Abstract
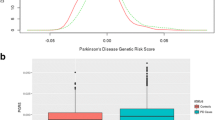
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is attributed to interactions among genes and environmental and lifestyle factors, but the genetic architecture of PD is complex and not completely understood. To evaluate whether the genetic profile modifies PD development and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pathological biomarkers, we enrolled 418 PD patients and 426 age- and sex-matched normal controls. Forty-six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that were reported to be significantly associated with PD in large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWASs) were genotyped and analysed. The alleles associated with PD were used to build polygenic risk score (PRS) models to represent polygenic risk. The Cox proportional hazards model and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were used to evaluate the prediction value of the PRS for PD risk and age at onset. The CSF α-synuclein levels were measured in a subgroup of control subjects (n = 262), and its relationship with the PRS was analysed. We found that some SNPs identified from other populations had significant correlations with PD in our Chinese cohort. The PRS we built had prediction value for PD risk and age at onset. The CSF α-synuclein level had no correlation with the PRS in normal subjects.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bu XL, Wang X, Xiang Y, Shen LL, Wang QH, Liu YH, Jiao SS, Wang YR, Cao HY, Yi X, Liu CH, Deng B, Yao XQ, Xu ZQ, Zhou HD, Wang YJ (2015) The association between infectious burden and Parkinson’s disease: a case-control study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21:877–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.05.015
Chang XL, Mao XY, Li HH, Zhang JH, Li NN, Burgunder JM, Peng R, Tan EK (2011) Association of GWAS loci with PD in China American journal of medical genetics part B, neuropsychiatric genetics : the official publication of the international society of. Psychiatr Genet 156B:334–339. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.31167
Chang KH, Wu YR, Chen YC, Fung HC, Lee-Chen GJ, Chen CM (2015) STK39, but not BST1, HLA-DQB1, and SPPL2B polymorphism, is associated with Han-Chinese Parkinson’s disease in Taiwan. Medicine 94:e1690. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000001690
Chen CM, Chen YC, Chiang MC, Fung HC, Chang KH, Lee-Chen GJ, Wu YR (2016) Association of GCH1 and MIR4697, but not SIPA1L2 and VPS13C polymorphisms, with Parkinson’s disease in Taiwan. Neurobiol Aging 39:221.e221–221.e225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.12.016
Dias V, Junn E, Mouradian MM (2013) The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. J Park Dis 3:461–491. https://doi.org/10.3233/jpd-130230
Escott-Price V, International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics C, Nalls MA, Morris HR, Lubbe S et al (2015) Polygenic risk of Parkinson disease is correlated with disease age at onset. Ann Neurol 77:582–591. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24335
Gao L, Tang H, Nie K, Wang L, Zhao J, Gan R, Huang J, Zhu R, Feng S, Duan Z, Zhang Y, Wang L (2014) Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Neurosci 125:645–654. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2014.961454
Guo JF, Li K, Yu RL, Sun QY, Wang L, Yao LY, Hu YC, Lv ZY, Luo LZ, Shen L, Jiang H, Yan XX, Pan Q, Xia K, Tang BS (2015) Polygenic determinants of Parkinson’s disease in a Chinese population. Neurobiol Aging 36:1765 e1761–1765 e1766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.12.030
Hall TO, Wan JY, Mata IF, Kerr KF, Snapinn KW et al (2013) Risk prediction for complex diseases: application to Parkinson disease. Genet Med 15:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2012.109
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Ibanez L, Dube U, Saef B, Budde J, Black K, Medvedeva A, del-Aguila JL, Davis AA, Perlmutter JS, Harari O, Benitez BA, Cruchaga C (2017) Parkinson disease polygenic risk score is associated with Parkinson disease status and age at onset but not with alpha-synuclein cerebrospinal fluid levels. BMC Neurol 17:198. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-017-0978-z
Kalia LV, Lang AE (2015) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet (London, England) 386:896–912. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)61393-3
Kalinderi K, Bostantjopoulou S, Fidani L (2016) The genetic background of Parkinson’s disease: current progress and future prospects. Acta Neurol Scand 134:314–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12563
Kang JH, Irwin DJ, Chen-Plotkin AS, Siderowf A, Caspell C et al (2013) Association of cerebrospinal fluid beta-amyloid 1-42, T-tau, P-tau181, and alpha-synuclein levels with clinical features of drug-naive patients with early Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 70:1277–1287. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.3861
Keller MF, Saad M, Bras J, Bettella F, Nicolaou N, Simon-Sanchez J, Mittag F, Buchel F, Sharma M, Gibbs JR, Schulte C, Moskvina V, Durr A, Holmans P, Kilarski LL, Guerreiro R, Hernandez DG, Brice A, Ylikotila P, Stefansson H, Majamaa K, Morris HR, Williams N, Gasser T, Heutink P, Wood NW, Hardy J, Martinez M, Singleton AB, Nalls MA, for the International Parkinson's Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC) and The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2) (2013) Using genome-wide complex trait analysis to quantify ‘missing heritability’ in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22:1696–1696. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt030
LeWitt PA, Hauser RA, Pahwa R, Isaacson SH, Fernandez HH et al (2019) Safety and efficacy of CVT-301 (levodopa inhalation powder) on motor function during off periods in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol 18:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30405-8
Li S, Le W (2017) Milestones of Parkinson’s disease research: 200 years of history and beyond. Neurosci Bull 33:598–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-017-0178-2
Li NN, Tan EK, Chang XL, Mao XY, Zhang JH, Zhao DM, Liao Q, Yu WJ, Peng R (2013) Genetic association study between STK39 and CCDC62/HIP1R and Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 8:e79211. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079211
Liguori C, Paoletti FP, Placidi F, Ruffini R, Sancesario GM, Eusebi P, Mercuri NB, Parnetti L (2019) CSF biomarkers for early diagnosis of synucleinopathies: focus on idiopathic RBD. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-019-0918-y
Liu J, Xiao Q, Wang Y, Xu ZM, Wang Y, Yang Q, Wang G, Tan YY, Ma JF, Zhang J, Huang W, Chen SD (2013) Analysis of genome-wide association study-linked loci in Parkinson’s disease of mainland China. Mov Disord 28:1892–1895. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25599
Liu ZH, Guo JF, Li K, Wang YQ, Kang JF, Wei Y, Sun QY, Xu Q, Wang DL, Xia K, Yan XX, Xu CS, Tang BS (2015) Analysis of several loci from genome-wide association studies in Parkinson’s disease in mainland China. Neurosci Lett 587:68–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.12.027
Lorraine V, Kalia AEL (2015) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 386:896–912. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61393-3
Lou F, Li M, Liu N, Li X, Ren Y, Luo X (2019) The polymorphism of SREBF1 gene rs11868035 G/A is associated with susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease in a Chinese population. Int J Neurosci 129:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2018.1526796
Meara J, Bhowmick BK, Hobson P (1999) Accuracy of diagnosis in patients with presumed Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing 28:99–102
Nalls MA, Plagnol V, Hernandez DG, Sharma M, Sheerin UM et al (2011) Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet 377:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(10)62345-8
Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Lill CM, Do CB, Hernandez DG et al (2014) Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 46:989–993. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3043
Polymeropoulos MH (1997) Mutation in the -synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5321.2045
Redensek S, Trost M, Dolzan V (2017) Genetic determinants of Parkinson’s disease: can they help to stratify the patients based on the underlying molecular defect? Front Aging Neurosci 9:20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00020
Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Mizuta I, Hirota Y, Ito C, Kubo M, Kawaguchi T, Tsunoda T, Watanabe M, Takeda A, Tomiyama H, Nakashima K, Hasegawa K, Obata F, Yoshikawa T, Kawakami H, Sakoda S, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Murata M, Nakamura Y, Toda T (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1303–1307. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.485
Shulman JM, De Jager PL, Feany MB (2011) Parkinson’s disease: genetics and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol 6:193–222. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130242
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R et al (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/42166
Wang L, Cheng L, Li NN, Yu WJ, Sun XY, Peng R (2016) Association of four new candidate genetic variants with Parkinson’s disease in a Han Chinese population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 171b:342–347. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32410
Wu HC, Chen CM, Chen YC, Fung HC, Chang KH, Wu YR (2018) DLG2, but not TMEM229B, GPNMB, and ITGA8 polymorphism, is associated with Parkinson’s disease in a Taiwanese population. Neurobiol Aging 64:158.e151–158.e156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.11.016
Yan YP, Mo XY, Tian J, Zhao GH, Yin XZ, Jin FY, Zhang BR (2011) An association between the PARK16 locus and Parkinson’s disease in a cohort from eastern China. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17:737–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.07.012
Zeng F, Shen C, Liu YH, Li J, Zhu J, Wang YR, Yan JC, Gao CY, Zhou HD, Deng J, Wang YJ (2015) Genetic association between APP, ADAM10 gene polymorphism, and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in the Chinese population. Neurotox Res 27:284–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9516-1
Zhou LL, Zhang X, Bao QQ, Liu RP, Gong MY, Mao GY, Zou M, Zhu JH (2014) Association analysis of PARK16-18 variants and Parkinson’s disease in a Chinese population. J Clin Neurosci 21:1029–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2013.09.015
Zou M, Li R, Wang JY, Wang K, Wang YN, Li Y, Ji FX, Sun SN, Huang SS, Fan HH, Huang CP, Zhang X, Zhu JH (2018) Association analyses of variants of SIPA1L2, MIR4697, GCH1, VPS13C, and DDRGK1 with Parkinson’s disease in East Asians. Neurobiol Aging 68:159.e157–159.e114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.03.005
Funding
This work was supported by the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (grant no. 2016YFC1306401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Daping Hospital, and all subjects and their caregivers provided informed consent.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 89 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, WW., Fan, DY., Shen, YY. et al. Association of the Polygenic Risk Score with the Incidence Risk of Parkinson’s Disease and Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein in a Chinese Cohort. Neurotox Res 36, 515–522 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00066-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00066-2