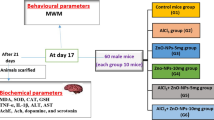
Abstract
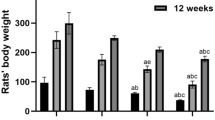
Aluminum oxide nanoparticles (nano-aluminum) have been known to be widespread in the environment for decades. Exposure to nano-aluminum may impair learning and memory, but the potential mechanism has not yet been elucidated. In neurons, efficient clearance of damaged mitochondria through mitophagy plays an important role in mitochondrial energy supply, neuronal survival, and health. However, abnormal mitophagy induces accumulation of damaged mitochondria, which induces cellular dysfunction, contributing to the impairment of learning and memory. It is currently unclear whether nano-aluminum interferes with the function of nerve cells through mitophagy, leading to learning and memory disorders. Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) female mice were randomly divided into four groups, and treated with normal saline (control) and 50 nm nano-aluminum at concentrations of 25, 50, and 75 mg/kg for 30 days. Our results showed that exposure to nano-aluminum impaired the spatial learning and memory of mice. Superoxide dismutase levels decreased, whereas the levels of malondialdehyde increased. Moreover, there were significant pathological changes in the ultra-structure and function of mitochondria. Finally, expression of autophagy-related proteins LC3-II and Beclin-1 was upregulated and p62 expression decreased, but the expression of apoptotic and necrosis-related proteins had no significant difference among groups. Our results suggest that learning and memory impairment induced by nano-aluminum could be related to mitophagy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghebati-Maleki A, Dolati S, Ahmadi M, Baghbanzhadeh A, Asadi M, Fotouhi A, Yousefi M, Aghebati-Maleki L (2020) Nanoparticles and cancer therapy: perspectives for application of nanoparticles in the treatment of cancers. J Cell Physiol 235:1962–1972. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29126
Andersen JV, Jakobsen E, Waagepetersen HS, Aldana BI (2019) Distinct differences in rates of oxygen consumption and ATP synthesis of regionally isolated non-synaptic mouse brain mitochondria. J Neurosci Res 97:961–974. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24371
Ashrafi G, Schwarz TL (2013) The pathways of mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 20:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.81
Bhat AH, Dar KB, Anees S, Zargar MA, Masood A, Sofi MA, Ganie SA (2015) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother 74:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.025
Bragoszewski P, Turek M, Chacinska A (2017) Control of mitochondrial biogenesis and function by the ubiquitin–proteasome system. Open Biol 7:7. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.170007
Cai Q, Jeong YY (2020) Mitophagy in Alzheimer’s disease and other age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 9:9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010150
Chien L, Liang MZ, Chang CY, Wang C, Chen L (2018) Mitochondrial therapy promotes regeneration of injured hippocampal neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis 1864:3001–3012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.06.012
de Pablo-Latorre R, Saide A, Polishhuck EV, Nusco E, Fraldi A, Ballabio A (2012) Impaired parkin-mediated mitochondrial targeting to autophagosomes differentially contributes to tissue pathology in lysosomal storage diseases. Hum Mol Genet 21:1770–1781. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr610
Djordjevic J, Roy Chowdhury S, Snow WM, Perez C, Cadonic C, Fernyhough P, Albensi BC (2020) Early onset of sex-dependent mitochondrial deficits in the cortex of 3xTg Alzheimer’s mice cells. 9 doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061541
Dong E, Wang Y, Yang ST, Yuan Y, Nie H, Chang Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Wang H (2011) Toxicity of nano gamma alumina to neural stem cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:7848–7856. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2011.4748
Dong L, Tang S, Deng F, Gong Y, Zhao K, Zhou J, Liang D, Fang J, Hecker M, Giesy JP, Bai X, Zhang H (2019) Shape-dependent toxicity of alumina nanoparticles in rat astrocytes. Sci Total Environ 690:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.532
Engin AB, Engin A (2019) Nanoparticles and neurotoxicity: dual response of glutamatergic receptors. Prog Brain Res 245:281–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pbr.2019.03.005
Fivenson EM, Lautrup S, Sun N, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Stevnsner T, Nilsen H, Bohr VA, Fang EF (2017) Mitophagy in neurodegeneration and aging. Neurochem Int 109:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.02.007
Granatiero V, Manfredi G (2019) Mitochondrial transport and turnover in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biology 8:8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8020036
Guo D, Bi H, Liu B, Wu Q, Wang D, Cui Y (2013) Reactive oxygen species-induced cytotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in rat retinal ganglion cells. Toxicol in Vitro 27:731–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2012.12.001
Hasz BM, Redish AD (2020) Dorsomedial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus represent strategic context even while simultaneously changing representation throughout a task session. Neurobiol Learn Mem 171:107215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2020.107215
He C, Jiang S, Yao H, Zhang L, Yang C, Jiang S, Ruan F, Zhan D, Liu G, Lin Z, Lin Y, Chen X (2019) High-content analysis for mitophagy response to nanoparticles: a potential sensitive biomarker for nanosafety assessment. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 15:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2018.09.003
Hebscher M, Gilboa A (2016) A boost of confidence: the role of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex in memory, decision-making, and schemas. Neuropsychologia 90:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2016.05.003
Irion CI, Parrish K, John-Williams K, Gultekin SH, Shehadeh LA (2018) Osteopontin expression in cardiomyocytes is increased in pediatric patients with sepsis or pneumonia. Front Physiol 9:1779. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01779
Ismail T, Lee HK, Kim C, Kim Y, Lee H, Kim JH, Kwon S, Huh TL, Khang D, Kim SH, Choi SC, Lee HS (2019) Comparative analysis of the developmental toxicity in Xenopus laevis and Danio rerio induced by Al(2) O(3) nanoparticle exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 38:2672–2681. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4584
Jones CF, Grainger DW (2009) In vitro assessments of nanomaterial toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:438–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2009.03.005
Jovaisaite V, Mouchiroud L, Auwerx J (2014) The mitochondrial unfolded protein response, a conserved stress response pathway with implications in health and disease. J Exp Biol 217:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.090738
Karmakar A, Zhang Q, Zhang Y (2014) Neurotoxicity of nanoscale materials. J Food Drug Anal 22:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.012
Keelan JA (2011) Nanotoxicology: nanoparticles versus the placenta. Nat Nanotechnol 6:263–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.65
Kerr JS, Adriaanse BA, Greig NH, Mattson MP, Cader MZ, Bohr VA, Fang EF (2017) Mitophagy and alzheimer's disease: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Neurosci 40:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.01.002
Komatsu M, Ichimura Y (2010) Physiological significance of selective degradation of p62 by autophagy. FEBS Lett 584:1374–1378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2010.02.017
Kulkarni VV, Maday S (2018) Compartment-specific dynamics and functions of autophagy in neurons. Dev Neurobiol 78:298–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.22562
Kwon JT, Seo GB, Jo, Lee M, Kim HM, Shim I, Lee BW, Yoon BI, Kim P, Choi K (2013) Aluminum nanoparticles induce ERK and p38MAPK activation in rat brain. Toxicol Res 29:181–185. https://doi.org/10.5487/tr.2013.29.3.181
Lemasters JJ (2005) Selective mitochondrial autophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Research 8:3–5. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2005.8.3
Lenaz G (2012) Mitochondria and reactive oxygen species. Which role in physiology and pathology? Adv Exp Med Biol 942:93–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2869-1_5
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05292
Lin CH, Chang LW, Wei YH, Wu SB, Yang CS, Chang WH, Chen YC, Lin PP (2012) Electronic microscopy evidence for mitochondria as targets for Cd/Se/Te-based quantum dot 705 toxicity in vivo. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 28:S53–S62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2012.05.011
Liu H, Zhang W, Fang Y, Yang H, Tian L, Li K, Lai W, Bian L, Lin B, Liu X, Xi Z (2020) Neurotoxicity of aluminum oxide nanoparticles and their mechanistic role in dopaminergic neuron injury involving p53-related pathways. J Hazard Mater 392:122312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122312
Markovic ZM, Ristic BZ, Arsikin KM, Klisic DG, Harhaji-Trajkovic LM, Todorovic-Markovic BM, Kepic DP, Kravic-Stevovic TK, Jovanovic SP, Milenkovic MM, Milivojevic DD, Bumbasirevic VZ, Dramicanin MD, Trajkovic VS (2012) Graphene quantum dots as autophagy-inducing photodynamic agents. Biomaterials 33:7084–7092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.060
McAvoy K, Kawamata H (2019) Glial mitochondrial function and dysfunction in health and neurodegeneration. Mol Cell Neurosci 101:103417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2019.103417
Mirshafa A, Nazari M, Jahani D, Shaki F (2018) Size-dependent neurotoxicity of aluminum oxide particles: a comparison between nano- and micrometer size on the basis of mitochondrial oxidative damage. Biol Trace Elem Res 183:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1142-8
Orlando A, Cazzaniga E, Tringali M, Gullo F, Becchetti A, Minniti S, Taraballi F, Tasciotti E, Re F (2017) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles trigger mitophagy in endothelial cells and perturb neuronal network activity in a size- and time-dependent manner. Int J Nanomedicine 12:3547–3559. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S127663
Pan Y, Leifert A, Ruau D, Neuss S, Bornemann J, Schmid G, Brandau W, Simon U, Jahnen-Dechent W (2009) Gold nanoparticles of diameter 1.4 nm trigger necrosis by oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 5:2067–2076. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200900466
Place R, Farovik A, Brockmann M, Eichenbaum H (2016) Bidirectional prefrontal-hippocampal interactions support context-guided memory. Nat Neurosci 19:992–994. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4327
Preston AR, Eichenbaum H (2013) Interplay of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in memory. Curr Biol 23:R764–R773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.05.041
Rangaraju V, Lewis TL Jr, Hirabayashi Y, Bergami M, Motori E, Cartoni R, Kwon SK, Courchet J (2019) Pleiotropic mitochondria: the influence of mitochondria on neuronal development and disease. J Neurosci 39:8200–8208. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1157-19.2019
Ravanan P, Srikumar IF, Talwar P (2017) Autophagy: the spotlight for cellular stress responses. Life Sci 188:53–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.029
Sahani MH, Itakura E, Mizushima N (2014) Expression of the autophagy substrate SQSTM1/p62 is restored during prolonged starvation depending on transcriptional upregulation and autophagy-derived amino acids. Autophagy 10:431–441. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.27344
Saito T, Sadoshima J (2015) Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial autophagy/mitophagy in the heart. Circ Res 116:1477–1490. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.116.303790
Sansanwal P, Yen B, Gahl WA, Ma Y, Ying L, Wong LJ, Sarwal MM (2010) Mitochondrial autophagy promotes cellular injury in nephropathic cystinosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2009040383
Sekeres MJ, Winocur G, Moscovitch M (2018) The hippocampus and related neocortical structures in memory transformation. Neurosci Lett 680:39–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.05.006
Shah SA, Yoon GH, Ahmad A, Ullah F, Ul Amin F, Kim MO (2015) Nanoscale-alumina induces oxidative stress and accelerates amyloid beta (Aβ) production in ICR female mice. Nanoscale 7:15225–15237. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr03598h
Sharma HS, Sharma A (2007) Nanoparticles aggravate heat stress induced cognitive deficits, blood-brain barrier disruption, edema formation and brain pathology. Prog Brain Res 162:245–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6123(06)62013-x
Shirakabe A, Fritzky L, Saito T, Zhai P, Miyamoto S, Gustafsson ÅB, Kitsis RN, Sadoshima J (2016) Evaluating mitochondrial autophagy in the mouse heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 92:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.02.007
Shrivastava R, Raza S, Yadav A, Kushwaha P, Flora SJ (2014) Effects of sub-acute exposure to TiO2, ZnO and Al2O3 nanoparticles on oxidative stress and histological changes in mouse liver and brain. Drug Chem Toxicol 37:336–347. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2013.866134
Song Y, Li X, Wang L, Rojanasakul Y, Castranova V, Li H, Ma J (2011) Nanomaterials in humans: identification, characteristics, and potential damage. Toxicol Pathol 39:841–849. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623311413787
Spalding KN, Schlichting ML, Zeithamova D, Preston AR, Tranel D, Duff MC, Warren DE (2018) Ventromedial prefrontal cortex is necessary for normal associative inference and memory integration. J Neurosci 38:3767–3775. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2501-17.2018
Stern ST, Adiseshaiah PP, Crist RM (2012) Autophagy and lysosomal dysfunction as emerging mechanisms of nanomaterial toxicity. Particle Fibre Toxicol 9:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-9-20
Tatsuta T, Langer T (2008) Quality control of mitochondria: protection against neurodegeneration and ageing. EMBO J 27:306–314. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601972
Um JH, Yun J (2017) Emerging role of mitophagy in human diseases and physiology. BMB Rep 50:299–307. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.6.056
Wadhwa R, Gupta R, Maurya PK (2018) Oxidative stress and accelerated aging in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorder. Curr Pharm Des 24:4711–4725. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666190115121018
Wang J, Gao S, Wang S, Xu Z, Wei L (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce toxicity in CAL 27 oral cancer cell lines by activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Int J Nanomedicine 13:3441–3450. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S165699
Wei PF, Zhang L, Nethi SK, Barui AK, Lin J, Zhou W, Shen Y, Man N, Zhang YJ, Xu J, Patra CR, Wen LP (2014) Accelerating the clearance of mutant huntingtin protein aggregates through autophagy induction by europium hydroxide nanorods. Biomaterials 35:899–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.10.024
Weilbächer RA, Gluth S (2016) The interplay of hippocampus and ventromedial prefrontal cortex in memory-based decision making. Brain Sci 7:7. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7010004
Yoo SM, Jung YK (2018) A molecular approach to mitophagy and mitochondrial dynamics. Mol Cell 41:18–26. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2018.2277
Yu KN, Yoon TJ, Minai-Tehrani A, Kim JE, Park SJ, Jeong MS, Ha SW, Lee JK, Kim JS, Cho MH (2013) Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced autophagic cell death and mitochondrial damage via reactive oxygen species generation. Toxicol in Vitro 27:1187–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2013.02.010
Yu S, Zheng S, Leng J, Wang S, Zhao T, Liu J (2016) Inhibition of mitochondrial calcium uniporter protects neurocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury via the inhibition of excessive mitophagy. Neurosci Lett 628:24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.06.012
Yu M, Yang J, Gao X, Sun W, Liu S, Han Y, Lu X, Jin C, Wu S, Cai Y (2020) Lanthanum chloride impairs spatial learning and memory by inducing [Ca(2+)](m) overload, mitochondrial fission-fusion disorder and excessive mitophagy in hippocampal nerve cells of rats. Metallomics 12:592–606. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9mt00291j
Zabirnyk O, Yezhelyev M, Seleverstov O (2007) Nanoparticles as a novel class of autophagy activators. Autophagy 3:278–281. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.3916
Zhang QL, Li MQ, Ji JW, Gao FP, Bai R, Chen CY, Wang ZW, Zhang C, Niu Q (2011) In vivo toxicity of nano-alumina on mice neurobehavioral profiles and the potential mechanisms. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24:23s–29s
Zhang Q, Xu L, Wang J, Sabbioni E, Piao L, Di Gioacchino M, Niu Q (2013) Lysosomes involved in the cellular toxicity of nano-alumina: combined effects of particle size and chemical composition. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 27:365–375
Zhang Q, Ding Y, He K, Li H, Gao F, Moehling TJ, Wu X, Duncan J, Niu Q (2018) Exposure to alumina nanoparticles in female mice during pregnancy induces neurodevelopmental toxicity in the offspring. Front Pharmacol 9:253. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00253
Zhu J, Yu Y, Ge G, Basis ZKJBEA, Communications (2014) Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor on behavior ability and neurons of the hippocampal CA3 area in Alzheimer’s disease model rats 26:S185-
Zlatković J, Todorović N, Bošković M, Pajović SB, Demajo M, Filipović D (2014) Different susceptibility of prefrontal cortex and hippocampus to oxidative stress following chronic social isolation stress. Mol Cell Biochem 393:43–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2045-z
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, Sollott SJ (2014) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev 94:909–950. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00026.2013
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81430078, 30972456), and Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 201901D111203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Co-first authors are Tao Huang and Weiwei Guo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, T., Guo, W., Wang, Y. et al. Involvement of Mitophagy in Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticle–Induced Impairment of Learning and Memory in Mice. Neurotox Res 39, 378–391 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00283-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00283-0