis C, Zarros A, Tsakiris S et al (2004) In vivo and in vitro effects of cadmium on adult rat brain total antioxidant status, acetylcholinesterase, (Na+, K+)-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities: protection by L-cysteine. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 94(3):112–118
Dar RA, Brahman PK, Khurana N, Wagay JA, Lone ZA, Ganaie MA, Pitre KS et al (2017) Evaluation of antioxidant activity of crocin, podophyllotoxin and kaempferol by chemical, biochemical and electrochemical assays. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 10:S1119–S1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.02.004
De Felice A, Ricceri L, Venerosi A, Chiarotti F, Calamandrei G et al (2015) Multifactorial origin of neurodevelopmental disorders: approaches to understanding complex etiologies. Toxics 3(1):89–129
De Vega L, Fernandez RP, Mateo MC, Bustamante JB, Herrero AM, Munguira EB et al (2002) Glutathione determination and a study of the activity of glutathione-peroxidase, glutathione-transferase, and glutathione-reductase in renal transplants. Ren Fail 24(4):421–432
El-Kott AF, Bin-Meferij MM, Eleawa SM, Alshehri MM (2020) Kaempferol protects against cadmium chloride-induced memory loss and hippocampal apoptosis by increased intracellular glutathione stores and activation of PTEN/AMPK induced inhibition of Akt/mTOR signaling. Neurochem Res 45(2):295–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02911-410.1007/s11064-019-02911-4[pii]
Elkhadragy MF, Abdel Moneim AE (2017) Protective effect of Fragaria ananassa methanolic extract on cadmium chloride (CdCl2)-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2017.1285973
Elkhadragy MF, Kassab RB, Metwally DM, Almeer R, Abdel-Gaber R, Al-Olayan EM, Essawy EA, Amin HK, Abdel Moneim AE (2018) Protective effects of Fragaria ananassa methanolic extract in a rat model of cadmium chloride-induced neurotoxicity. Biosci Rep 38(6): BSR20180861. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20180861
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Ensibi C, Daly Yahia MN (2017) Toxicity assessment of cadmium chloride on planktonic copepods Centropages ponticus using biochemical markers. Toxicology Reports 4:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.01.005
Fasitsas CD, Theocharis SE, Zoulas D, Chrissimou S, Deliconstantinos G et al (1991) Time-dependent cadmium-neurotoxicity in rat brain synaptosomal plasma membranes. Comp Biochem Physiol C 100(1–2):271–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/0742-8413(91)90167-r
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126(1):131–138
Hao ML, Pan N, Zhang QH, Wang XH (2015) Therapeutic efficacy of chlorogenic acid on cadmium-induced oxidative neuropathy in a murine model. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 9(5):1887–1894. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2367ETM-0-0-2367[pii]
Haouem S, El Hani A (2013) Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation and on some antioxidants in the liver, kidneys and testes of rats given diet containing cadmium-polluted Radish Bulbs. J Toxicol Pathol 26(4):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1293/tox.2013-00252013-0006[pii]
Hossein-Khannazer N, Azizi G, Eslami S, Alhassan Mohammed H, Fayyaz F, Hosseinzadeh R, Usman AB, Kamali AN, Mohammadi H, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Dehghanifard E, Noorisepehr M (2019) The effects of cadmium exposure in the induction of inflammation. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 42(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923973.2019.1697284
Imran M, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad J, Aslam Gondal T, Saeed F, Imran A, Shahbaz M, Tsouh Fokou PV, Umair Arshad M, Khan H, Guerreiro SG, Martins N, Estevinho LM et al (2019) Kaempferol: A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential. Molecules 24 (12). doi:molecules24122277 [pii] https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122277
Kassab RB, Lokman MS, Essawy EA (2018) Neurochemical alterations following the exposure to di-n-butyl phthalate in rats. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0341-0
Klein JA, Ackerman SL (2003) Oxidative stress, cell cycle, and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 111(6):785–793. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI18182
Kurutas EB (2016) The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: current state. Nutr J 15(1):71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-016-0186-510.1186/s12937-016-0186-5[pii]
Lee Y, Kim S, Oh Y, Kim YM, Chin YW, Cho J et al (2019) Inhibition of Oxidative Neurotoxicity and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment by gamma-Mangostin: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2019:3640753. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3640753
Lin MK, Yu YL, Chen KC, Chang WT, Lee MS, Yang MJ, Cheng HC, Liu CH, Chen Dz C, Chu CL (2011) Kaempferol from Semen cuscutae attenuates the immune function of dendritic cells. Immunobiology 216(10):1103–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2011.05.002
Liu J, Qu W, Kadiiska MB (2009) Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.01.029
Lizarraga LE, Cholanians AB, Phan AV, Herndon JM, Lau SS, Monks TJ (2015) Vesicular monoamine transporter 2 and the acute and long-term response to 3,4-(±)-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Toxicol Sci 143(1):209–219
Mahdavi S, Khodarahmi P, Roodbari NH (2018) Effects of cadmium on Bcl-2/ Bax expression ratio in rat cortex brain and hippocampus. Hum Exp Toxicol 37(3):321–328. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327117703687
Malkiewicz MA, Szarmach A, Sabisz A, Cubala WJ, Szurowska E, Winklewski PJ (2019) Blood-brain barrier permeability and physical exercise. Journal of neuroinflammation 16(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1403-x10.1186/s12974-019-1403-x[pii]
Maodaa SN, Allam AA, Ajarem J, Abdel-Maksoud MA, Al-Basher GI, Wang ZY et al (2016) Effect of parsley (Petroselinum crispum, Apiaceae) juice against cadmium neurotoxicity in albino mice (Mus Musculus). Behav Brain Funct 12(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12993-016-0090-3
Messaoudi I, El Heni J, Hammouda F, Said K, Kerkeni A (2009) Protective effects of selenium, zinc, or their combination on cadmium-induced oxidative stress in rat kidney. Biol Trace Elem Res 130(2):152–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8324-y
Messner B, Turkcan A, Ploner C, Laufer G, Bernhard D (2016) Cadmium overkill: autophagy, apoptosis and necrosis signalling in endothelial cells exposed to cadmium. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(8):1699–1713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2094-910.1007/s00018-015-2094-9[pii]
Monastero RN, Vacchi-Suzzi C, Marsit C, Demple B, Meliker JR et al (2018) Expression of Genes Involved in Stress, Toxicity, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity in Relation to Cadmium, Mercury, and Lead in Human Blood: A Pilot Study. Toxics 6 (3). doi:toxics6030035 [pii] https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6030035
Niederlehner JR, DiFazio CA, Foster J, Westfall TC et al (1982) Cerebral monoamines and lidocaine toxicity in rats. Anesthesiology 56(3):184–187. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-198203000-00005
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K et al (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46(2):849–854
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K et al (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358
Ozyurek M, Bektasoglu B, Guclu K, Apak R et al (2009) Measurement of xanthine oxidase inhibition activity of phenolics and flavonoids with a modified cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) method. Anal Chim Acta 636(1):42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.01.037
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70(1):158–169
Ren J, Lu Y, Qian Y, Chen B, Wu T, Ji G et al (2019) Recent progress regarding kaempferol for the treatment of various diseases. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 18(4):2759–2776. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7886ETM-0-0-7886[pii]
Rubino FM (2015) Toxicity of glutathione-binding metals: a review of targets and mechanisms. Toxics 3(1):20–62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3010020
Sloley BD, Urichuk LJ, Morley P, Durkin J, Shan JJ, Pang PK, Coutts RT et al (2000) Identification of kaempferol as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor and potential neuroprotectant in extracts of Ginkgo biloba leaves. J Pharm Pharmacol 52(4):451–459. https://doi.org/10.1211/0022357001774075
Svob Strac D, Pivac N, Muck-Seler D et al (2016) The serotonergic system and cognitive function. Transl Neurosci 7(1):35–49. https://doi.org/10.1515/tnsci-2016-0007tnsci-2016-0007[pii]
Tang K-K, Liu X-Y, Wang Z-Y, Qu K-C, Fan R-F et al (2019) Trehalose alleviates cadmium-induced brain damage by ameliorating oxidative stress, autophagy inhibition, and apoptosis. Metallomics 11(12):2043–2051
Vitrac C, Benoit-Marand M (2017) Monoaminergic modulation of motor cortex function. Front Neural Circuits 11:72. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2017.00072
Wang X, Wang T, Pan T, Huang M, Ren W, Xu G, Amin HK, Kassab RB, Abdel Moneim AE et al (2019) Senna alexandrina extract supplementation reverses hepatic oxidative, inflammatory, and apoptotic effects of cadmium chloride administration in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(6):5981–5992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-11019-07117-11353.10.1007/s11356-019-07117-3
Winiarska-Mieczan A (2018) Protective effect of tea against lead and cadmium-induced oxidative stress—a review. Biometals 31(6):909–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-018-0153-z
Yang X, Han Y, Mu Y, Yang P, Gu W, Zhang M et al (2019) Multigenerational effects of cadmium on the lifespan and fertility of Drosophila melanogaster. Chemosphere 245:125533–125533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125533
Yuan Y, Jiang CY, Xu H, Sun Y, Hu FF, Bian JC, Liu XZ, Gu JH, Liu ZP (2013) Cadmium-induced apoptosis in primary rat cerebral cortical neurons culture is mediated by a calcium signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 8(5):e64330. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064330
Yuan Y, Wang Y, Hu FF, Jiang CY, Zhang YJ, Yang JL, Zhao SW, Gu JH, Liu XZ, Bian JC, Liu ZP (2016) Cadmium activates reactive oxygen species-dependent AKT/mTOR and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in neuronal cells. Biomed Environ Sci 29(2):117–126. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2016.013
Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Zhao S, Chen J, Yang J, Wang T, Zou H, Wang Y, Gu J, Liu X, Bian J, Liu Z et al (2018) Cadmium-induced apoptosis in neuronal cells is mediated by Fas/FasL-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway. Scientific Reports 8(1):8837. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27106-9
Zhou M, Ren H, Han J, Wang W, Zheng Q, Wang D et al (2015) Protective Effects of Kaempferol against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Isolated Rat Heart via Antioxidant Activity and Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3beta. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2015:481405. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/481405
Zou H, Wang T, Yuan J, Sun J, Yuan Y, Gu J, Liu X, Bian J, Liu Z et al (2019) Cadmium-induced cytotoxicity in mouse liver cells is associated with the disruption of autophagic flux via inhibiting the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes. Toxicology Letters:S0378–4274(0319)30412–30416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.12.019
Funding
This work was supported by Taif University Researchers Supporting Program (Project number: TURSP-2020/151), Taif University, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Brakati, A., Albarakati, A.J.A., Lokman, M.S. et al. Possible Role of Kaempferol in Reversing Oxidative Damage, Inflammation, and Apoptosis-Mediated Cortical Injury Following Cadmium Exposure. Neurotox Res 39, 198–209 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00300-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00300-2