Abstract
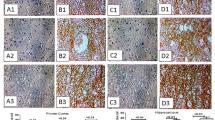
Several studies have recently revealed that cognitive function can be affected by paracetamol (APAP) treatment. However, the exact impact of this drug treatment on learning and memory has not been clarified. This study aimed to investigate the effect of APAP treatment on the alteration of synapses and oxidative stress in the rat frontal cortex and hippocampus. APAP at a dose of 200 mg/kg bw was fed to adult male Wistar rats through either acute (n = 10), 15-day (n = 10), or 30-day (n = 10) treatment regimens. The synaptic ultrastructure and proteins, synaptophysin (SYP) and postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95), were monitored. The amount of protein carbonyl oxidation (PCO) and glutathione (GSH) levels were examined. Our results demonstrated that acute treatment with APAP had no effect on synapses and oxidative stress. However, the synapses obtained from rats with 15-day APAP treatment showed a marked shortening of active zones and widening of the synaptic cleft. Decrement of SYP and PSD-95 proteins were demonstrated in these rats as well. With 30-day APAP treatment, the alteration of the synaptic ultrastructure and proteins was more evident. Moreover, the depletion of GSH and the elevation of PCO levels were demonstrated in the rats treated with APAP for 30 days. These results suggest that long-term APAP treatment can induce synaptic degeneration in the hippocampus and frontal cortex. The increase in oxidative stress in these brain areas may be due to the deleterious effect of this drug.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulkhaleq FM, Alhussainy TM, Badr MM, Khalil AAA, Gammoh O, Ghanim BY, Qinna NA (2018) Antioxidative stress effects of vitamins C, E, and B12, and their combination can protect the liver against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:3525–3533
Alonso M, Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Vianna MR, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2005) Endogenous BDNF is required for long-term memory formation in the rat parietal cortex. Learn Mem 12:504–510
Bjorkman R (1995) Central antinociceptive effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and paracetamol. Experimental studies in the rat. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl 103:1–44
Blecharz-Klin K, Joniec-Maciejak I, Piechal A, Pyrzanowska J, Wawer A, Widy-Tyszkiewicz E (2014) Paracetamol impairs the profile of amino acids in the rat brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:95–102
Blecharz-Klin K, Wawer A, Jawna-Zboinska K, Pyrzanowska J, Piechal A, Mirowska-Guzel D, Widy-Tyszkiewicz E (2018) Early paracetamol exposure decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in striatum and affects social behaviour and exploration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 168:25–32
Brandlistuen RE, Ystrom E, Nulman I, Koren G, Nordeng H (2013) Prenatal paracetamol exposure and child neurodevelopment: a sibling-controlled cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 42:1702–1713
Burgess N, Maguire EA, O’Keefe J (2002) The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron 35:625–641
Chantong C, Yisarakun W, Thongtan T, Maneesri-le Grand S (2013) Increases of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in hippocampus following chronic paracetamol treatment in rats. Asian Arch Pathol 9:137–146
DeKosky ST, Scheff SW (1990) Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurol 27:457–464
Dodart JC, Bales KR, Gannon KS, Greene SJ, DeMattos RB, Mathis C, DeLong CA, Wu S, Wu X, Holtzman DM et al (2002) Immunization reverses memory deficits without reducing brain Abeta burden in Alzheimer’s disease model. Nat Neurosci 5:452–457
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59
Euston DR, Gruber AJ, McNaughton BL (2012) The role of medial prefrontal cortex in memory and decision making. Neuron 76:1057–1070
Fakunle PB, Ajibade AJ, Oyewo EB, Alamu OA, Daramola AK (2011) Neurohistological degeneration of the hippocampal formation following chronic simultaneous Administration of Ethanol and Acetaminophen in adult Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus). J Pharmacol Toxiol 6:701–709
Ge Q, Wang Z, Wu Y, Huo Q, Qian Z, Tian Z, Ren W, Zhang X, Han J (2017) High salt diet impairs memory-related synaptic plasticity via increased oxidative stress and suppressed synaptic protein expression. Mol Nutr Food Res 61
Gonzalez-Barcala FJ, Pertega S, Castro TP, Sampedro M, Lastres JS, Gonzalez MASJ, Bamonde L, Garnelo L, Valdes L, Carreira J-M, Moure J, Silvarrey AL (2013) Exposure to paracetamol and asthma symptoms. Eur J Pub Health 23:706–710
Good P (2009) Did acetaminophen provoke the autism epidemic? Altern Med Rev 14:364–372
Guldner FH, Ingham CA (1980) Increase in postsynaptic density material in optic target neurons of the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus after bilateral enucleation. Neurosci Lett 17:27–31
Hansson T, Tindberg N, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Kohler C (1990) Regional distribution of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P450 IIE1 in the rat central nervous system. Neurosci 34:451–463
Haorah J, Knipe B, Leibhart J, Ghorpade A, Persidsky Y (2005) Alcohol-induced oxidative stress in brain endothelial cells causes blood-brain barrier dysfunction. J Leukoc Biol 78:1223–1232
Honer WG, Dickson DW, Gleeson J, Davies P (1992) Regional synaptic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 13:375–382
Hou Y, Zhou L, Yang QD, Du XP, Li M, Yuan M, Zhou ZW (2012) Changes in hippocampal synapses and learning-memory abilities in a streptozotocin-treated rat model and intervention by using fasudil hydrochloride. Neurosci 200:120–129
Howard LA, Miksys S, Hoffmann E, Mash D, Tyndale RF (2003) Brain CYP2E1 is induced by nicotine and ethanol in rat and is higher in smokers and alcoholics. Br J Pharmacol 138:1376–1386
Jaeschke H, Bajt ML (2006) Intracellular signaling mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver cell death. Toxicol Sci 89:31–41
James LP, McCullough SS, Knight TR, Jaeschke H, Hinson JA (2003) Acetaminophen toxicity in mice lacking NADPH oxidase activity: role of peroxynitrite formation and mitochondrial oxidant stress. Free Radic Res 37:1289–1297
Kaneai N, Arai M, Takatsu H, Fukui K, Urano S (2012) Vitamin E inhibits oxidative stress-induced denaturation of nerve terminal proteins involved in neurotransmission. J Alzheimers Dis 28:183–189
Keith D, El-Husseini A (2008) Excitation control: balancing PSD-95 function at the synapse. Front Mol Neurosci 1:4
Kumpulainen E, Kokki H, Halonen T, Heikkinen M, Savolainen J, Laisalmi M (2007) Paracetamol (acetaminophen) penetrates readily into the cerebrospinal fluid of children after intravenous administration. Pediatrics 119:766–771
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, Ahn BW, Shaltiel S, Stadtman ER (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–78
Martin JH (1991) Neuroanatomy: Text and atlas. Elsevier, New York
Moyer AM, Fridley BL, Jenkins GD, Batzler AJ, Pelleymounter LL, Kalari KR, Ji Y, Chai Y, Nordgren KK, Weinshilboum RM (2011) Acetaminophen-NAPQI hepatotoxicity: a cell line model system genome-wide association study. Toxicol Sci 120:33–41
Pickering G, Loriot MA, Libert F, Eschalier A, Beaune P, Dubray C (2006) Analgesic effect of acetaminophen in humans: first evidence of a central serotonergic mechanism. Clin Pharmacol Ther 79:371–378
Posadas I, Santos P, Blanco A, Munoz-Fernandez M, Cena V (2010) Acetaminophen induces apoptosis in rat cortical neurons. PLoS One 5:e15360
Qing H, He G, Ly PT, Fox CJ, Staufenbiel M, Cai F, Zhang Z, Wei S, Sun X, Chen CH et al (2008) Valproic acid inhibits Abeta production, neuritic plaque formation, and behavioral deficits in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. J Exp Med 205:2781–2789
Rosenmund C, Rettig J, Brose N (2003) Molecular mechanisms of active zone function. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13:509–519
Scheff SW, Price DA, Schmitt FA, DeKosky ST, Mufson EJ (2007) Synaptic alterations in CA1 in mild Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 68:1501–1508
Sharpe RJ (2008) Acetaminophen: the case for a link to neurodegenerative diseases. Med Hypotheses 71:813–814
Skalska J, Frontczak-Baniewicz M, Struzynska L (2015) Synaptic degeneration in rat brain after prolonged oral exposure to silver nanoparticles. Neurotoxicology 46:145–154
Smith HS (2009) Potential analgesic mechanisms of acetaminophen. Pain Physician 12:269–280
Spiwoks-Becker I, Vollrath L, Seeliger MW, Jaissle G, Eshkind LG, Leube RE (2001) Synaptic vesicle alterations in rod photoreceptors of synaptophysin-deficient mice. Neurosci 107:127–142
Sudano I, Flammer AJ, Periat D, Enseleit F, Hermann M, Wolfrum M, Hirt A, Kaiser P, Hurlimann D, Neidhart M et al (2010) Acetaminophen increases blood pressure in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 122:1789–1796
Supornsilpchai W, le Grand SM, Srikiatkhachorn A (2010a) Cortical hyperexcitability and mechanism of medication-overuse headache. Cephalalgia 30:1101–1109
Supornsilpchai W, le Grand SM, Srikiatkhachorn A (2010b) Involvement of pro-nociceptive 5-HT2A receptor in the pathogenesis of medication-overuse headache. Headache 50:185–197
Takamori S, Holt M, Stenius K, Lemke EA, Gronborg M, Riedel D, Urlaub H, Schenck S, Brugger B, Ringler P et al (2006) Molecular anatomy of a trafficking organelle. Cell 127:831–846
Tarsa L, Goda Y (2002) Synaptophysin regulates activity-dependent synapse formation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1012–1016
Uysal N, Tugyan K, Kayatekin BM, Acikgoz O, Bagriyanik HA, Gonenc S, Ozdemir D, Aksu I, Topcu A, Semin I (2005) The effects of regular aerobic exercise in adolescent period on hippocampal neuron density, apoptosis and spatial memory. Neurosci Lett 383:241–245
Wanasuntronwong A, Jansri U, Srikiatkhachorn A (2017) Neural hyperactivity in the amygdala induced by chronic treatment of rats with analgesics may elucidate the mechanisms underlying psychiatric comorbidities associated with medication-overuse headache. BMC Neurosci 18:1
Wiedenmann B, Franke WW (1985) Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell 41:1017–1028
Wu A, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F (2004) The interplay between oxidative stress and brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates the outcome of a saturated fat diet on synaptic plasticity and cognition. Eur J Neurosci 19:1699–1707
Xiao Y, Fu H, Han X, Hu X, Gu H, Chen Y, Wei Q, Hu Q (2014) Role of synaptic structural plasticity in impairments of spatial learning and memory induced by developmental lead exposure in Wistar rats. PLoS One 9:e115556
Yan M, Huo Y, Yin S, Hu H (2018) Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol 17:274–283
Yisarakun W, Chantong C, Supornsilpchai W, Thongtan T, Srikiatkhachorn A, Reuangwechvorachai P, Maneesri-le Grand S (2015) Up-regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide in trigeminal ganglion following chronic exposure to paracetamol in a CSD migraine animal model. Neuropeptides 51:9–16
Yisarakun W, Supornsilpchai W, Chantong C, Srikiatkhachorn A, Maneesri-le Grand S (2014) Chronic paracetamol treatment increases alterations in cerebral vessels in cortical spreading depression model. Microvasc Res 94:36–46
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT, GB-B_60_074_30_18) and the Thailand Research Fund (PHD/0109/2557).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lalert, L., Ji-au, W., Srikam, S. et al. Alterations in Synaptic Plasticity and Oxidative Stress Following Long-Term Paracetamol Treatment in Rat Brain. Neurotox Res 37, 455–468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00090-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00090-2