Abstract
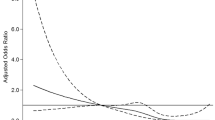
In this study, we examined the association between serum uric acid levels and epilepsy secondary to cerebral infarction. Clinical data including age, gender, epileptic seizure type, imaging, and serum uric acid levels before and after seizures in patients with cerebral infarction that were collected and analyzed. One hundred patients with cerebral infarction but without epilepsy, 147 patients with epilepsy secondary to cerebral infarction, and 55 patients with status epilepticus secondary to cerebral infarction were recruited. Interestingly, epilepsy secondary to cerebral infarction was associated with both reduced uric acid (adjusted OR 2.09; 95% CI 1.07–4.08) and increased uric acid (adjusted OR 4.05; 95% CI 1.99–8.25); however, status epilepsy secondary to cerebral infarction was only associated with increased uric acid (adjusted OR 2.60; 95% CI 1.05–6.45). A U-shaped association between uric acid levels and seizures was observed by using a multivariable logistic regression model with restricted cubic spline. Serum uric acid levels are associated with both epilepsy secondary to cerebral infarction and status epilepticus secondary to cerebral infarction in patients with cerebral infarction. The appropriate intervention of serum uric acid level might be a therapeutic strategy to reduce epileptic seizures or inhibit the development of status epilepticus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaro S, Urra X, Gomez-Choco M, Obach V, Cervera A, Vargas M, Torres F, Rios J, Planas AM, Chamorro A (2011) Uric acid levels are relevant in patients with stroke treated with thrombolysis. Stroke 42:S28–S32. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.110.596528
Ando K, Takahashi H, Watanabe T, Daidoji H, Otaki Y, Nishiyama S, Arimoto T, Shishido T, Miyashita T, Miyamoto T, Kubota I (2016) Impact of serum uric acid levels on coronary plaque stability evaluated using integrated backscatter intravascular ultrasound in patients with coronary artery disease. J Atheroscler Thromb 23:932–939. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.33951
Banerjee PN, Filippi D, Allen Hauser W (2009) The descriptive epidemiology of epilepsy-a review. Epilepsy Res 85:31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.03.003
Chan L, Hu CJ, Fan YC, Li FY, Hu HH, Hong CT, Bai CH (2018) Incidence of poststroke seizures: a meta-analysis. J Clin Neurosci 47:347–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.10.088
Coppola G, Pascotto A (1996) Double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial of allopurinol as add-on therapy in childhood refractory epilepsy. Brain and Development 18:50–52
Cutler RG, Camandola S, Malott KF, Edelhauser MA, Mattson MP (2015) The role of uric acid and methyl derivatives in the prevention of age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Top Med Chem 15:2233–2238
De Marco P, Zagnoni P (1988) Allopurinol in severe epilepsy. A preliminary report. Neuropsychobiology 19:51–53. https://doi.org/10.1159/000118433
Durrleman S, Simon R (1989) Flexible regression models with cubic splines. Stat Med 8:551–561
Fang P, Li X, Luo JJ, Wang H, Yang XF (2013) A double-edged sword: uric acid and neurological disorders. Brain Disord Ther 2:109. https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-975x.1000109
Fisher RS, Cross JH, French JA, Higurashi N, Hirsch E, Jansen FE, Lagae L, Moshe SL, Peltola J, Roulet Perez E, Scheffer IE, Zuberi SM (2017) Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 58:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13670
Glantzounis GK, Tsimoyiannis EC, Kappas AM, Galaris DA (2005) Uric acid and oxidative stress. Curr Pharm Des 11:4145–4151
Guieu R, Couraud F, Pouget J, Sampieri F, Bechis G, Rochat H (1996) Adenosine and the nervous system: clinical implications. Clin Neuropharmacol 19:459–474
Guzeva VI, Gusel VA, Mikhailov IB (1988) Allopurinol in the combined therapy of severe forms of epilepsy in children. Zh Nevropatol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova 88:69–72
Hamed SA, Hamed EA, Hamdy R, Nabeshima T (2007) Vascular risk factors and oxidative stress as independent predictors of asymptomatic atherosclerosis in adult patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 74:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2007.03.010
Harrison R (2002) Structure and function of xanthine oxidoreductase: where are we now? Free Radic Biol Med 33:774–797
Hemery C, Ryvlin P, Rheims S (2014) Prevention of generalized tonic-clonic seizures in refractory focal epilepsy: a meta-analysis. Epilepsia 55:1789–1799. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12765
Ishizaka Y, Yamakado M, Toda A, Tani M, Ishizaka N (2014) Relationship between serum uric acid and serum oxidative stress markers in the Japanese general population. Nephron Clin Pract 128:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1159/000362456
Jin M, Yang F, Yang I, Yin Y, Luo JJ, Wang H, Yang XF (2012) Uric acid, hyperuricemia and vascular diseases. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 17:656–669
Kovacs Z, Kekesi KA, Juhasz G, Barna J, Heja L, Lakatos R, Dobolyi A (2015) Non-adenosine nucleoside inosine, guanosine and uridine as promising antiepileptic drugs: a summary of current literature. Mini Rev Med Chem 14:1033–1042
Li R, Huang C, Chen J, Guo Y, Tan S (2015) The role of uric acid as a potential neuroprotectant in acute ischemic stroke: a review of literature. Neurol Sci 36:1097–1103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2151-z
Llull L, Amaro S, Chamorro A (2016) Administration of uric acid in the emergency treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 16:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-015-0604-7
Mares P (2010) Anticonvulsant action of 2-chloroadenosine against pentetrazol-induced seizures in immature rats is due to activation of A1 adenosine receptors. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 117:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0465-9
Marrosu F, Marrosu G, Rachele MG, Masala C, Giagheddu M (1990) Allopurinol add-on treatment in intractable seizures. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 12:207–213
Okafor ON, Farrington K, Gorog DA (2017) Allopurinol as a therapeutic option in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Ther 172:139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.12.004
Saito Y, Nakayama T, Sugimoto K, Fujimoto Y, Kobayashi Y (2015) Relation of lipid content of coronary plaque to level of serum uric acid. Am J Cardiol 116:1346–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.07.059
Scheffer IE, Berkovic S, Capovilla G, Connolly MB, French J, Guilhoto L, Hirsch E, Jain S, Mathern GW, Moshe SL, Nordli DR, Perucca E, Tomson T, Wiebe S, Zhang YH, Zuberi SM (2017) ILAE classification of the epilepsies: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 58:512–521. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13709
Song C, Zhao X (2017) Uric acid promotes oxidative stress and enhances vascular endothelial cell apoptosis in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20170939
Suchomelova L, Lopez-Meraz ML, Niquet J, Kubova H, Wasterlain CG (2015) Hyperthermia aggravates status epilepticus-induced epileptogenesis and neuronal loss in immature rats. Neuroscience 305:209–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.006
Tada H, Morooka K, Arimoto K, Matsuo T (1991) Clinical effects of allopurinol on intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 32:279–283
Terrone G, Salamone A, Vezzani A (2017) Inflammation and epilepsy: preclinical findings and potential clinical translation. Curr Pharm Des. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612823666170926113754
Thyrion L, Raedt R, Portelli J, Van Loo P, Wadman WJ, Glorieux G, Lambrecht BN, Janssens S, Vonck K, Boon P (2016) Uric acid is released in the brain during seizure activity and increases severity of seizures in a mouse model for acute limbic seizures. Exp Neurol 277:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.01.001
Togha M, Akhondzadeh S, Motamedi M, Ahmadi B, Razeghi S (2007) Allopurinol as adjunctive therapy in intractable epilepsy: a double-blind and placebo-controlled trial. Arch Med Res 38:313–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2006.10.010
Truglio JJ, Theis K, Leimkuhler S, Rappa R, Rajagopalan KV, Kisker C (2002) Crystal structures of the active and alloxanthine-inhibited forms of xanthine dehydrogenase from Rhodobacter capsulatus. Structure 10:115–125
Vezzani A, Auvin S, Ravizza T, Aronica E (2012) Glia-neuronal interactions in ictogenesis and epileptogenesis: role of inflammatory mediators. In: th, Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV (eds) Jasper’s basic mechanisms of the epilepsies. Michael A Rogawski, Antonio V Delgado-Escueta, Jeffrey L Noebels, Massimo Avoli and Richard W Olsen., Bethesda MD
Wang Z, Lin Y, Liu Y, Chen Y, Wang B, Li C, Yan S, Wang Y, Zhao W (2016) Serum uric acid levels and outcomes after acute ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 53:1753–1759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9134-1
Wang L, Hu W, Miao D, Zhang Q, Wang C, Pan E, Wu M (2017) Relationship between serum uric acid and ischemic stroke in a large type 2 diabetes population in China: a cross-sectional study. J Neurol Sci 376:176–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2017.03.023
Zagnoni PG, Bianchi A, Zolo P, Canger R, Cornaggia C, D’Alessandro P, DeMarco P, Pisani F, Gianelli M, Verze L (1994) Allopurinol as add-on therapy in refractory epilepsy: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized study. Epilepsia 35:107–112
Zhang X, Huang ZC, Lu TS, You SJ, Cao YJ, Liu CF (2016) Prognostic significance of uric acid levels in ischemic stroke patients. Neurotox Res 29:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9561-9
Funding
This study was supported by the grant from Suzhou science and technology development program (SYSD2011087 to ZX).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The research was approved by the local Ethics Committee of Soochow University. We confirm that we have read the journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Key point box
• The serum uric acid levels within 12 h after acute epileptic seizures were higher than the baseline level of uric acid.
• There was a U-shaped dose-effect relationship between the serum uric acid level and epilepsy secondary to cerebral infarction.
• Epilepsy or status epilepsy secondary to cerebral infarction is associated with both reduced uric acid and increased uric acid.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Hu, B., Dai, Y. et al. Serum Uric Acid Is Highly Associated with Epilepsy Secondary to Cerebral Infarction. Neurotox Res 35, 63–70 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9930-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9930-2