Abstract
Manganese (Mn) is an essential element required for many biological processes and systems in the human body. Mn intoxication increases brain glutamate (Glu) levels causing neuronal damage. Recent studies have reported that ephrin-A3 regulates this glutamate transporter. However, none has explored the role of this crucial molecule in Mn-induced excitotoxicity. The present study investigated whether ephrin-A3/GLAST-GLT-1/Glu signaling pathway participates in Mn-induced excitotoxicity using astrocytes and Kunming mice. The mechanisms were explored using fluoxetine (ephrin-A3 inhibitor) and riluzole (a Glu release inhibitor). Firstly, we demonstrated that Mn exposure (500 μM or 50 mg/kg MnCl2) significantly increased Mn, ephrin-A3, and Glu levels, and inhibited Na+-K+ ATPase activity, as well as mRNA and protein levels of GLAST and GLT-1. Secondly, we found that astrocytes and mice pretreated with fluoxetine (100 μM or 15 mg/kg) and riluzole (100 μM or 32 μmol/kg) prior to Mn exposure had lower ephrin-A3 and Glu levels, but higher Na+-K+ ATPase activity, expression levels of GLAST and GLT-1 than those exposed to 500 μM or 50 mg/kg MnCl2. Moreover, the morphology of cells and the histomorphology of mice striatum were injured. Results showed that pretreatment with fluoxetine and riluzole attenuated the Mn-induced motor dysfunctions. Together, these results suggest that the ephrin-A3/GLAST-GLT-1/Glu signaling pathway participates in Mn-induced excitotoxicity, and fluoxetine and riluzole can mitigate the Mn-induced excitotoxicity in mice brain.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 September 2020
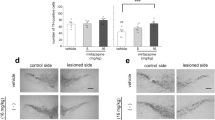
The original article contains mistake. Figure 3d and Figure 3e were repeated.
References
Aschner M, Gannon M, Kimelberg HK (1992) Manganese uptake and efflux in cultured rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 58(2):730–735
Brouillet EP, Shinobu L, McGarvey U, Hochberg F, Beal MF (1993) Manganese injection into the rat striatum produces excitotoxic lesions by impairing energy metabolism. Exp Neurol 120(1):89–94
Carmona MA, Murai KK, Wang L, Roberts AJ, Pasquale EB (2009) Glial ephrin-A3 regulates hippocampal dendritic spine morphology and glutamate transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(30):12524–12529
Chen Y, Fu AK, Ip NY (2012) Eph receptors at synapses: implications in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Signal 24(3):606–611
Danbolt NC, Storm-Mathisen J, Kanner BI (1992) An [Na+ + K+]coupled L-glutamate transporter purified from rat brain is located in glial cell processes. Neuroscience 51(2):295–310
Das G, Yu Q, Hui R, Reuhl K, Gale NW, Zhou R (2016) EphA5 and EphA6: regulation of neuronal and spine morphology. Cell Biosci 6:48
Deng Y, Xu Z, Xu B, Tian Y, Xin X, Deng X, Gao J (2009) The protective effect of riluzole on manganese caused disruption of glutamate-glutamine cycle in rats. Brain Res 1289:106–117
Deng Y, Xu Z, Xu B, Xu D, Tian Y, Feng W (2012) The protective effects of riluzole on manganese-induced disruption of glutamate transporters and glutamine synthetase in the cultured astrocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 148(2):242–249
Deng Y, Jiao C, Mi C, Xu B, Li Y, Wang F, Liu W, Xu Z (2015) Melatonin inhibits manganese-induced motor dysfunction and neuronal loss in mice: involvement of oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol 51(1):68–88
Dobson AW, Erikson KM, Aschner M (2004) Manganese neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1012:115–128
Egea J, Klein R (2007) Bidirectional Eph-ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol 17(5):230–238
Erikson KM, Shihabi ZK, Aschner JL, Aschner M (2002a) Manganese accumulates in iron-deficient rat brain regions in a heterogeneous fashion and is associated with neurochemical alterations. Biol Trace Elem Res 87(1–3):143–156
Erikson KM, Suber RL, Aschner M (2002b) Glutamate/aspartate transporter (GLAST), taurine transporter and metallothionein mRNA levels are differentially altered in astrocytes exposed to manganese chloride, manganese phosphate or manganese sulfate. Neurotoxicology 23(3):281–288
Filosa A, Paixão S, Honsek SD, Carmona MA, Becker L, Feddersen B, Gaitanos L, Rudhard Y, Schoepfer R, Klopstock T, Kullander K, Rose CR, Pasquale EB, Klein R (2009) Neuron-glia communication via EphA4/ephrin-A3 modulates LTP through glial glutamate transport. Nat Neurosci 12(10):1285–1292
Fitsanakis VA, Aschner M (2005) The importance of glutamate, glycine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid transport and regulation in manganese, mercury and lead neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204(3):343–354
Fumagalli E, Funicello M, Rauen T, Gobbi M, Mennini T (2008) Riluzole enhances the activity of glutamate transporters GLAST, GLT1 and EAAC1. Eur J Pharmacol 578(2–3):171–176
Galimberti I, Bednarek E, Donato F, Caroni P (2010) EphA4 signaling in juveniles establishes topographic specificity of structural plasticity in the hippocampus. Neuron 65(5):627–642
Genda EN, Jackson JG, Sheldon AL, Locke SF, Greco TM, O'Donnell JC, Spruce LA, Xiao R, Guo W, Putt M, Seeholzer S, Ischiropoulos H, Robinson MB (2011) Co-compartmentalization of the astroglial glutamate transporter, GLT-1, with glycolytic enzymes and mitochondria. J Neurosci 31(50):18275–18288
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F, Hau P, Langmann T, Dietmaier W, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2004) Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem 50(3):490–499
Hazell AS, Norenberg MD (1997) Manganese decreases glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem Res 22(12):1443–1447
Huang CC, Chu NS, Lu CS, Wang JD, Tsai JL, Tzeng JL, Wolters EC, Calne DB (1989) Chronic manganese intoxication. Arch Neurol 46(10):1104–1106
Irifune M, Kikuchi N, Saida T, Takarada T, Shimizu Y, Endo C, Morita K, Dohi T, Sato T, Kawahara M (2007) Riluzole, a glutamate release inhibitor, induces loss of righting reflex, antinociception, and immobility in response to noxious stimulation in mice. Anesth Analg 104(6):1415–1421
Johnson J Jr, Pajarillo E, Karki P, Kim J, Son DS, Aschner M, Lee E (2018) Valproic acid attenuates manganese-induced reduction in expression of GLT-1 and GLAST with concomitant changes in murine dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 67:112–120
Juan WS, Huang SY, Chang CC, Hung YC, Lin YW et al (2014) Melatonin improves neuroplasticity by upregulating the growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) and NMDAR postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95) proteins in cultured neurons exposed to glutamate excitotoxicity and in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia even during a long-term recovery period. J Pineal Res 56(2):213–223
Kanjhan R, Noakes PG, Bellingham MC (2016) Emerging roles of filopodia and dendritic spines in motoneuron plasticity during development and disease. Neural Plast 2016:3423267
Karki P, Smith K, Johnson J Jr, Aschner M, Lee E (2015) Role of transcription factor yin yang 1 in manganese-induced reduction of astrocytic glutamate transporters: putative mechanism for manganese-induced neurotoxicity. Neurochem Int 88:53–59
Kawahara Y, Ito K, Sun H, Aizawa H, Kanazawa I, Kwak S (2004) Glutamate receptors: RNA editing and death of motor neurons. Nature 427(6977):801
Kikuchihara Y, Abe H, Tanaka T, Kato M, Wang L, Ikarashi Y, Yoshida T, Shibutani M (2015) Relationship between brain accumulation of manganese and aberration of hippocampal adult neurogenesis after oral exposure to manganese chloride in mice. Toxicology 331:24–34
Killestein J, Kalkers NF, Polman CH (2005) Glutamate inhibition in MS: the neuroprotective properties of riluzole. J Neurol Sci 233(1–2):113–115
Kollmann K, Damme M, Markmann S, Morelle W, Schweizer M, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Röchert AK, Pohl S, Lübke T, Michalski JC, Käkelä R, Walkley SU, Braulke T (2012) Lysosomal dysfunction causes neurodegeneration in mucolipidosis II 'knock-in' mice. Brain 135(Pt 9):2661–2675
Krachler M, Rossipal E (2000) Concentrations of trace elements in extensively hydrolysed infant formulae and their estimated daily intakes. Ann Nutr Metab 44(2):68–74
Kwak S, Weiss JH (2006) Calcium-permeable AMPA channels in neurodegenerative disease and ischemia. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16(3):281–287
Kwakye GF, Paoliello MM, Mukhopadhyay S, Bowman AB, Aschner M (2015) Manganese-induced parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease: shared and distinguishable features. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(7):7519–7540
Larsson HP, Wang X, Lev B, Baconguis I, Caplan DA, Vyleta NP, Koch HP, Diez-Sampedro A, Noskov SY (2010) Evidence for a third sodium-binding site in glutamate transporters suggests an ion/substrate coupling model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(31):13912–13917
Lee ES, Sidoryk M, Jiang H, Yin Z, Aschner M (2009) Estrogen and tamoxifen reverse manganese-induced glutamate transporter impairment in astrocytes. J Neurochem 110(2):530–544
Lee E, Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Yin Z, Webb A, Son DS, Aschner M (2012) Transforming growth factor-alpha mediates estrogen-induced upregulation of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in rat primary astrocytes. Glia 60(7):1024–1036
Lee E, Karki P, Johnson J Jr, Hong P, Aschner M (2017) Manganese control of glutamate transporters’ gene expression. Adv Neurobiol 16:1–12
Li J, Liu N, Wang Y, Wang R, Guo D, Zhang C (2012) Inhibition of EphA4 signaling after ischemia-reperfusion reduces apoptosis of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neurosci Lett 518(2):92–95
Li Y, Wang H, Wang X, Liu Z, Wan Q, Wang G (2014) Differential expression of hippocampal EphA4 and ephrinA3 in anhedonic-like behavior, stress resilience, and antidepressant drug treatment after chronic unpredicted mild stress. Neurosci Lett 566:292–297
Liebl DJ, Morris CJ, Henkemeyer M, Parada LF (2003) mRNA expression of ephrins and Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in the neonatal and adult mouse central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 71(1):7–22
Martin D, Thompson MA, Nadler JV (1993) The neuroprotective agent riluzole inhibits release of glutamate and aspartate from slices of hippocampal area CA1. Eur J Pharmacol 250(3):473–476
Mehta A, Prabhakar M, Kumar P, Deshmukh R, Sharma PL (2013) Excitotoxicity: bridge to various triggers in neurodegenerative disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 698(1–3):6–18
Mirhashemi SM, Shahabaddin ME (2011) Evaluation of aluminium, manganese, copper and selenium effects on human islets amyloid polypeptide hormone aggregation. Pak J Biol Sci 14(4):288–292
Morello M, Canini A, Mattioli P, Sorge RP, Alimonti A, Bocca B, Forte G, Martorana A, Bernardi G, Sancesario G (2008) Sub-cellular localization of manganese in the basal ganglia of normal and manganese-treated rats an electron spectroscopy imaging and electron energy-loss spectroscopy study. Neurotoxicology 29(1):60–72
Murai KK, Pasquale EB (2003) ‘Eph’ective signaling: forward, reverse and crosstalk. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 14):2823–2832
Murai KK, Nguyen LN, Irie F, Yamaguchi Y, Pasquale EB (2003) Control of hippocampal dendritic spine morphology through ephrin-A3/EphA4 signaling. Nat Neurosci 6(2):153–160
Myers JE, Thompson ML, Ramushu S, Young T, Jeebhay MF, London L, Esswein E, Renton K, Spies A, Boulle A, Naik I, Iregren A, Rees DJ (2003) The nervous system effects of occupational exposure on workers in a South African manganese smelter. Neurotoxicology 24(6):885–894
Nagatomo S, Umehara F, Hanada K, Nobuhara Y, Takenaga S et al (1999) Manganese intoxication during total parenteral nutrition: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci 162(1):102–105
Noristani HN, Meadows RS, Olabarria M, Verkhratsky A, Rodríguez JJ (2011) Increased hippocampal CA1 density of serotonergic terminals in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: an ultrastructural study. Cell Death Dis 2:e210
Parmentier-Batteur S, Finger EN, Krishnan R, Rajapakse HA, Sanders JM et al (2011) Attenuation of scratch-induced reactive astrogliosis by novel EphA4 kinase inhibitors. J Neurochem 18(6):1016–1031
Pena F, Tapia R (2000) Seizures and neurodegeneration induced by 4-aminopyridine in rat hippocampus in vivo: role of glutamate- and GABA-mediated neurotransmission and of ion channels. Neuroscience 101(3):547–561
Petr GT, Sun Y, Frederick NM, Zhou Y, Dhamne SC, Hameed MQ, Miranda C, Bedoya EA, Fischer KD, Armsen W, Wang J, Danbolt NC, Rotenberg A, Aoki CJ, Rosenberg PA (2015) Conditional deletion of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 reveals that astrocytic GLT-1 protects against fatal epilepsy while neuronal GLT-1 contributes significantly to glutamate uptake into synaptosomes. J Neurosci 35(13):5187–5201
Pulkkinen K, Malm T, Turunen M, Koistinaho J, Ylä-Herttuala S (2008) Hypoxia induces microRNA miR-210 in vitro and in vivo ephrin-A3 and neuronal pentraxin 1 are potentially regulated by miR-210. FEBS Lett 582(16):2397–2401
Richter M, Murai KK, Bourgin C, Pak DT, Pasquale EB (2007) The EphA4 receptor regulates neuronal morphology through SPAR-mediated inactivation of rap GTPases. J Neurosci 27(51):14205–14215
Rose EM, Koo JC, Antflick JE, Ahmed SM, Angers S et al (2009) Glutamate transporter coupling to Na,K-ATPase. J Neurosci 29(25):8143–8155
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Aschner M (2013) Manganese toxicity in the central nervous system: the glutamine/glutamate-gamma-aminobutyric acid cycle. J Intern Med 273(5):466–477
Stokes PE, Holtz A (1997) Fluoxetine tenth anniversary update: the progress continues. Clin Ther 19(5):1135–1250
Sugiyama K, Aida T, Nomura M, Takayanagi R, Zeilhofer HU, Tanaka K (2017) Calpain-dependent degradation of nucleoporins contributes to motor neuron death in a mouse model of chronic excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 37(36):8830–8844
Toklu HZ, Uysal MK, Kabasakal L, Sirvanci S, Ercan F, Kaya M (2009) The effects of riluzole on neurological, brain biochemical, and histological changes in early and late term of sepsis in rats. J Surg Res 152(2):238–248
Ustün TB, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Chatterji S, Mathers C, Murray CJ (2004) Global burden of depressive disorders in the year 2000. Br J Psychiatry 184:386–392
Vandenberg RJ, Ryan RM (2004) Mechanisms of glutamate transport. Physiol Rev 93(4):1621–1657
Vizi ES, Kisfali M, Lőrincz T (2013) Role of nonsynaptic GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in excitotoxicity: evidence that fluoxetine selectively inhibits these receptors and may have neuroprotective effects. Brain Res Bull 93:32–38
Wang SJ, Wang KY, Wang WC (2004) Mechanisms underlying the riluzole inhibition of glutamate release from rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals (synaptosomes). Neuroscience 125(1):191–201
Wang T, Li X, Yang D, Zhang H, Zhao P, Fu J, Yao B, Zhou Z (2015) ER stress and ER stress-mediated apoptosis are involved in manganese-induced neurotoxicity in the rat striatum in vivo. Neurotoxicology 48:109–119
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Ahsan H, Levy D, Factor-Litvak P, Kline J, van Geen A, Slavkovich V, LoIacono NJ, Cheng Z, Zheng Y, Graziano JH (2006) Water manganese exposure and children's intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 114(1):124–129
Wilkinson DG (2001) Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(3):155–164
Williams M, Todd GD, Roney N, Crawford J, Coles C et al (2012) Toxicological profile for manganese. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US), Atlanta
Yang J, Luo X, Huang X, Ning Q, Xie M, Wang W (2014) Ephrin-A3 reverse signaling regulates hippocampal neuronal damage and astrocytic glutamate transport after transient global ischemia. J Neurochem 131(3):383–394
Yang X, Yang H, Wu F, Qi Z, Li J et al (2018) Mn inhibits GSH synthesis via downregulation of neuronal EAAC1 and astrocytic xCT to cause oxidative damage in the striatum of mice. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:4235695
Yue Y, Chen ZY, Gale NW, Blair-Flynn J, Hu TJ, Yue X, Cooper M, Crockett DP, Yancopoulos GD, Tessarollo L, Zhou R (2002) Mistargeting hippocampal axons by expression of a truncated Eph receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(16):10777–10782
Zayed J, Gérin M, Loranger S, Sierra P, Bégin D, Kennedy G (1994) Occupational and environmental exposure of garage workers and taxi drivers to airborne manganese arising from the use of methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl in unleaded gasoline. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 55(1):53–58
Zerangue N, Kavanaugh MP (1996) Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 383(6601):634–637
Zhang W, Zhang L, Liang B, Schroeder D, Zhang ZW, Cox GA, Li Y, Lin DT (2016) Hyperactive somatostatin interneurons contribute to excitotoxicity in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Neurosci 19(4):557–559
Zink M, Rapp S, Donev R, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Thome J (2011) Fluoxetine treatment induces EAAT2 expression in rat brain. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 118(6):849–855
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Hui Yuan, Fengdi Wu, Minghui Li, Xianchao Du, Haiying Wang, Bingchen Liu, Lei Zhang, Shuang Wang, and Xuda Liu for their valuable advices.
Availability of Data and Material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the funding from the National Key Research and Development Project of China (Grant No. 521/2600019004), the Basic Research Fund of Young Program of Higher Education of Liaoning Province (Grant No. QNK201735), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81302406), and the Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists in School of Public Health, China Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author substantially contributed to the article. Zhipeng Qi, conception and design and drafting the article; Xinxin Yang, Yanqi Sang, Yanan Liu, Jiashuo Li, Bin Xu, Wei Liu, Miao He, and Zhaofa Xu, revising the manuscript; and Yu Deng and Jinghai Zhu, conception and design, revising it critically for important intellectual content, and final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The animal use protocol listed below has been reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethical and the Scientific Research Committee of China Medical University.
Consent for Publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Z., Yang, X., Sang, Y. et al. Fluoxetine and Riluzole Mitigates Manganese-Induced Disruption of Glutamate Transporters and Excitotoxicity via Ephrin-A3/GLAST-GLT-1/Glu Signaling Pathway in Striatum of Mice. Neurotox Res 38, 508–523 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00209-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00209-w