Abstract
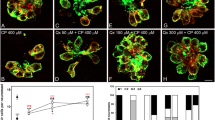
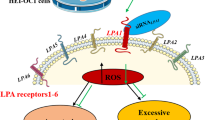
Cisplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy compound effective against a variety of cancers. However, it can cause increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in auditory and vestibular tissue leading to permanent hearing and balance loss. The amino acid, L-serine, has been shown to reduce ROS in some tissue types. In this project, we first investigated whether L-serine could reduce cisplatin-mediated ROS generation in zebrafish utricular tissue culture using spectrophotometry and the fluorescent ROS detector dye, H2DCFDA. Then, we examined whether L-serine could prevent the effect of cisplatin against cellular viability in the mouse auditory hybridoma cell line, HEI-OC1, using the spectrophotometric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) (MTT) assay. As a final step, we used H2DCFDA dye and flow cytometry analysis to determine if L-serine could counteract the effect of cisplatin on ROS production in this cell line. We found that cisplatin and L-serine treatment may influence ROS production in utricular tissue. Further, although L-serine did not counteract the effect of cisplatin against HEI-OC1 cellular viability, the amino acid did prevent the platinum compound’s effect to increase ROS in these cells. These results suggest that L-serine may act in auditory and vestibular tissues as an effective protectant against cisplatin-mediated toxicity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cepeda V, Fuertes MA, Castilla J, Alonso C, Quevedo C, Pérez JM (2007) Biochemical mechanisms of cisplatin cytotoxicity. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 7:3–18
Chen X, Zhong Z, Xu Z, Chen L, Wang Y (2010) 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein as a fluorescent probe for reactive oxygen species measurement: forty years of application and controversy. Free Radic Res 44:587–604
Choi Y-M, Kim H-K, Shim W, Anwar MA, Kwon J-W, Kwon H-K, Kim HJ, Jyeong H, Kim HM, Hwang D, Kim HS, Choi S (2015) Mechanism of cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity is correlated to impaired metabolism due to mitochondrial ROS generation. PLoS One 10:e0135083
Cox PA, Davis DA, Mash DC, Metcalf JS, Banack SA (2016) Dietary exposure to an environmental toxin triggers neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid deposits in the brain. Proc R Soc B 283:20152397
Dasari S, Tchounwou PB (2014) Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740:364–378
Dunlop RA, Cox PA, Banack SA, Rodgers KJ (2013) The non-protein amino acid BMAA is misincorporated into human proteins in place of L-serine causing protein misfolding and aggregation. PLoS One 8:e75376
Goncharov NV, Belinskaia DA, Shmurak VI, Terpilowski MA, Jenkins RO, Avdonin PV (2017) Serum albumin binding and esterase activity: mechanistic interactions with organophosphates. Molecules 22:1201
Jesus VPS, Raniero L, Lemes GM, Bhattacharjee TT, Caetano Júnior PC, Castilho ML (2018) Nanoparticles of methylene blue enhance photodynamic therapy. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 23:212–217
Kalinec GM, Webster P, Lim DJ, Kalinec F (2003) A cochlear cell line as an in vitro system for drug ototoxicity screening. Audiol Neurootol 8:177–189
Kalinec GM, Thein P, Park C, Kalinec F (2016) HEI-OC1 cells as a model for investigating drug cytotoxicity. Hear Res 335:105–117
Karasawa T, Steyger PS (2015) An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol Lett 237:219–227
Kim MJ, Choi J, Kim N, Han GC (2014) Behavioral changes of zebrafish according to cisplatin- induced toxicity of the balance system. Hum Exp Toxicol 33:1167–1175
Kim KY, Hwang SK, Park SY, Kim MJ, Jun DY, Kim YH (2019) L-serine protects mouse hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells against oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial damage and apoptotic cell death. Free Radic Biol Med 141:447–460
Locasale JW (2013) Serine, glycine and the one-carbon cycle: cancer metabolism in full circle. Nat Rev Cancer 13:572–583
Maralani MN, Movahedian A, Javanmard SH (2012) Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of L-serine on human endothelial cells. Research in Pharm Sci 7:209–215
Martínez-Reyes I, Chandel NS (2014) Mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism maintains redox balance during hypoxia. Cancer Disc 4:1371–1373
Metcalf JS, Dunlop RA, Powell JT, Banack SA, Cox PA (2018) L-serine: a naturally-occurring amino acid with therapeutic potential. Neurotox Res 33:213–221
Monroe JD, Hruska HL, Ruggles HK, Williams KM, Smith ME (2018a) Anti-cancer characteristics and ototoxicity of platinum(II) amine complexes with only one leaving ligand. PLoS One 13:e0192505
Monroe JD, Millay MH, Patty BG, Smith ME (2018b) The curcuminoid, EF-24, reduces cisplatin-mediated reactive oxygen species in zebrafish inner ear auditory and vestibular tissues. J Clin Neurosci 57:152–156
Popper AN, Fay RR (1993) Sound detection and processing by fish: critical review and major research questions. Brain Behav Evol 41:14–38
Salvi A, Carrupt P, Mayer JM, Testa B (1997) Esterase-like activity of human serum albumin toward prodrug esters of nicotinic acid. Drug Metab Dispos 25:395–398
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24:R453–R462
Sheth S, Mukherjea D, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2017) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and otoprotection. Frontiers in Cell Neurosci 11:338
Teppo H-R, Soini Y, Karihtala P (2017) Reactive oxygen species-mediated mechanisms of action of targeted cancer therapy. Oxidative Med and Cell Longevity 2017:1485283
Westerfield M (1994) The Zebrafish book: a guide for the laboratory use of Zebrafish, 4th edn. Institute of Neuroscience, University of Oregon, Eugene
Wu X, Cai J, Li X, Li H, Li J, Bai X, Liu W, Han Y, Xu L, Zhang D, Wang H, Fan Z (2017) Allicin protects against cisplatin-induced vestibular dysfunction by inhibiting the apoptotic pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 805:108–117
Zhang J, Wang M, Li Z, Bi X, Song J, Weng S, Fu G (2016) NADPH oxidase activation played a critical role in the oxidative stress process in stable coronary artery disease. Am J of Trans Res 8:5199–5210
Zhou X, Zhang H, He L, Wu X, Yin Y (2018) Long-term L-serine administration reduces food intake and improves oxidative stress and Sirt1/NFκB signaling in the hypothalamus of aging mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:476
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Paul A. Cox for the L-serine that was used in our initial experiments.
Funding
This project was funded by the National Institutes of Health awards T1 R15 CA188890-01A1 and 2 P20 GM103436-19 to M.E.S. and through the Western Kentucky University Gatton Academy of Mathematics and Science Summer Research Internship Grant to both Elvin Irihamye and Satya Moolani.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monroe, J.D., Moolani, S.A., Irihamye, E.N. et al. Effects of L-Serine Against Cisplatin-Mediated Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Zebrafish Vestibular Tissue Culture and HEI-OC1 Auditory Hybridoma Cells. Neurotox Res 39, 36–41 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00188-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00188-y