Abstract
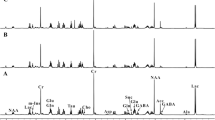
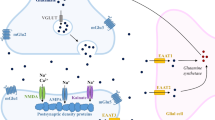
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with deterioration of brain structure and function. Here, we tested the hypothesis that T2D induces a reorganization of the brain metabolic networks that support brain function. For that, alterations of neuronal and glial energy metabolism were investigated in a T2D model, the Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rat. 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo at 14.1 T was used to detect 13C labeling incorporation into carbons of glutamate, glutamine, and aspartate in the brain of GK (n = 7) and Wistar (n = 13) rats during intravenous [1,6-13C]glucose administration. Labeling of brain glucose and amino acids over time was analyzed with a two-compartment mathematical model of brain energy metabolism to determine the rates of metabolic pathways in neurons and glia. Compared to controls, GK rats displayed lower rates of brain glutamine synthesis (− 32%, P < 0.001) and glutamate-glutamine cycle (− 40%, P < 0.001), and mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle rate in neurons (− 7%, P = 0.036). In contrast, the TCA cycle rate of astrocytes was larger in GK rats than controls (+ 21%, P = 0.042). We conclude that T2D alters brain energy metabolism and impairs the glutamate-glutamine cycle between neurons and astrocytes, in line with diabetes-induced neurodegeneration and astrogliosis underlying brain dysfunction.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CMRglc(ox) :
-
Oxidative fraction of CMRglc
- CMRglc :
-
Cerebral metabolic rate of glucose
- FE:
-
Fractional enrichment
- GTT:
-
Glucose tolerance test
- K t :
-
Apparent Michaelis constant of glucose transport
- MRS:
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- TCA cycle:
-
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- V dil :
-
Dilution of glial acetyl-CoA
- V g :
-
Rate of glial TCA cycle resulting in full pyruvate oxidation
- V GS :
-
Rate of glutamine synthetase
- V in :
-
Dilution of pyruvate
- V NT :
-
Rate of apparent glutamatergic neurotransmission
- VOI:
-
Volume of interest
- V out :
-
Pyruvate efflux
- V PC :
-
Rate of pyruvate carboxylase
- V TCA g :
-
Glial TCA cycle
- V TCA n :
-
Neuronal TCA cycle
- V X g :
-
Rate of oxoacid-amino acid exchange in glia
- V X n :
-
Rate of oxoacid-amino acid exchange in neurons
- ZDF:
-
Zucker diabetic fatty
References
Abdul-Rahman O, Sasvari-Szekely M, Ver A et al (2012) Altered gene expression profiles in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of type 2 diabetic rats. BMC Genomics 13:81
Andersen JV, Christensen SK, Nissen JD, Waagepetersen HS (2017) Improved cerebral energetics and ketone body metabolism in db/db mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37(3):1137–1147
Ates O, Cayli SR, Yucel N et al (2007) Central nervous system protection by resveratrol in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Clin Neurosci 14:256–260
Baker LD, Cross D, Minoshima S, Belongia D, Watson GS, Craft S (2011) Insulin resistance is associated with Alzheimer-like reductions in regional cerebral glucose metabolism for cognitively impaired normal adults with pre-diabetes or early type 2 diabetes. Arch Neurol 68:51–57
Baumgart M, Snyder HM, Carrillo MC, Fazio S, Kim H, Johns H (2015) Summary of the evidence on modifiable risk factors for cognitive decline and dementia: a population-based perspective. Alzheimers Dement 11(6):718–726
Baydas G, Nedzvetskii VS, Tuzcu M, Yasar A, Kirichenko SV (2003) Increase of glial fibrillary acidic protein and S-100B in hippocampus and cortex of diabetic rats: effects of vitamin E. Eur J Pharmacol 462:67–71
Biessels GJ, Staekenborg S, Brunner E, Brayne C, Scheltens P (2006) Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 5(1):64–74
Calvo-Ochoa E, Hernández-Ortega K, Ferrera P, Morimoto S, Arias C (2014) Short-term high-fat-and-fructose feeding produces insulin signaling alterations accompanied by neurite and synaptic reduction and astroglial activation in the rat hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34(6):1001–1008
Candeias E, Duarte AI, Carvalho C et al (2012) The impairment of insulin signaling in Alzheimer's disease. IUBMB Life 64(12):951–957
Candeias E, Duarte AI, Sebastião I, Fernandes MA, Plácido AI, Carvalho C, Correia S, Santos RX, Seiça R, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Moreira PI (2016) Middle-aged diabetic females and males present distinct susceptibility to Alzheimer disease-like pathology. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0155-1
Duarte JMN (2015) Metabolic alterations associated to brain dysfunction in diabetes. Aging Dis 6(5):304–321
Duarte JMN, Agostinho PM, Carvalho RA, Cunha RA (2012) Caffeine consumption prevents diabetes-induced memory impairment and synaptotoxicity in the hippocampus of NONcNZO10/LtJ mice. PLoS One 7:e21899
Duarte JMN, Carvalho RA, Cunha RA, Gruetter R (2009) Caffeine consumption attenuates neurochemical modifications in the hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Neurochem 111(2):368–379
Duarte JMN, Cunha RA, Carvalho RA (2007) Different metabolism of glutamatergic and GABAergic compartments in superfused hippocampal slices characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurosci 144:1305–1313
Duarte JMN, Gruetter R (2012) Characterization of cerebral glucose dynamics in vivo with a four-state conformational model of transport at the blood-brain-barrier. J Neurochem 121:396–406
Duarte JMN, Gruetter R (2013) Glutamatergic and GABAergic energy metabolism measured in the rat brain by 13C NMR spectroscopy at 14.1 T. J Neurochem 126(5):579–590
Duarte JMN, Lanz B, Gruetter R (2011) Compartmentalised cerebral metabolism of [1,6-13C]glucose determined by in vivo 13C NMR spectroscopy at 14.1 T. Front Neuroenergetics 3: 3
Francis GJ, Martinez JA, Liu WQ et al (2008) Intranasal insulin prevents cognitive decline, cerebral atrophy and white matter changes in murine type I diabetic encephalopathy. Brain 131:3311–3334
García-Espinosa MA, García-Martín ML, Cerdán S (2003) Role of glial metabolism in diabetic encephalopathy as detected by high resolution 13C NMR. NMR Biomed 16(6–7):440–449
Geijselaers SL, Sep SJ, Stehouwer CD, Biessels GJ (2015) Glucose regulation, cognition, and brain MRI in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 3(1):75–89
Henry PG, Tkác I, Gruetter R (2003) 1H-localized broadband 13C NMR spectroscopy of the rat brain in vivo at 9.4 T. Magn Reson Med 50:684–692
Hussain S, Mansouri S, Sjöholm Å, Patrone C, Darsalia V (2014) Evidence for cortical neuronal loss in male type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Alzheimers Dis 41(2):551–660
Kapogiannis D, Mattson MP (2011) Disrupted energy metabolism and neuronal circuit dysfunction in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 10:187–198
Kleinridders A, Ferris HA, Cai W, Kahn CR (2014) Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function. Diabetes 63(7):2232–2243
Lang BT, Yan Y, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R (2009) Impaired neurogenesis in adult type-2 diabetic rats. Brain Res 1258:25–33
Lanz B, Gruetter R, Duarte JMN (2013) Metabolic flux and compartmentation analysis in the brain in vivo. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:156
Leffa DD, Rezin GT, Daumann F et al (2017) Effects of Acerola (Malpighia emarginata DC.) juice intake on brain energy metabolism of mice fed a cafeteria diet. Mol Neurobiol 54(2):954–963
Li XH, Xin X, Wang Y et al (2013) Pentamethylquercetin protects against diabetes-related cognitive deficits in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Alzheimers Dis 34(3):755–767
Li ZG, Zhang W, Sima AA (2007) Alzheimer-like changes in rat models of spontaneous diabetes. Diabetes 56(7):1817–1824
Mason GF, Petersen KF, Lebon V, Rothman DL, Shulman GI (2006) Increased brain monocarboxylic acid transport and utilization in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 55(4):929–934
Messier C (2005) Impact of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes on cognitive aging. Neurobiol Aging 26(Suppl 1):26–30
Moheet A, Mangia S, Seaquist ER (2015) Impact of diabetes on cognitive function and brain structure. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1353:60–71
Moreira PI, Santos MS, Seiça R, Oliveira CR (2007) Brain mitochondrial dysfunction as a link between Alzheimer's disease and diabetes. J Neurol Sci 257(1–2):206–214
Nitta A, Murai R, Suzuki N et al (2002) Diabetic neuropathies in brain are induced by deficiency of BDNF. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24:695–701
Palta P, Schneider AL, Biessels GJ, Touradji P, Hill-Briggs F (2014) Magnitude of cognitive dysfunction in adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of six cognitive domains and the most frequently reported neuropsychological tests within domains. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 20(3):278–291
Portha B (2005) Programmed disorders of beta-cell development and function as one cause for type 2 diabetes? The GK rat paradigm. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 21(6):495–504
Prakash R, Johnson M, Fagan SC, Ergul A (2013) Cerebral neovascularization and remodeling patterns in two different models of type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 8(2):e56264
Raza H, John A, Howarth FC (2015) Increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in zucker diabetic rat liver and brain. Cell Physiol Biochem 35(3):1241–1251
Rönnemaa E, Zethelius B, Sundelöf J et al (2008) Impaired insulin secretion increases the risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 71:1065–1071
Saravia FE, Revsin Y, Gonzalez Deniselle MC et al (2002) Increased astrocyte reactivity in the hippocampus of murine models of type 1 diabetes: the nonobese diabetic (NOD) and streptozotocin-treated mice. Brain Res 957:345–353
Shockley RP, LaManna JC (1988) Determination of rat cerebral cortical blood volume changes by capillary mean transit time analysis during hypoxia, hypercapnia and hyperventilation. Brain Res 454(1–2):170–178
Sickmann HM, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A, Benie AJ, Bouman SD (2010) Obesity and type 2 diabetes in rats are associated with altered brain glycogen and amino-acid homeostasis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(8):1527–1537
Sonnay S, Duarte JMN, Just N, Gruetter R (2016) Compartmentalised energy metabolism supporting glutamatergic neurotransmission in response to increased activity in the rat cerebral cortex: a 13C MRS study in vivo at 14.1 T. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(5):928–940
Sonnay S, Duarte JMN, Just N, Gruetter R (2017a) Energy metabolism in the rat cortex under thiopental anaesthesia measured in vivo by 13C MRS. J Neurosci Res in press doi. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24032
Sonnay S, Gruetter R, Duarte JMN (2017b) How energy metabolism supports cerebral function: insights from 13C magnetic resonance studies in vivo. Front Neurosci 11:288
Sonnewald U, Wang AY, Petersen SB et al (1995) 13C NMR study of IGF-I- and insulin-effects on mitochondrial function in cultured brain cells. Neuroreport 6(6):878–880
Spauwen PJ, Köhler S, Verhey FR, Stehouwer CD, van Boxtel MP (2013) Effects of type 2 diabetes on 12-year cognitive change: results from the Maastricht Aging Study. Diabetes Care 36(6):1554–1561
Stranahan AM, Arumugam TV, Cutler RG, Lee K, Egan JM, Mattson MP (2008) Diabetes impairs hippocampal function through glucocorticoid-mediated effects on new and mature neurons. Nat Neurosci 11(3):309–317
Tomlinson DR, Gardiner NJ (2008) Glucose neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:36–45
van den Berg E, Dekker JM, Nijpels G et al (2008) Cognitive functioning in elderly persons with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome: the Hoorn study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 26(3):261–269
van der Graaf M, Janssen SW, van Asten JJ et al (2004) Metabolic profile of the hippocampus of Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats assessed by in vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 17(6):405–410
Wang WT, Lee P, Yeh HW, Smirnova IV, Choi IY (2012) Effects of acute and chronic hyperglycemia on the neurochemical profiles in the rat brain with streptozotocin-induced diabetes detected using in vivo 1H MR spectroscopy at 9.4 T. J Neurochem 121(3):407–417
Zheng H, Zheng Y, Wang D et al (2017) Analysis of neuron-astrocyte metabolic cooperation in the brain of db/db mice with cognitive decline using 13C NMR spectroscopy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37(1):332–343
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Ana F. Soares (LIFMET, EPFL) for fruitful discussions.
Funding
This research was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant 148250), National Competence Center in Biomedical Imaging (NCCBI), and by Centre d’Imagerie BioMédicale (CIBM) of the UNIL, UNIGE, HUG, CHUV, EPFL, and the Leenaards and Jeantet Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were performed in accordance with the Swiss federal law on animal experimentation and approved by the local authority (EXPANIM-SCAV), and are reported according to the ARRIVE guidelines.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girault, FM., Sonnay, S., Gruetter, R. et al. Alterations of Brain Energy Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats Measured In Vivo by 13C Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Neurotox Res 36, 268–278 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9821-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9821-y