Abstract
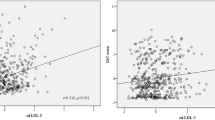
Correlation between the level of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and the incidence of intracranial arterial stenosis (ICAS) is unclear. We aim to investigate the relationship between hs-CRP levels and ICAS. A total of 1458 patients aged ≥ 40 years were enrolled in this study. All the participants had a magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) examination for the evaluation of ICAS. Participants were classified into four groups according to stroke and ICAS. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to assess the relationship of hs-CRP levels and ICAS status. A total of 432 (29.63%) subjects had ICAS. The levels of hs-CRP in stroke group were significantly higher than those in non-stroke group (p < 0.001). Patients with ICAS tend to have higher hs-CRP levels (p < 0.001). In multivariate analysis, the fourth hs-CRP quartile had the strongest association with ICAS in both stroke group and non-stroke group (OR 2.512, 95% CI 1.651–3.853, p < 0.001 for stroke group, and OR 2.534, 95% CI 1.435–4.595, p = 0.002 for non-stroke group) among the four quartiles of hs-CRP levels. Our study suggests that elevated serum hs-CRP levels are associated with higher risk of ICAS, in both stroke patients and non-stroke participants.


Similar content being viewed by others

Abbreviations
- ACA:
-
anterior cerebral artery
- AIS:
-
acute ischemic stroke
- BA:
-
basilar artery
- HDL:
-
high-density lipoprotein
- hs-CRP:
-
high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
- ICA:
-
internal carotid artery
- ICAS:
-
intracranial arterial stenosis
- IL-6:
-
interleukin-6
- LDL:
-
low-density lipoprotein
- MCA:
-
middle cerebral artery
- MRA:
-
magnetic resonance angiography
- NICAS:
-
non-acute ischemic stroke
- PCA:
-
posterior cerebral artery
- TC:
-
total cholesterol
- TG:
-
triglyceride
- VA:
-
vertebral artery
References
Arthurs ZM, Andersen C, Starnes BW, Sohn VY, Mullenix PS, Perry J (2008) A prospective evaluation of C-reactive protein in the progression of carotid artery stenosis. J Vasc Surg 47:744–750 discussion 751
Bae HJ, Lee J, Park JM, Kwon O, Koo JS, Kim BK, Pandey DK (2007) Risk factors of intracranial cerebral atherosclerosis among asymptomatics. Cerebrovasc Dis 24:355–360
Bassuk SS, Rifai N, Ridker PM (2004) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Curr Probl Cardiol 29:439–493
Buja LM, Willerson JT (1994) Role of inflammation in coronary plaque disruption. Circulation 89:503–505
Calabro P, Willerson JT, Yeh ET (2003) Inflammatory cytokines stimulated C-reactive protein production by human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Circulation 108:1930–1932
Feldmann E, Daneault N, Kwan E, Ho KJ, Pessin MS, Langenberg P, Caplan LR (1990) Chinese-white differences in the distribution of occlusive cerebrovascular disease. Neurology 40:1541–1545
Flegar-Mestric Z, Vrhovski-Hebrang D, Preden-Kerekovic V, Perkov S, Hebrang A, Grga A, Janus D, Vidjak V (2007) C-reactive protein level in severe stenosis of cerebral arteries. Cerebrovasc Dis 23:430–434
Gonzalez NR, Liebeskind DS, Dusick JR, Mayor F, Saver J (2013) Intracranial arterial stenoses: current viewpoints, novel approaches, and surgical perspectives. Neurosurg Rev 36:175–184 discussion 184-175
Grant EG, Benson CB, GL, M. (2003) Carotid artery stenosis: grayscale and Doppler ultrasound diagnosis-Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus Conference. Ultrasound Quarterly 19:190–198
Huang X, Wang A, Liu X, Chen S, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Huang K, Wu J, Chen S, Wu S, Zhao X (2016) Association between high sensitivity C-reactive protein and prevalence of asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Atherosclerosis 246:44–49
Ishwarlal Jialal, Devaraj S (2001) Inflammation and atherosclerosis: the value of the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein assay as a risk marker. Am J Clin Pathol 116:S108–S115
Jabs WJ, Theissing E, Nitschke M, Bechtel JF, Duchrow M, Mohamed S, Jahrbeck B, Sievers HH, Steinhoff J, Bartels C (2003) Local generation of C-reactive protein in diseased coronary artery venous bypass grafts and normal vascular tissue. Circulation 108:1428–1431
Jia L, Hao F, Wang W, Qu Y (2015) Circulating miR-145 is associated with plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in acute ischemic stroke patients. Cell Biochem Funct 33:314–319
Ladenvall C, Jood K, Blomstrand C, Nilsson S, Jern C, Ladenvall P (2006) Serum C-reactive protein concentration and genotype in relation to ischemic stroke subtype. Stroke 37:2018–2023
Landry KK, Alexander KS, Zakai NA, Judd SE, Kleindorfer DO, Howard VJ, Howard G, Cushman M (2017) Association of stroke risk biomarkers with stroke symptoms: the reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke cohort. J Thromb Haemost: JTH 15:21–27
Li H, Wong KS (2003) Racial distribution of intracranial and extracranial atherosclerosis. J Clin Neurosci 10:30–34
Li J, Wang A, Zhao X, Liu L, Meng X, Lin J, Jing J, Zou X, Wang Y, Wang Y et al (2018) High-sensitive C-reactive protein and dual antiplatelet in intracranial arterial stenosis. Neurology 90:e447–e454
Libby P (2002) Atherosclerosis: the new view. Sci Am 286:46–55
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri M (2002) Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 105:1135–1143
Liu H, Yao Y, Wang Y, Ji L, Zhu K, Hu H, Chen J, Yang J, Cui Q, Geng B, Liu Q, Li D, Zhou Y (2018) Association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and carotid atherosclerosis: a cross-sectional study. J Cell Mol Med 22:5145–5150
Mazighi M, Labreuche J, Gongora-Rivera F, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ, Amarenco P (2008) Autopsy prevalence of intracranial atherosclerosis in patients with fatal stroke. Stroke 39:1142–1147
Mullenix PS, Steele SR, Martin MJ, Starnes BW, Andersen CA (2007) C-reactive protein level and traditional vascular risk factors in the prediction of carotid stenosis. Arch Surg 142:1066–1071
Rost NS, Wolf PA, Kase CS, Kelly-Hayes M, Silbershatz H, Massaro JM, D'Agostino RB, Franzblau C, Wilson PWF (2001) Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein and risk of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: the Framingham Study. Stroke 32:2575–2579
Sakata K, Gamou T, Tada H, Hayashi K, Ino H, Yamagishi M, Masa-aki K, behalf of the, M.S.G (2018) Low baseline high-sensitive C-reactive protein is associated with coronary atherosclerosis regression: insights from the MILLION Study. J Atheroscler Thromb 25:000–000
Samuels OB, Joseph GJ, Lynn MJ, Smith HA, Chimowitz MI (2000) A standardized method for measuring intracranial arterial stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:643–646
Schulze Horn C, Ilg R, Sander K, Bickel H, Briesenick C, Hemmer B, Poppert H, Sander D (2009) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein at different stages of atherosclerosis: results of the INVADE study. J Neurol 256:783–791
Shimizu K, Shimomura K, Tokuyama Y, Sakurai K, Isahaya K, Takaishi S, Kato B, Usuki N, Shimizu T, Yamada K, Hasegawa Y (2013) Association between inflammatory biomarkers and progression of intracranial large artery stenosis after ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis: Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 22:211–217
Shoamanesh A, Preis SR, Beiser AS, Kase CS, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ, Seshadri S, Romero JR (2016) Circulating biomarkers and incident ischemic stroke in the Framingham Offspring Study. Neurology 87:1206–1211
Takahashi W, Ohnuki T, Ohnuki Y, Kawada S, Takagi S (2008) The role of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in asymptomatic intra- and extracranial large artery diseases. Cerebrovasc Dis 26:549–555
Volanakis JE (2001) Human C-reactive protein: expression, structure, and function. Mol Immunol 9:189–197
Wang J, Liu Y, Zhang L, Li N, Wang C, Gao X, Zhou Y, Wang A, Wu S, Zhao X (2014a) Associations of high sensitivity C-reactive protein levels with the prevalence of asymptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. Eur J Neurol 21:512–518
Wang Y, Zhao X, Liu L, Soo YO, Pu Y, Pan Y, Wang Y, Zou X, Leung TW, Cai Y et al (2014b) Prevalence and outcomes of symptomatic intracranial large artery stenoses and occlusions in China: the Chinese Intracranial Atherosclerosis (CICAS) Study. Stroke 45:663–669
Wityk RJ, Lehman D, Klag M, e.a. (1996) Race and sex differences in the distribution of cerebral atherosclerosis. Stroke 27:1974–1980
Wong KS, Huang YN, Yang HB, Gao S, Li H, Liu JY, Liu Y, Tang A (2007) A door-to-door survey of intracranial atherosclerosis in Liangbei County, China. Neurology 68:2031–2034
Yu H, Huang Y, Chen X, Nie W, Wang Y, Jiao Y, Reed GL, Gu W, Chen H (2017) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein in stroke patients - the importance in consideration of influence of multiple factors in the predictability for disease severity and death. J Clin Neurosci: Off J Neurosurg Soc Aust 36:12–19
Zhang S, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Gao X, Zhang Q, Wang A, Jia Z, Wu S, Zhao X (2013) Prevalence and risk factors of asymptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis in a community-based population of Chinese adults. Eur J Neurol 20:1479–1485
Acknowledgments
We thank all the study participants for their assistants and supports.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province (ts201511109 and tsqn20161079) and Qingdao Key Health Discipline Development Fund; Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2018SHZDZX01) and ZHANGJIANG LAB; Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute; and the State Key Laboratory of Neurobiology and Frontiers Center for Brain Science of Ministry of Education, Fudan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JTY, LT, and QD conceptualized the study, analyzed and interpreted the data, and drafted and revised the manuscript. BJS, YD, and CCT analyzed and interpreted the data, drafted and revised the manuscript, did the statistical analysis, and prepared all the figures. XHH, WX, MC, and FRS did the interpretation of the data and revision of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the writing and revisions of the paper and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Written informed consent form was obtained from all participants or their legal representatives. This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committees of Qingdao Municipal Hospital
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, BJ., Dong, Y., Tan, CC. et al. Elevated Hs-CRP Levels Are Associated with Higher Risk of Intracranial Arterial Stenosis. Neurotox Res 37, 425–432 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00108-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00108-9